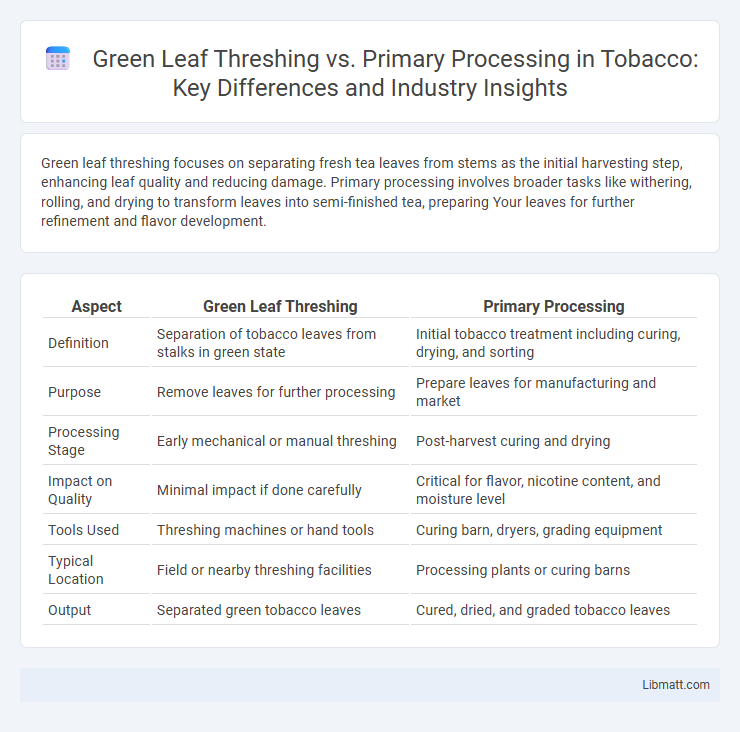
Green leaf threshing focuses on separating fresh tea leaves from stems as the initial harvesting step, enhancing leaf quality and reducing damage. Primary processing involves broader tasks like withering, rolling, and drying to transform leaves into semi-finished tea, preparing Your leaves for further refinement and flavor development.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Green Leaf Threshing | Primary Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separation of tobacco leaves from stalks in green state | Initial tobacco treatment including curing, drying, and sorting |
| Purpose | Remove leaves for further processing | Prepare leaves for manufacturing and market |
| Processing Stage | Early mechanical or manual threshing | Post-harvest curing and drying |
| Impact on Quality | Minimal impact if done carefully | Critical for flavor, nicotine content, and moisture level |
| Tools Used | Threshing machines or hand tools | Curing barn, dryers, grading equipment |
| Typical Location | Field or nearby threshing facilities | Processing plants or curing barns |
| Output | Separated green tobacco leaves | Cured, dried, and graded tobacco leaves |
Introduction to Green Leaf Threshing and Primary Processing
Green leaf threshing involves the mechanical separation of tea leaves from the stems immediately after plucking, preserving the freshness and aroma of the leaves for optimal flavor development. Primary processing encompasses initial tea production stages such as withering, rolling, and oxidation, which are critical for developing the distinct characteristics and quality of the final tea product. Efficient green leaf threshing enhances the effectiveness of primary processing by providing uniform leaf material, directly impacting tea quality and consistency.
Defining Green Leaf Threshing in Tea Production
Green leaf threshing in tea production refers to the process of separating tea leaves from their stems immediately after harvesting, preserving the leaf's freshness and quality for further processing. This step is crucial in retaining essential oils and enzymes that influence tea flavor and aroma before primary processing stages such as withering, rolling, and fermentation. Efficient green leaf threshing enhances leaf uniformity and consistency, directly impacting the final tea quality and yield.
Understanding Primary Processing Techniques
Primary processing techniques in green leaf threshing involve the initial stage of separating leaves from the stems and other impurities to ensure purity and quality. Methods such as mechanical threshing, hand stripping, and air separation enhance the efficiency of leaf collection while minimizing damage. Optimizing these techniques improves the overall yield and prepares the leaves for subsequent drying and production stages.
Key Differences Between Green Leaf Threshing and Primary Processing
Green leaf threshing separates tea leaves from stems immediately after plucking, optimizing leaf integrity and minimizing oxidation for high-quality green tea production. Primary processing involves initial stages such as withering, rolling, and fermentation, crucial for developing the flavor and aroma profiles of black or oolong teas. The key differences lie in the timing and method of leaf separation, affecting oxidation levels and final tea characteristics.
Equipment Used in Green Leaf Threshing vs Primary Processing
Green leaf threshing utilizes specialized threshers designed to carefully separate leaf material without damaging the delicate fibers, often employing rotary or drum mechanisms optimized for high-throughput and gentle handling. Primary processing involves equipment such as conveyors, sorters, and initial drying machines that prepare the raw leaves for further refinement by removing stems and impurities while maintaining leaf integrity. The distinction in equipment emphasizes threshers for physical separation in green leaf threshing, whereas primary processing relies on a combination of mechanical sorting and controlled environmental conditions to enhance leaf quality.
Impact on Leaf Quality and End Product
Green leaf threshing preserves the leaf's structural integrity by minimizing mechanical damage, resulting in higher quality raw material compared to primary processing methods that often involve harsher handling and increased leaf breakage. The improved leaf quality from green leaf threshing enhances the end product's flavor, aroma, and overall sensory characteristics, making it preferable for premium tea or tobacco production. In contrast, primary processing techniques may lead to lower-grade end products due to compromised leaf texture and increased contamination.
Efficiency and Labor Requirements Comparison
Green leaf threshing offers higher efficiency by directly separating leaves from stems, reducing processing time and minimizing material loss compared to primary processing methods that handle whole plants. This method demands less labor input as mechanical threshers automate leaf separation, whereas primary processing is more labor-intensive, often requiring manual handling for initial breakdown. Your choice between green leaf threshing and primary processing can significantly impact operational efficiency and workforce allocation based on scale and available technology.
Environmental Considerations for Each Process
Green leaf threshing minimizes environmental impact by preserving soil integrity and reducing carbon emissions compared to energy-intensive primary processing methods. Primary processing often involves heavy machinery and chemical usage, which can lead to higher pollution levels and increased resource consumption. Evaluating your operations can help choose greener practices, enhancing sustainability and reducing your ecological footprint.
Industry Applications and Preferences
Green leaf threshing is favored in tea and tobacco industries for its ability to preserve leaf integrity and enhance flavor profiles, whereas primary processing is commonly used in grain and cereal sectors to efficiently separate edible parts from chaff. The tea industry prefers green leaf threshing due to its gentle handling that maintains leaf quality critical for premium product output, while primary processing suits large-scale grain operations emphasizing throughput and volume. Preferences vary based on product sensitivity and intended final use, with green leaf threshing aligning with quality-focused applications and primary processing supporting bulk agricultural commodity production.
Choosing the Right Method for Optimal Yield
Selecting between green leaf threshing and primary processing depends on crop type and moisture content to maximize yield efficiency. Green leaf threshing preserves leaf integrity and nutrient content, ideal for fresh forage harvesting, while primary processing involves initial cleaning and sorting, enhancing quality for storage and market readiness. Evaluating specific crop characteristics and end-use goals ensures optimal method selection for superior yield and product quality.
green leaf threshing vs primary processing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com