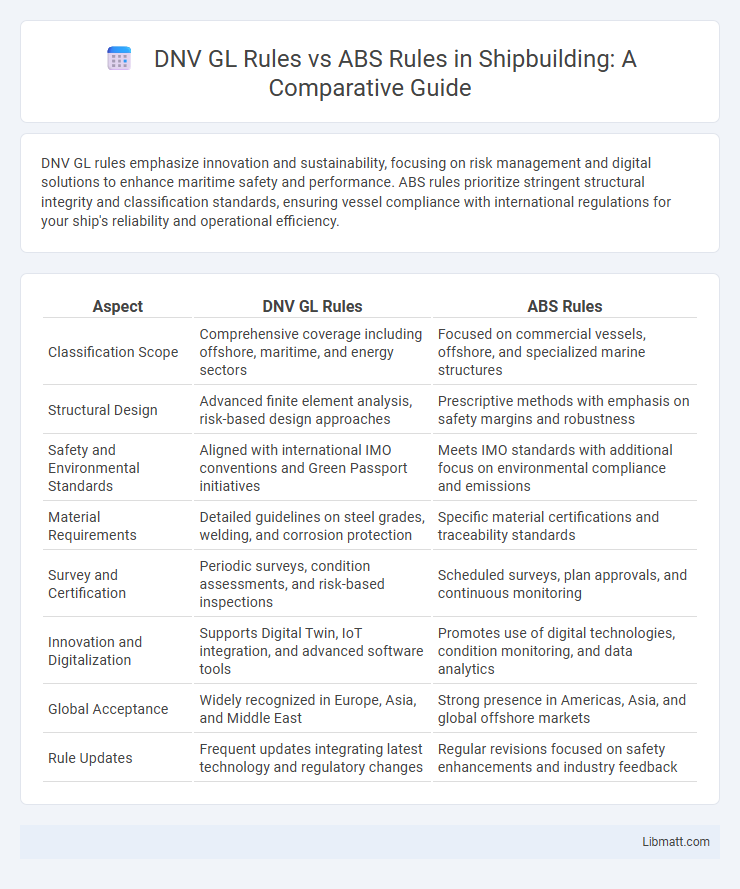
DNV GL rules emphasize innovation and sustainability, focusing on risk management and digital solutions to enhance maritime safety and performance. ABS rules prioritize stringent structural integrity and classification standards, ensuring vessel compliance with international regulations for your ship's reliability and operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | DNV GL Rules | ABS Rules |
|---|---|---|
| Classification Scope | Comprehensive coverage including offshore, maritime, and energy sectors | Focused on commercial vessels, offshore, and specialized marine structures |
| Structural Design | Advanced finite element analysis, risk-based design approaches | Prescriptive methods with emphasis on safety margins and robustness |
| Safety and Environmental Standards | Aligned with international IMO conventions and Green Passport initiatives | Meets IMO standards with additional focus on environmental compliance and emissions |
| Material Requirements | Detailed guidelines on steel grades, welding, and corrosion protection | Specific material certifications and traceability standards |
| Survey and Certification | Periodic surveys, condition assessments, and risk-based inspections | Scheduled surveys, plan approvals, and continuous monitoring |
| Innovation and Digitalization | Supports Digital Twin, IoT integration, and advanced software tools | Promotes use of digital technologies, condition monitoring, and data analytics |
| Global Acceptance | Widely recognized in Europe, Asia, and Middle East | Strong presence in Americas, Asia, and global offshore markets |
| Rule Updates | Frequent updates integrating latest technology and regulatory changes | Regular revisions focused on safety enhancements and industry feedback |
Overview of DNV GL and ABS Classification Societies
DNV GL and ABS are leading classification societies providing technical standards for maritime safety, vessel construction, and operation. DNV GL, based in Norway, emphasizes innovation in risk management and digital solutions, supporting energy and maritime sectors globally. ABS, headquartered in the United States, specializes in setting stringent rules for ship classification, offshore structures, and marine systems with a strong focus on regulatory compliance and reliability.
