A Fluidized Bed Dryer uses a stream of hot air to suspend and dry particles effectively, offering faster drying times and uniform heat distribution compared to a Tray Dryer, which dries materials placed on trays through static airflow. Understanding these differences helps you choose the optimal drying method based on your product's sensitivity and processing speed requirements.
Table of Comparison
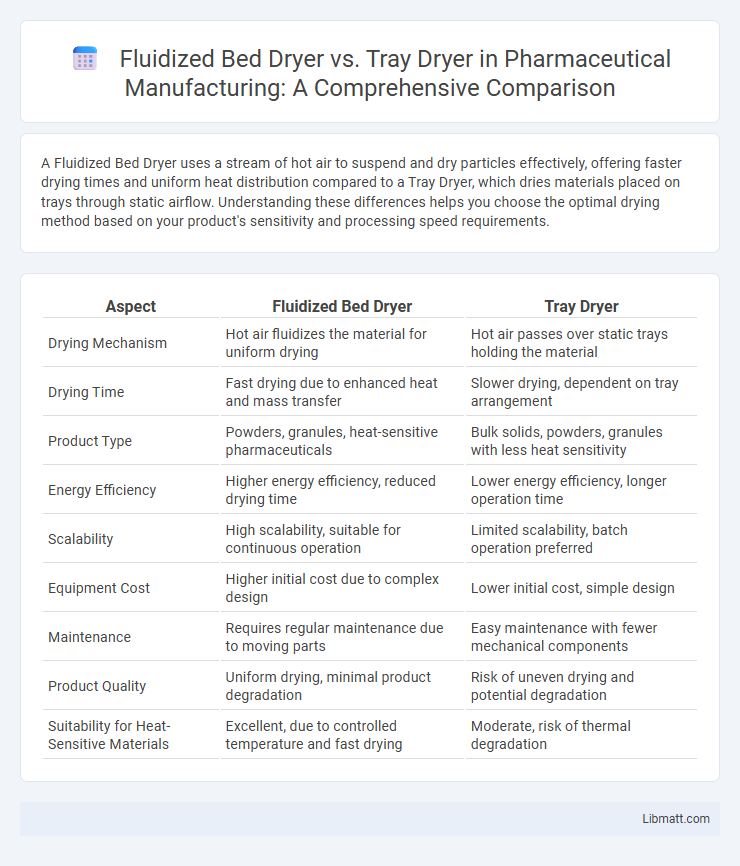
| Aspect | Fluidized Bed Dryer | Tray Dryer |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Mechanism | Hot air fluidizes the material for uniform drying | Hot air passes over static trays holding the material |
| Drying Time | Fast drying due to enhanced heat and mass transfer | Slower drying, dependent on tray arrangement |
| Product Type | Powders, granules, heat-sensitive pharmaceuticals | Bulk solids, powders, granules with less heat sensitivity |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy efficiency, reduced drying time | Lower energy efficiency, longer operation time |
| Scalability | High scalability, suitable for continuous operation | Limited scalability, batch operation preferred |
| Equipment Cost | Higher initial cost due to complex design | Lower initial cost, simple design |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance due to moving parts | Easy maintenance with fewer mechanical components |
| Product Quality | Uniform drying, minimal product degradation | Risk of uneven drying and potential degradation |
| Suitability for Heat-Sensitive Materials | Excellent, due to controlled temperature and fast drying | Moderate, risk of thermal degradation |
Introduction to Industrial Drying Technologies
Fluidized bed dryers utilize a suspension of solid particles in a rising stream of air or gas, ensuring efficient heat and mass transfer for drying powders and granular materials with uniform temperature distribution. Tray dryers operate by placing material on trays inside a heated chamber where hot air circulates, suitable for drying heat-sensitive products with controlled temperature and humidity. Industrial drying technologies optimize drying time, energy consumption, and product quality depending on material properties and processing requirements.
What is a Fluidized Bed Dryer?
