Echosounders use sound pulses to measure water depth by detecting the time it takes for the echo to return from the seabed, providing precise depth readings ideal for navigation and fishing. Sonar encompasses a broader range of technologies, including echosounders, to detect and locate underwater objects by emitting sound waves and analyzing their reflections, enhancing your ability to map underwater terrain and identify obstacles.
Table of Comparison
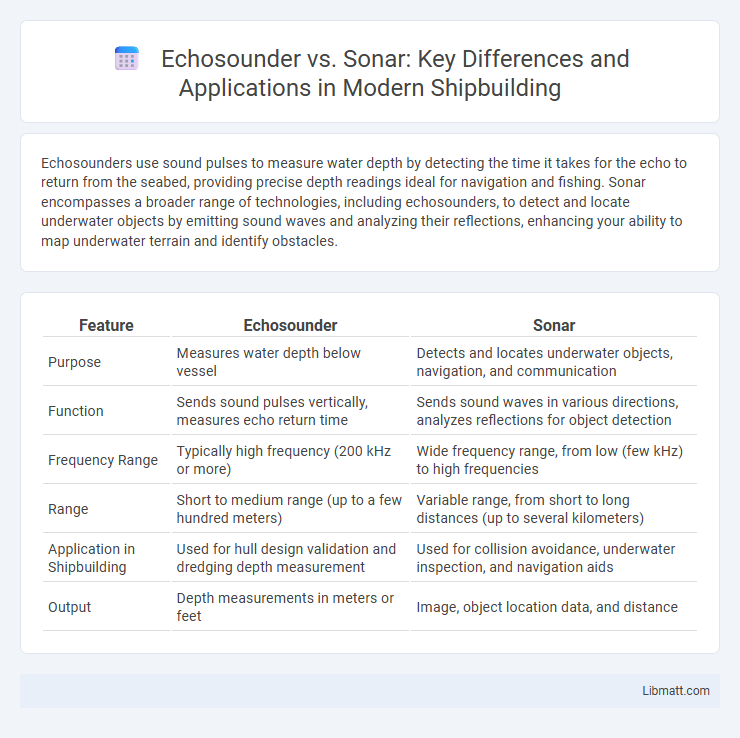
| Feature | Echosounder | Sonar |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures water depth below vessel | Detects and locates underwater objects, navigation, and communication |
| Function | Sends sound pulses vertically, measures echo return time | Sends sound waves in various directions, analyzes reflections for object detection |
| Frequency Range | Typically high frequency (200 kHz or more) | Wide frequency range, from low (few kHz) to high frequencies |
| Range | Short to medium range (up to a few hundred meters) | Variable range, from short to long distances (up to several kilometers) |
| Application in Shipbuilding | Used for hull design validation and dredging depth measurement | Used for collision avoidance, underwater inspection, and navigation aids |
| Output | Depth measurements in meters or feet | Image, object location data, and distance |
Introduction to Echosounders and Sonar
Echosounders use sound pulses to measure water depth by timing the return of echoes from the seabed, providing precise bathymetric data critical for navigation and underwater mapping. Sonar encompasses a broader technology that detects objects, measures distances, and gathers environmental information through sound wave reflection, often used in military, fishing, and scientific applications. Your choice between echosounder and sonar depends on whether you require detailed depth measurement or comprehensive underwater detection capabilities.
How Echosounders Work
Echosounders operate by emitting sound pulses downward into the water and measuring the time it takes for the echoes to return from the seabed or underwater objects, calculating depth based on the speed of sound in water. These devices use high-frequency sound waves, typically between 20 kHz and 200 kHz, enabling precise depth readings and detailed underwater mapping. Unlike general sonar systems that can detect various underwater features, echosounders primarily focus on depth measurement for navigation and fishing applications.
Principles of Sonar Technology
Sonar technology operates by emitting sound pulses and measuring the time it takes for echoes to return after reflecting off objects underwater. Echosounders, a specific type of sonar, focus on determining water depth by analyzing the time interval between the emitted sound pulse and its echo. Understanding these principles helps you interpret sonar data accurately for navigation, fishing, or underwater exploration.
Key Differences Between Echosounder and Sonar
Echosounders are specialized sonar devices that emit sound pulses directly downward to measure water depth by calculating the time it takes for the echo to return. Sonar systems encompass a broader range of applications, including underwater navigation, object detection, and communication, using sound waves in various directions. Your choice depends on whether precise depth measurement (echosounder) or versatile underwater sensing capabilities (sonar) are required.
Applications of Echosounders
Echosounders are primarily used in marine navigation, underwater mapping, and fish finding by emitting sound pulses and measuring the time it takes for echoes to return from the seabed or objects. Unlike broader sonar systems, echosounders provide precise depth measurements, making them essential for hydrographic surveys, dredging operations, and habitat monitoring. Your ability to accurately assess underwater topography and detect marine life depends on the high-resolution data delivered by advanced echosounder technology.
Common Uses of Sonar Systems
Sonar systems are extensively used in marine navigation, underwater exploration, and fisheries management by detecting and mapping objects or terrain beneath the water surface. Commercial shipping relies on sonar for safe navigation and collision avoidance, while scientific research employs sonar technology to study oceanographic features and marine life behavior. Submarine and military applications use sonar for target detection, mine hunting, and underwater communication, highlighting its versatility across multiple maritime sectors.
Advantages of Echosounders
Echosounders provide high-resolution depth measurements by emitting focused sound pulses and analyzing their echoes, enabling precise seabed mapping and obstacle detection. These devices offer rapid data acquisition and greater accuracy compared to traditional sonar, making them ideal for hydrographic surveying and navigation safety. Echosounders also feature advanced signal processing techniques that enhance target discrimination and reduce interference from noise.
Benefits of Using Sonar
Sonar technology provides precise underwater mapping and object detection, enhancing navigation safety and resource exploration. It offers greater range and accuracy compared to traditional echosounders, capable of identifying underwater obstacles and marine life. Sonar systems support diverse applications like fisheries management, submarine communication, and oceanographic research by delivering real-time, high-resolution data.
Limitations and Challenges
Echosounders face limitations in depth accuracy and resolution due to sound absorption and scattering in turbid or complex underwater environments. Sonar systems can struggle with signal interference and noise, impacting target detection and interpretation in cluttered or shallow waters. Both technologies encounter challenges in distinguishing between closely spaced objects and adapting to varying water conditions, which affect overall performance and reliability.
Choosing Between Echosounder and Sonar
Choosing between an echosounder and sonar depends on the specific marine application and desired data accuracy. Echosounders provide precise depth measurements by emitting sound pulses and timing their return, ideal for navigation and hydrographic surveys. Sonar systems offer broader detection capabilities, including object identification and underwater mapping, making them suitable for fishing, military use, and underwater exploration.
Echosounder vs sonar Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com