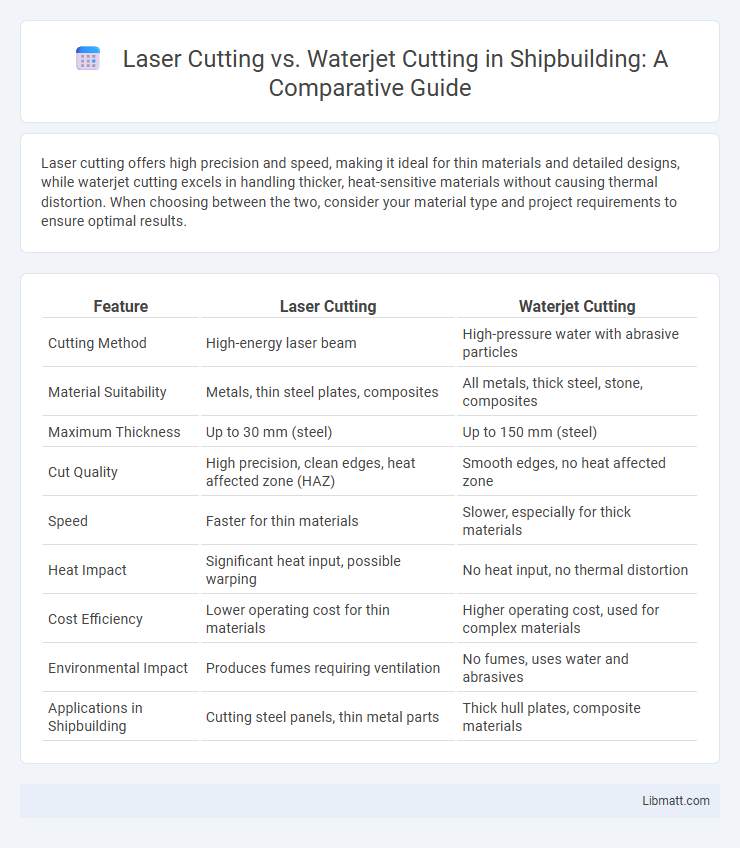
Laser cutting offers high precision and speed, making it ideal for thin materials and detailed designs, while waterjet cutting excels in handling thicker, heat-sensitive materials without causing thermal distortion. When choosing between the two, consider your material type and project requirements to ensure optimal results.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laser Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-energy laser beam | High-pressure water with abrasive particles |
| Material Suitability | Metals, thin steel plates, composites | All metals, thick steel, stone, composites |
| Maximum Thickness | Up to 30 mm (steel) | Up to 150 mm (steel) |
| Cut Quality | High precision, clean edges, heat affected zone (HAZ) | Smooth edges, no heat affected zone |
| Speed | Faster for thin materials | Slower, especially for thick materials |
| Heat Impact | Significant heat input, possible warping | No heat input, no thermal distortion |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operating cost for thin materials | Higher operating cost, used for complex materials |
| Environmental Impact | Produces fumes requiring ventilation | No fumes, uses water and abrasives |
| Applications in Shipbuilding | Cutting steel panels, thin metal parts | Thick hull plates, composite materials |
Introduction to Laser and Waterjet Cutting
Laser cutting utilizes a high-powered focused laser beam to precisely cut or engrave materials such as metal, plastic, and wood, offering exceptional speed and accuracy. Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure jet of water, sometimes mixed with abrasive substances, to cut through a wide range of materials including stone, metal, and composites without generating heat, preserving material integrity. Both technologies serve diverse industrial applications by providing distinct advantages in precision, material compatibility, and finishing quality.
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting works by focusing a high-powered laser beam onto a material's surface, which heats, melts, or vaporizes the targeted area with precision. The laser's concentrated energy enables clean and accurate cuts, especially in thin metals, plastics, and wood. This process relies on computer numerical control (CNC) for detailed shaping, offering advantages in speed and fine resolution over other cutting methods like waterjet cutting.
How Waterjet Cutting Works
Waterjet cutting operates by propelling a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive particles like garnet, to erode materials with precision. This method enables cutting through metals, stone, glass, and composites without generating heat-affected zones, preserving material integrity. The process allows intricate shapes and detailed cuts, making it ideal for materials sensitive to high temperatures or mechanical stress.
Materials Supported by Each Method
Laser cutting excels in processing materials like metals, plastics, wood, and fabrics with high precision, particularly effective for thin to medium thicknesses such as steel up to 25mm. Waterjet cutting supports a broader range of materials, including metals, stone, glass, ceramics, and composites, capable of handling thicker and harder materials without thermal distortion. Your choice depends on the specific material properties and thickness, with waterjet offering versatility and laser providing faster, more precise cuts on select materials.
Precision and Tolerance Comparison
Laser cutting offers superior precision with tolerances typically within +-0.1 mm, making it ideal for intricate designs and fine details on thin materials. Waterjet cutting provides slightly lower precision, with tolerances around +-0.2 mm, but excels in cutting thicker or heat-sensitive materials without thermal distortion. Both methods deliver high accuracy, but laser cutting is preferred for tighter tolerances and cleaner edges in thin metals and plastics.
Speed and Efficiency Analysis
Laser cutting offers higher speeds and precision for thinner materials, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and high-volume production. Waterjet cutting, while slower due to its abrasive process, provides versatility in cutting thicker materials without heat distortion. Your choice depends on the specific material thickness and production speed requirements to maximize efficiency.
Cost Considerations: Laser vs Waterjet
Laser cutting generally offers lower operating costs due to faster processing speeds and reduced material waste, especially for thin metals and plastics. Waterjet cutting involves higher expenses from abrasive materials and slower cutting times, but it excels in cutting thicker or heat-sensitive materials without thermal distortion. Choosing between laser and waterjet cutting depends on balancing initial investment, material type, and production volume to optimize overall cost-efficiency.
Edge Quality and Finishing Differences
Laser cutting offers high precision with smooth, clean edges ideal for detailed metal and thin material work, but may produce slight heat-affected zones causing minor discoloration or warping. Waterjet cutting generates superior edge quality on thicker, heat-sensitive materials by using high-pressure water jets mixed with abrasive particles, resulting in burr-free, cool cuts without thermal distortion. The choice between the two depends largely on material type and thickness, with waterjet preferred for preserving structural integrity and laser favored for intricate designs requiring fine detail.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Laser cutting produces fewer airborne particles but generates intense heat and laser radiation, necessitating stringent protective measures for operators to prevent burns and eye injuries. Waterjet cutting eliminates thermal hazards and significantly reduces airborne contaminants, making it safer for personnel while using high-pressure water mixed with abrasives which must be handled carefully to avoid equipment damage and injury. Environmentally, laser cutting consumes more energy and may emit harmful gases, whereas waterjet cutting uses water recycling systems and non-toxic abrasives, minimizing ecological impact and waste generation.
Choosing the Right Cutting Method
Laser cutting excels in precision and speed for thin to medium-thickness materials such as metal, plastic, and wood, ideal for detailed designs and clean edges. Waterjet cutting suits thicker or heat-sensitive materials, including stone, glass, and composites, as it avoids heat-affected zones and material distortion. Selecting the right cutting method depends on material thickness, thermal sensitivity, edge quality requirements, and production speed demands.
Laser cutting vs waterjet cutting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com