Brightleaf tobacco features a mild, sweet flavor with a light golden color due to air-curing, making it ideal for cigarettes and lighter cigars. Dark tobacco undergoes fire-curing, resulting in a stronger, smokier taste and a richer, darker leaf often used in pipe tobacco and some premium cigars, giving your smoke a more robust experience.
Table of Comparison
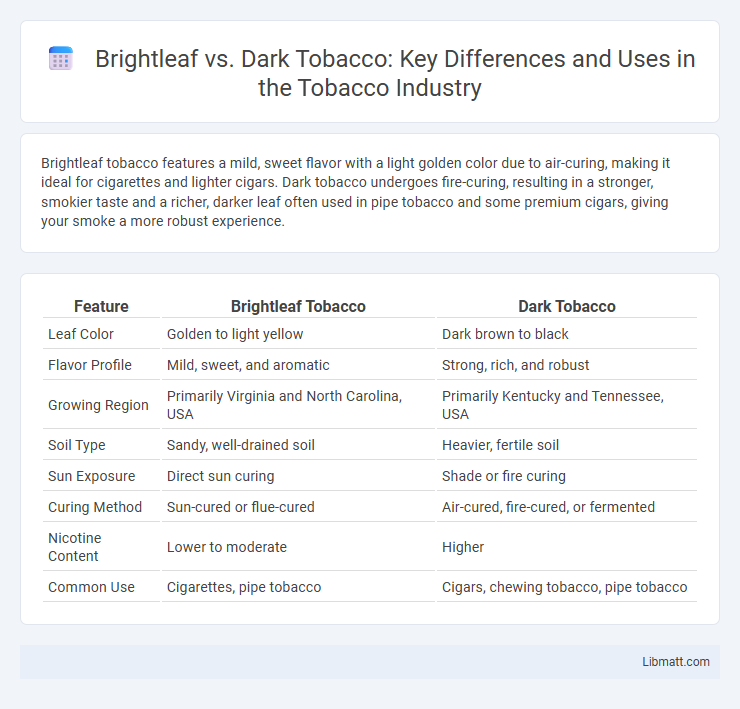
| Feature | Brightleaf Tobacco | Dark Tobacco |
|---|---|---|
| Leaf Color | Golden to light yellow | Dark brown to black |
| Flavor Profile | Mild, sweet, and aromatic | Strong, rich, and robust |
| Growing Region | Primarily Virginia and North Carolina, USA | Primarily Kentucky and Tennessee, USA |
| Soil Type | Sandy, well-drained soil | Heavier, fertile soil |
| Sun Exposure | Direct sun curing | Shade or fire curing |
| Curing Method | Sun-cured or flue-cured | Air-cured, fire-cured, or fermented |
| Nicotine Content | Lower to moderate | Higher |
| Common Use | Cigarettes, pipe tobacco | Cigars, chewing tobacco, pipe tobacco |
Introduction to Brightleaf and Dark Tobacco
Brightleaf tobacco, known for its light color and mild flavor, undergoes a curing process using direct heat and air that enhances its sweetness and smoothness. Dark tobacco, typically stronger and richer, is air-cured or fire-cured, resulting in a robust taste with smoky, earthy undertones. Your choice between brightleaf and dark tobacco influences the overall smoking experience, balancing flavor intensity and aroma preference.
Historical Background of Tobacco Types
Brightleaf tobacco, developed in the 19th century in the southeastern United States, gained prominence for its mild flavor and golden color due to sun-curing methods. Dark tobacco, often originating from regions like Kentucky and Virginia, has a richer, more robust flavor because of its air-curing process that results in a darker leaf. Your choice between brightleaf and dark tobacco reflects centuries of agricultural and cultural evolution shaping the distinct characteristics of these tobacco types.
Key Differences in Leaf Characteristics
Brightleaf tobacco features light, golden-yellow leaves that are thin and flexible due to flue-curing, resulting in a milder flavor and smooth texture. Dark tobacco leaves are thicker, darker, and coarser, often air-cured or fire-cured, which imparts a stronger, more robust flavor suited for cigars or chewing. The curing process and leaf structure directly influence the chemical composition, nicotine content, and flavor profiles distinguishing brightleaf from dark tobacco.
Growing Regions and Climate Preferences
Brightleaf tobacco thrives in the sandy soils and warm, humid climate of the southeastern United States, particularly in North Carolina and Virginia, where long growing seasons promote its light color and mild flavor. Dark tobacco favors the cooler, more temperate regions of Kentucky and Tennessee, growing well in richer, loamy soils that contribute to its robust flavor profile and darker leaves. Both types require carefully managed heat and moisture levels, but their distinct regional growing conditions significantly influence their final tobacco characteristics.
Cultivation Methods: Brightleaf vs Dark Tobacco
Brightleaf tobacco is cultivated using a flue-curing method where leaves are grown in sandy, well-drained soils and cured using controlled heat in barns to develop a mild flavor and bright yellow color. Dark tobacco thrives in richer, clay-like soils and undergoes air-curing or smoke-curing processes, resulting in a stronger, more robust flavor with darker leaves. The differences in soil type, curing environment, and heat application significantly impact the chemical composition and taste profiles of brightleaf versus dark tobacco.
Harvesting and Curing Processes
Brightleaf tobacco undergoes a flue-curing process where leaves are dried in enclosed barns using controlled heat, preserving the tobacco's light color and mild flavor. Dark tobacco, on the other hand, is air-cured or fire-cured, involving natural airflow or smoke exposure that results in a darker, stronger tobacco with richer, robust flavors. Harvesting for brightleaf involves picking the leaves at specific maturity stages to maintain brightness, whereas dark tobacco harvesting emphasizes full maturity to enhance the leaf's depth and intensity.
Flavor Profiles and Chemical Composition
Brightleaf tobacco offers a mild, sweet flavor profile with notes of honey and citrus, attributed to its high sugar content and lower nicotine levels. Dark tobacco, by contrast, delivers a robust, earthy flavor enriched by higher nicotine and tar concentrations, resulting from a slower curing process and greater chemical complexity. Understanding these differences helps you choose tobacco that best suits your taste preferences and desired intensity.
Uses in Cigarette and Cigar Production
Brightleaf tobacco, known for its mild flavor and light, golden appearance, is predominantly used in cigarette production due to its smooth taste and high combustibility. Dark tobacco, often air-cured and richer in nicotine, is favored in cigar manufacturing for its robust flavor and thicker smoke profile. The choice between brightleaf and dark tobacco significantly influences the strength, aroma, and overall smoking experience in cigarettes and cigars.
Economic Impact on Local and Global Markets
Brightleaf tobacco, known for its mild flavor and high demand in cigarette manufacturing, significantly boosts the economies of regions like North Carolina by providing substantial employment and export revenues. Dark tobacco, valued for its robust flavor in products such as cigars and pipe tobacco, supports smaller but stable markets, influencing local economies in areas like Kentucky and Pennsylvania. The global tobacco market balances these varieties' production, with brightleaf dominating mass-market cigarettes and dark tobacco maintaining niche but profitable sectors, collectively driving billions in international trade annually.
Health Considerations and Industry Trends
Brightleaf tobacco, known for its mild flavor and lower tar content, is often perceived as a less harmful option compared to dark tobacco, which contains higher nicotine levels and more tar, increasing health risks. Recent industry trends reveal a growing consumer shift towards brightleaf products due to heightened awareness of the health implications associated with darker tobaccos. Regulatory pressures and health campaigns also drive manufacturers to innovate with milder blends and reduced harm alternatives within brightleaf tobacco offerings.
brightleaf vs dark tobacco Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com