OSD (Oil Seam Detergent) devices are designed for easy installation and effective delivery, while sterile equipment guarantees a contamination-free environment essential for medical or laboratory applications. Your choice depends on whether ease of use or strict sterility is the top priority for your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
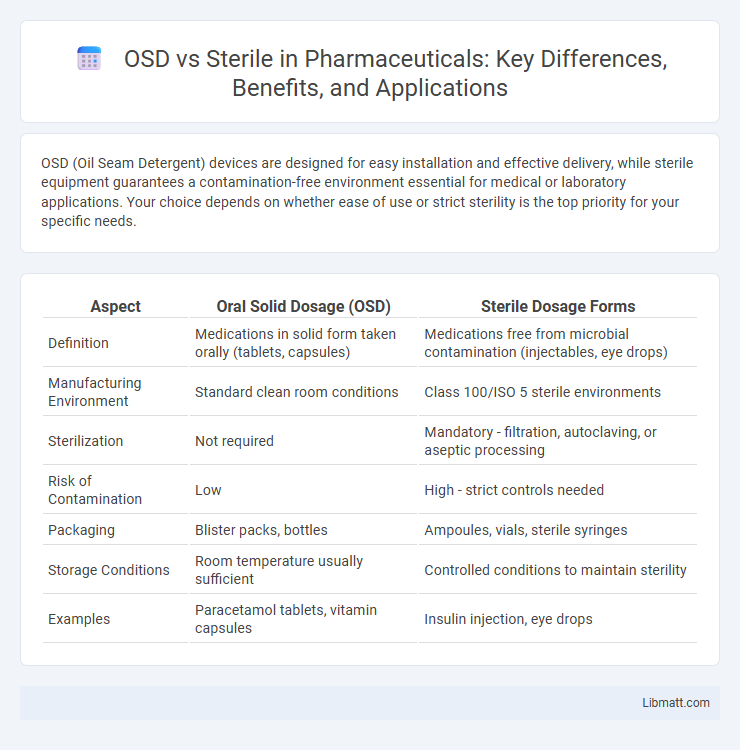
| Aspect | Oral Solid Dosage (OSD) | Sterile Dosage Forms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Medications in solid form taken orally (tablets, capsules) | Medications free from microbial contamination (injectables, eye drops) |
| Manufacturing Environment | Standard clean room conditions | Class 100/ISO 5 sterile environments |
| Sterilization | Not required | Mandatory - filtration, autoclaving, or aseptic processing |
| Risk of Contamination | Low | High - strict controls needed |
| Packaging | Blister packs, bottles | Ampoules, vials, sterile syringes |
| Storage Conditions | Room temperature usually sufficient | Controlled conditions to maintain sterility |
| Examples | Paracetamol tablets, vitamin capsules | Insulin injection, eye drops |
Understanding OSD and Sterile: Key Definitions
Ocular Surface Disease (OSD) encompasses a range of disorders affecting the eye's tear film and surface, leading to symptoms like dryness, irritation, and inflammation. Sterile conditions refer to environments or products free from all living microorganisms, crucial for preventing infections during ocular treatments. Differentiating OSD from sterile states highlights the importance of maintaining sterile techniques in managing OSD to avoid secondary infections and promote healing.
Core Differences Between OSD and Sterile Manufacturing
OSD (Oral Solid Dosage) manufacturing primarily involves producing tablets and capsules with a focus on formulation, blending, compression, and coating processes, while sterile manufacturing centers on aseptic techniques to ensure products like injectables and ophthalmics remain free from microbial contamination. OSD environments typically require controlled humidity and dust control, whereas sterile manufacturing demands stringent cleanroom classifications, laminar airflow, and sterilization methods such as autoclaving or filtration. Validation protocols and environmental monitoring are more rigorous in sterile production to maintain compliance with FDA and USP <797> standards.
