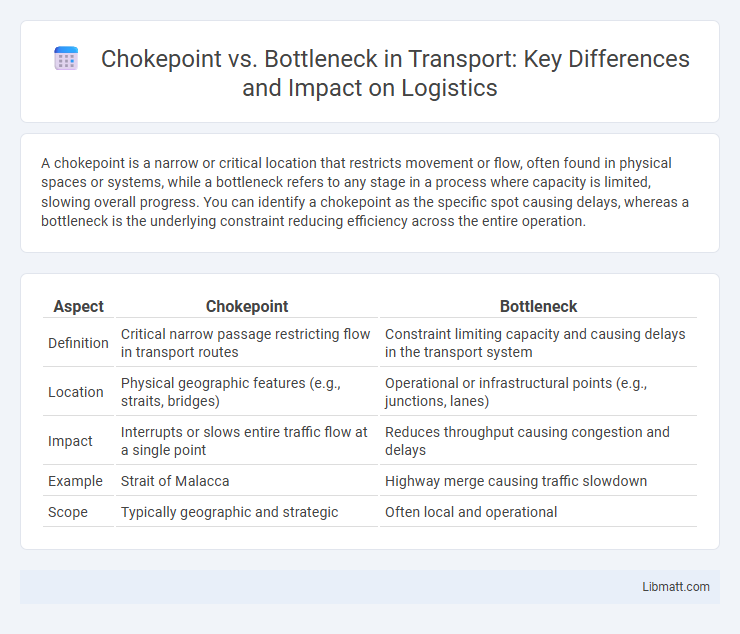
A chokepoint is a narrow or critical location that restricts movement or flow, often found in physical spaces or systems, while a bottleneck refers to any stage in a process where capacity is limited, slowing overall progress. You can identify a chokepoint as the specific spot causing delays, whereas a bottleneck is the underlying constraint reducing efficiency across the entire operation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Chokepoint | Bottleneck |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Critical narrow passage restricting flow in transport routes | Constraint limiting capacity and causing delays in the transport system |
| Location | Physical geographic features (e.g., straits, bridges) | Operational or infrastructural points (e.g., junctions, lanes) |
| Impact | Interrupts or slows entire traffic flow at a single point | Reduces throughput causing congestion and delays |
| Example | Strait of Malacca | Highway merge causing traffic slowdown |
| Scope | Typically geographic and strategic | Often local and operational |
Introduction to Chokepoint and Bottleneck
A chokepoint refers to a narrow or constricted passage that limits the flow of traffic, goods, or information, often causing delays or congestion in supply chains or networks. A bottleneck, in contrast, represents a specific stage or resource in a process that restricts overall throughput and reduces efficiency, commonly identified in production lines or project workflows. Understanding the differences between chokepoints and bottlenecks is crucial for optimizing performance and mitigating operational risks.
Defining Chokepoint: Meaning and Context
A chokepoint is a strategic narrow passage or location where the flow of resources, traffic, or information is restricted, causing potential delays or vulnerabilities. Unlike a bottleneck, which refers to any process limitation reducing overall capacity, a chokepoint specifically highlights the critical geographic or structural constraint in supply chains, logistics, or communication networks. Your understanding of chokepoints is essential for identifying risks and ensuring smoother operations in environments like maritime routes, internet data flow, or manufacturing systems.
Understanding Bottleneck: Key Characteristics
A bottleneck is a point in a process where the flow of production is limited or slowed down, causing overall system inefficiency and reduced throughput. Key characteristics include limited capacity, excessive queue build-up, and significant impact on the entire operational workflow. Identifying bottlenecks is crucial for optimizing performance and increasing output in manufacturing, software development, and supply chain management.
Differences Between Chokepoint and Bottleneck
Chokepoints are strategic locations where movement or flow is restricted due to narrow passageways, often relevant in geography, military, or logistics contexts, whereas bottlenecks refer to any stage in a process or system where the throughput is limited, causing delays and reduced efficiency. Chokepoints are physical constraints that can be controlled or defended, while bottlenecks can occur in both physical and abstract systems, such as production lines or data processing. Understanding the differences helps optimize resource allocation and improve flow in transportation, supply chains, and workflow management.
Real-World Examples of Chokepoints
Real-world examples of chokepoints include the Strait of Hormuz, a critical passage for global oil shipments, and the Panama Canal, which connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, significantly influencing international trade routes. These geographical chokepoints can restrict the flow of goods and create vulnerabilities in supply chains, causing delays and increased costs. Understanding how chokepoints impact your logistics or strategic planning is essential for mitigating risks in global transportation networks.
Common Scenarios for Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks commonly occur in manufacturing lines, where a single slow machine limits overall production speed, or in network systems experiencing high traffic that exceeds bandwidth capacity. In software development, inefficient code or database queries can create processing delays, impacting application performance. Identifying and addressing these bottlenecks enhances Your system's efficiency and throughput.
Causes of Chokepoints in Systems and Processes
Chokepoints in systems and processes often arise from limited resources, such as insufficient bandwidth, reduced processing capacity, or constrained physical space that restricts the flow of operations. Inefficient task allocation, outdated technology, and rigid procedures further exacerbate these constraints, impeding overall system performance. Understanding these causes helps you identify critical areas to optimize and improve workflow efficiency.
Identifying Bottlenecks: Methods and Tools
Identifying bottlenecks involves analyzing workflow processes using methods like value stream mapping, process flowcharts, and time-motion studies to pinpoint areas causing delays or inefficiencies. Tools such as performance monitoring software, throughput analysis, and capacity utilization metrics help quantify the impact of bottlenecks in systems. Your ability to detect and address these constraints ensures smoother operations and improved overall productivity.
Solutions to Address Chokepoints and Bottlenecks
Addressing chokepoints and bottlenecks requires targeted strategies such as capacity expansion, process optimization, and technology upgrades to improve flow and reduce delays. Implementing real-time monitoring systems helps identify and mitigate congestion before it escalates, while load balancing redistributes resources to prevent localized overloads. Your operations benefit from continuous improvement practices and automation tools that streamline workflows and enhance overall efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Term for Your Situation
Chokepoint describes a critical narrow passage in a system causing significant limitations or risks, while bottleneck refers to any stage in a process that restricts overall flow or performance. Selecting the right term depends on context: use chokepoint when emphasizing strategic vulnerabilities or geographical constraints, and bottleneck when highlighting productivity or efficiency issues. Accurate terminology enhances communication clarity and supports targeted problem-solving in operations or supply chain management.
chokepoint vs bottleneck Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com