Stalk position significantly influences leaf maturity by determining exposure to sunlight and nutrient flow, which affects chlorophyll development and overall leaf size. Your understanding of this relationship helps optimize harvesting times for maximum yield and quality in crops.
Table of Comparison
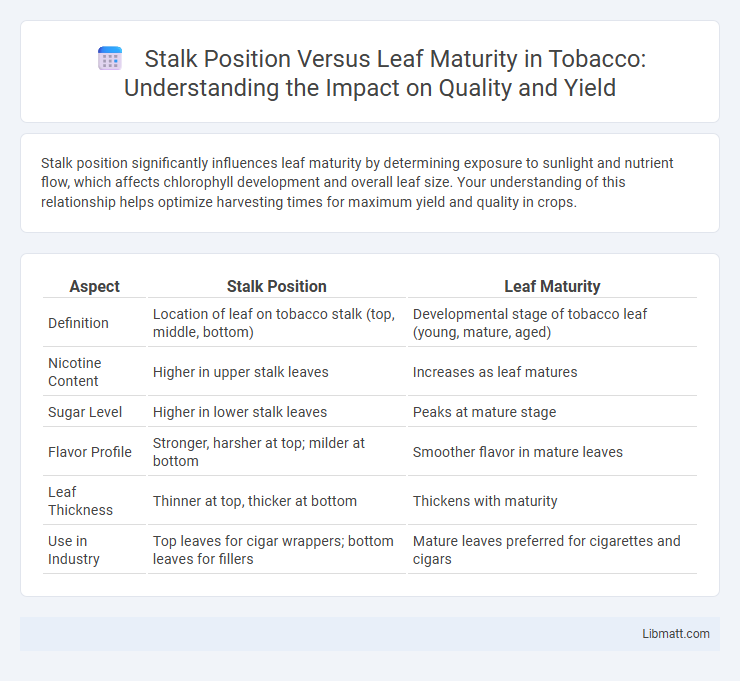
| Aspect | Stalk Position | Leaf Maturity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Location of leaf on tobacco stalk (top, middle, bottom) | Developmental stage of tobacco leaf (young, mature, aged) |
| Nicotine Content | Higher in upper stalk leaves | Increases as leaf matures |
| Sugar Level | Higher in lower stalk leaves | Peaks at mature stage |
| Flavor Profile | Stronger, harsher at top; milder at bottom | Smoother flavor in mature leaves |
| Leaf Thickness | Thinner at top, thicker at bottom | Thickens with maturity |
| Use in Industry | Top leaves for cigar wrappers; bottom leaves for fillers | Mature leaves preferred for cigarettes and cigars |
Introduction to Stalk Position and Leaf Maturity
Stalk position and leaf maturity are critical parameters in assessing crop health and development stages in agriculture. Stalk position refers to the specific location of leaves or other plant structures along the stem, which influences nutrient distribution and photosynthetic efficiency. Leaf maturity describes the developmental stage of a leaf, affecting its size, color, and physiological functions essential for growth and yield optimization.
Defining Stalk Position in Plant Anatomy
Stalk position in plant anatomy refers to the specific location of a leaf or internode along the main stem, influencing leaf maturity and physiological functions. Lower stalk positions typically support older, fully mature leaves, while higher positions correspond to younger, developing leaves essential for growth and photosynthesis. Understanding your plant's stalk position aids in optimizing nutrient management and assessing overall health.
Understanding Leaf Maturity Stages
Leaf maturity stages significantly influence stalk position by indicating the developmental phase of the plant. Immature leaves near the stalk base often show active growth and higher nutrient allocation, while mature leaves toward the outer stalk areas demonstrate full photosynthetic capacity and contribute to overall plant energy. Monitoring these stages helps optimize resource distribution and improve management practices in crop development.
Relationship Between Stalk Position and Leaf Age
Stalk position closely correlates with leaf maturity, as leaves positioned lower on the stalk are typically older and more mature compared to those at the top. This gradient in leaf age influences physiological functions such as nutrient allocation and photosynthetic efficiency. Understanding the relationship between stalk position and leaf age is crucial for optimizing crop management and improving yield quality.
Physiological Changes by Stalk Position
Physiological changes in plants vary significantly by stalk position, influencing leaf maturity and nutrient allocation. Lower stalk positions typically exhibit older leaves with increased lignification and reduced photosynthetic activity, while upper stalk positions support younger, more metabolically active leaves with higher chlorophyll content. These gradients impact the overall growth dynamics and yield quality by optimizing resource distribution within the plant.
Biochemical Variations with Leaf Maturity
Biochemical variations in stalk position versus leaf maturity significantly influence plant nutrient content and metabolic activity. Younger leaves exhibit higher concentrations of amino acids and soluble sugars, while mature leaves accumulate more structural carbohydrates and phenolic compounds. Understanding these variations helps optimize nutrient management and improve crop quality by targeting specific developmental stages for harvest or treatment.
Impact on Photosynthesis Efficiency
Stalk position significantly influences photosynthesis efficiency by affecting leaf maturity and light exposure, where mature leaves located in the upper stalk positions typically exhibit higher chlorophyll content and photosynthetic rates. Lower stalk leaves, being older and more shaded, experience reduced photosynthetic efficiency due to decreased light interception and chlorophyll degradation. Optimizing leaf position and maturity balance enhances overall canopy photosynthesis, improving plant growth and crop yield.
Role in Nutrient Distribution
Stalk position directly influences nutrient distribution within a plant, affecting leaf maturity and overall health. Nutrients are often transported upward from the stalk to younger leaves, with older leaves receiving fewer resources as the plant prioritizes new growth. Your understanding of this dynamic can improve nutrient management strategies for optimal crop yield and quality.
Implications for Crop Harvest and Quality
Stalk position directly influences leaf maturity, affecting nutrient allocation and crop development, which are critical factors determining optimal harvest timing. Older leaves in lower stalk positions often exhibit nutrient remobilization, impacting grain filling and overall crop quality. Understanding these dynamics enables farmers to schedule harvests more precisely, enhancing yield and ensuring superior crop quality.
Conclusion: Stalk Position’s Influence on Leaf Maturity
Stalk position significantly influences leaf maturity, with leaves closer to the base typically exhibiting more advanced physiological development compared to upper leaves. This gradient in maturity affects nutrient allocation and photosynthetic efficiency throughout the plant, impacting overall growth and yield. Understanding how stalk position correlates with leaf maturity can help you optimize management practices to enhance crop performance.
Stalk position vs leaf maturity Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com