Historical Background of DNV GL and ABS
DNV GL originated from the 1864 foundation of Det Norske Veritas in Norway, focusing on maritime classification and risk management, while the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) was established in 1862 in the United States, dedicated to ship classification and safety standards. Both organizations evolved through mergers and expansions, with DNV GL formed in 2013 by the merger of Det Norske Veritas and Germanischer Lloyd, enhancing expertise in maritime, energy, and offshore industries. ABS maintains a long-standing reputation for rigorous classification rules and statutory certification, rooted in its origins serving the US maritime industry and expanding globally.
Scope and Application of DNV GL Rules
DNV GL rules cover a broad range of industries, including maritime, offshore, and energy sectors, emphasizing safety, reliability, and environmental protection throughout the asset lifecycle. These rules provide detailed requirements for design, construction, operation, and maintenance, ensuring compliance with international standards and industry best practices. Your projects benefit from DNV GL's comprehensive approach, which integrates risk management and innovation to enhance structural integrity and system performance.
Scope and Application of ABS Rules
ABS Rules primarily apply to the classification and certification of ships, offshore structures, and marine systems, ensuring safety, environmental protection, and structural integrity. Their scope includes design, construction, and maintenance standards tailored for vessels operating worldwide, emphasizing compliance with international maritime regulations. In contrast, while DNV GL also covers similar sectors, it places stronger emphasis on risk management, lifecycle services, and digital solutions for asset performance optimization.
Key Differences Between DNV GL and ABS Rules
DNV GL rules emphasize risk management and innovation with a focus on environmental sustainability, while ABS rules prioritize prescriptive compliance and operational safety. DNV GL integrates probabilistic methods and digital tools for certification, contrasting with ABS's traditional deterministic approach. ABS rules cater extensively to operational reliability in extreme conditions, whereas DNV GL promotes flexible design solutions aligned with future technologies.
Structural Design Standards Comparison
DNV GL rules emphasize a risk-based approach to structural design, integrating advanced fatigue analysis and material modeling to ensure long-term durability, while ABS rules focus on prescriptive criteria with robust safety margins derived from extensive empirical data. You will find DNV GL's framework offers greater flexibility for innovative designs, whereas ABS provides well-established, conservative guidelines widely accepted in regulatory practices. Both standards prioritize structural integrity but differ in their methodologies and optimization levels for specific vessel types and operational conditions.
Machinery and Systems Requirements
DNV GL rules emphasize risk-based inspections and advanced condition monitoring technologies for machinery and systems to ensure operational reliability and safety. ABS rules prioritize prescriptive maintenance intervals and detailed equipment classification standards to maintain system integrity and compliance. Your machinery will benefit from DNV GL's adaptive guidelines if focusing on innovation, whereas ABS provides robust frameworks suitable for traditional operational models.
Safety and Environmental Regulations
DNV GL rules emphasize a risk-based approach to safety and environmental management, integrating advanced digital tools for real-time monitoring and compliance verification. ABS rules focus on stringent prescriptive standards and robust classification systems designed to minimize hazards and ensure environmental protection throughout the vessel's lifecycle. Your choice between these frameworks depends on whether you prioritize innovative, data-driven safety strategies or well-established, comprehensive regulatory guidelines.
Survey and Certification Processes
DNV GL's survey and certification processes emphasize risk-based assessment and continuous improvement, using digital tools and streamlined workflows to enhance efficiency and accuracy. ABS rules prioritize stringent compliance and prescriptive inspections, focusing on heritage-based standards to ensure safety and reliability in marine and offshore assets. Your choice between DNV GL and ABS will depend on whether you value adaptive risk management or proven traditional methodologies in certification.
Choosing Between DNV GL and ABS: Factors to Consider
Choosing between DNV GL and ABS rules depends on your project's specific requirements, vessel type, and operational regions, as DNV GL emphasizes innovative sustainability practices while ABS focuses on proven safety standards and regulatory compliance. Assessing factors such as certification processes, technical support, and industry recognition helps ensure adherence to the most relevant classification standards for your maritime assets. Your decision will ultimately impact the structural integrity, operational efficiency, and regulatory acceptance of your vessel or offshore structure.
DNV GL rules vs ABS rules Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com