A fluidized bed dryer is an industrial drying equipment that uses a fluidization process to dry particulate materials by suspending them in an upward-flowing hot air stream, enhancing heat and mass transfer rates. Compared to a tray dryer, the fluidized bed dryer provides faster drying times, more uniform drying, and improved energy efficiency due to its dynamic particle movement and efficient airflow. This technology is commonly used in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical industries to dry granules, powders, and crystals with consistent temperature control and reduced risk of thermal degradation.
How Does a Tray Dryer Work?
A tray dryer operates by placing materials on perforated trays inside a heated chamber, where hot air circulates to remove moisture through evaporation. This drying method relies on consistent airflow and controlled temperature to ensure uniform drying of heat-sensitive products. Commonly used in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical industries, tray dryers offer precise drying control but generally have longer drying times compared to fluidized bed dryers.
Key Differences Between Fluidized Bed Dryer and Tray Dryer
Fluidized Bed Dryers utilize a fluidization process, where hot air passes through a perforated bed to suspend and dry particles efficiently, resulting in faster drying times and uniform heat distribution. Tray Dryers operate by placing materials on trays inside a heated chamber, relying on conduction and convection for moisture removal, which can lead to slower drying and potential uneven drying for bulkier products. While Fluidized Bed Dryers are ideal for granular and particulate materials with high drying rates, Tray Dryers are better suited for heat-sensitive materials that require gentle drying at controlled temperatures.
Efficiency Comparison: Fluidized Bed vs Tray Dryer
Fluidized bed dryers offer higher thermal efficiency and faster drying rates compared to tray dryers due to enhanced heat and mass transfer from fluidization. Tray dryers experience longer drying times and uneven moisture removal because of limited air circulation and slower heat penetration. In industrial applications, fluidized bed dryers reduce energy consumption and improve product uniformity, making them more efficient than traditional tray drying methods.
Applications and Suitability of Fluidized Bed Dryers
Fluidized bed dryers are ideal for drying granular and particulate materials, offering excellent heat and mass transfer efficiency for substances like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food powders. Their suitability for handling heat-sensitive materials with uniform drying makes them preferred in industries requiring consistent moisture content and reduced drying times. You benefit from their ability to process bulk quantities with minimal product degradation and improved energy efficiency compared to tray dryers.
Applications and Suitability of Tray Dryers
Tray dryers are ideal for drying heat-sensitive materials such as pharmaceuticals, herbs, and food products that require gentle processing to preserve quality and potency. Their suitability extends to batch drying applications where uniform airflow and controlled temperature help maintain material integrity. You benefit from precise moisture control and ease of loading and unloading, making tray dryers suitable for small to medium-scale production requiring consistent drying outcomes.
Energy Consumption: Which Dryer is More Cost-effective?
Fluidized bed dryers typically consume less energy than tray dryers due to their efficient heat transfer and faster drying times, making them more cost-effective for large-scale operations. Tray dryers have higher energy consumption as they rely on slower convective heat transfer and longer drying cycles, leading to increased operational costs. Your choice should consider energy rates and throughput requirements to determine the most economical drying solution.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Dryer Type
Fluidized bed dryers offer rapid drying with uniform heat distribution due to their high gas velocity, making them ideal for granular or particulate materials, although they can cause attrition and are less suitable for fragile products. Tray dryers provide precise control over drying parameters and are suitable for heat-sensitive materials, but they require longer drying times and have lower energy efficiency. Choosing between these dryers depends on factors such as material sensitivity, desired drying time, and operational costs.
Choosing the Right Dryer for Your Process Needs
Selecting the right dryer between a Fluidized Bed Dryer and a Tray Dryer depends on factors such as product characteristics, drying time, and energy efficiency. Fluidized Bed Dryers offer faster drying rates and uniform heat distribution, making them ideal for granular or particulate materials with high moisture content. Tray Dryers provide gentle drying for heat-sensitive or bulky products, ensuring precise control over drying conditions and reduced risk of product degradation.
Fluidized Bed Dryer vs Tray Dryer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com