Regulatory Requirements: OSD vs Sterile
Regulatory requirements for Oral Solid Dosage (OSD) forms primarily focus on ensuring product stability, accurate dosage, and contamination control through Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) specific to dry formulations. Sterile products demand stricter regulations including aseptic processing, environmental monitoring, and rigorous validation protocols to prevent microbial contamination, as mandated by agencies such as the FDA and EMA. Understanding these differences helps you maintain compliance with regulatory standards tailored to formulation type and patient safety.
Facility Design and Environmental Controls
Facility design for OSD (Oral Solid Dosage) manufacturing emphasizes stringent segregation between sterile and non-sterile areas to prevent cross-contamination, incorporating cleanroom classification ISO 7 or higher. Environmental controls in sterile production require validated HVAC systems with HEPA filtration achieving unidirectional airflow, maintaining particulate counts and microbial limits substantially lower than OSD environments. Temperature, humidity, and pressure differentials are closely monitored and managed in sterile settings to uphold aseptic conditions, contrasting with the less rigorous controls needed for typical OSD operations.
Critical Equipment Used in OSD and Sterile Production
Critical equipment used in OSD (Oral Solid Dosage) production includes tablet presses, capsule fillers, and coating machines designed for precise dosage and uniformity. Sterile production relies heavily on isolators, laminar airflow hoods, and autoclaves to maintain aseptic conditions and prevent contamination. Both OSD and sterile manufacturing utilize high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and environmental monitoring systems, but sterile production demands more stringent controls and specialized equipment for sterile barrier maintenance.
Quality Assurance Practices: OSD vs Sterile
Quality assurance practices for Oral Solid Dosage (OSD) forms emphasize uniformity in tablet weight, content potency, and dissolution rates, ensuring consistent bioavailability and patient compliance. In sterile product manufacturing, rigorous aseptic processing, environmental monitoring, and sterility testing are critical to prevent microbial contamination and maintain product safety. Both dosage forms require comprehensive validation protocols, yet sterile products demand heightened control measures due to their administration routes and susceptibility to contamination.
Common Challenges in OSD and Sterile Processing
Common challenges in OSD and sterile processing include ensuring consistent compliance with stringent regulatory standards and maintaining product integrity during handling and packaging. Cross-contamination risks and the need for precise environmental controls demand rigorous process validation and continuous monitoring. Your operation's efficiency relies on addressing these issues through advanced sterilization techniques and robust quality management systems.
Cost Implications: OSD vs Sterile Manufacturing
Oral solid dosage (OSD) manufacturing generally incurs lower production costs compared to sterile manufacturing due to simpler processing steps and less stringent environmental controls. Sterile manufacturing requires specialized cleanroom facilities, advanced contamination control measures, and rigorous validation protocols, significantly increasing capital expenditure and operational expenses. These cost differences impact pricing structures and investment decisions within pharmaceutical production pipelines.
Market Trends and Demand: OSD vs Sterile Drugs
The market for Oral Solid Dosage (OSD) forms continues to dominate due to ease of manufacturing, stable shelf life, and patient compliance, driving sustained demand across chronic therapeutic segments globally. In contrast, sterile drugs, including injectables and biologics, are experiencing accelerated growth fueled by increasing prevalence of complex diseases, rising preference for biologic therapies, and advancements in aseptic processing technologies. The sterile drug segment is projected to expand at a higher compound annual growth rate (CAGR), reflecting significant investment and innovation to meet stringent regulatory standards and growing market needs for personalized medicine.
Choosing the Right Manufacturing Approach: OSD or Sterile
Choosing between oral solid dosage (OSD) and sterile manufacturing hinges on product stability, patient safety, and administration route. OSD forms offer cost-effective, convenient dosing for stable compounds, while sterile production is essential for injectables, ophthalmics, or products requiring aseptic conditions. Your decision should align with regulatory standards, formulation characteristics, and therapeutic requirements to ensure optimal efficacy and safety.
OSD vs sterile Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com