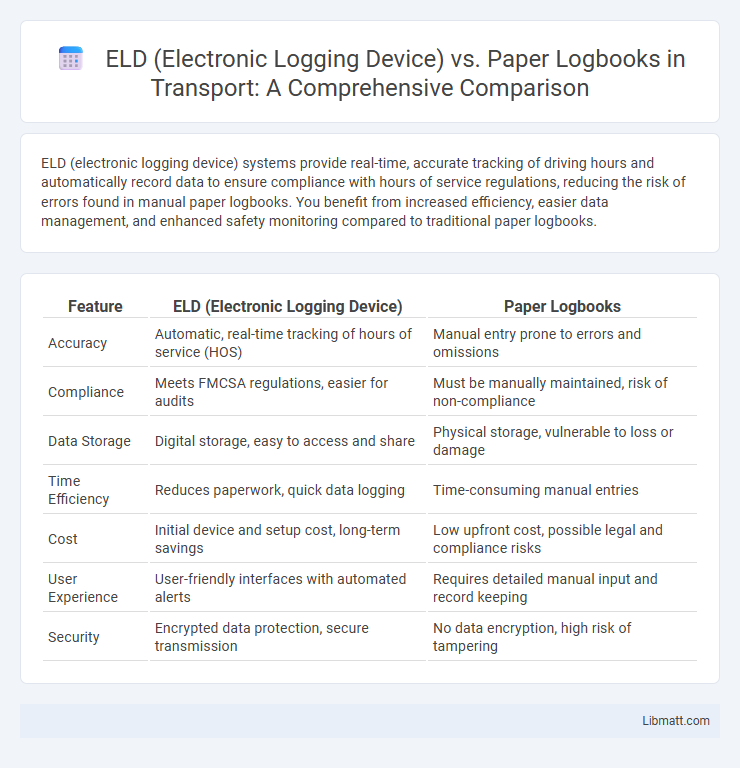
ELD (electronic logging device) systems provide real-time, accurate tracking of driving hours and automatically record data to ensure compliance with hours of service regulations, reducing the risk of errors found in manual paper logbooks. You benefit from increased efficiency, easier data management, and enhanced safety monitoring compared to traditional paper logbooks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | ELD (Electronic Logging Device) | Paper Logbooks |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Automatic, real-time tracking of hours of service (HOS) | Manual entry prone to errors and omissions |
| Compliance | Meets FMCSA regulations, easier for audits | Must be manually maintained, risk of non-compliance |
| Data Storage | Digital storage, easy to access and share | Physical storage, vulnerable to loss or damage |
| Time Efficiency | Reduces paperwork, quick data logging | Time-consuming manual entries |
| Cost | Initial device and setup cost, long-term savings | Low upfront cost, possible legal and compliance risks |
| User Experience | User-friendly interfaces with automated alerts | Requires detailed manual input and record keeping |
| Security | Encrypted data protection, secure transmission | No data encryption, high risk of tampering |
Introduction to ELDs and Paper Logbooks
ELDs (Electronic Logging Devices) automatically record driving hours and engine data, ensuring compliance with Hours of Service (HOS) regulations and reducing the risk of manual errors inherent in paper logbooks. Paper logbooks require drivers to manually document their hours, often leading to inaccuracies and increased administrative burdens for trucking companies. Your fleet management can significantly benefit from the precision and real-time data accessibility offered by ELDs compared to traditional paper logs.
Regulatory Requirements for Drivers
ELD (electronic logging device) regulations require commercial drivers to electronically record Hours of Service (HOS) to ensure accurate and tamper-proof tracking, reducing errors and violations compared to traditional paper logbooks. The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) mandates ELD compliance for most drivers, aiming to enhance roadside inspections and improve safety measures. You must transition to an ELD system to meet federally enforced standards and avoid penalties associated with outdated paper logbooks.
Accuracy and Reliability of Recordkeeping
Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) provide superior accuracy and reliability compared to paper logbooks by automatically recording driving hours and vehicle data, minimizing human errors and tampering. ELDs use GPS and engine synchronization to generate precise, tamper-resistant records that comply with regulatory standards, ensuring consistent and verifiable data for audits and inspections. Paper logbooks are prone to falsification, misplaced entries, and calculation mistakes, making them less reliable for accurate compliance and safety monitoring.
Ease of Use and Learning Curve
Electronic logging devices (ELDs) offer a streamlined, user-friendly interface that reduces the time spent on manual entries compared to traditional paper logbooks. Drivers often find ELDs easier to learn due to automated features, real-time data tracking, and integrated alert systems that ensure compliance with Hours of Service regulations. You can benefit from improved accuracy and a shorter learning curve, especially when transitioning from paper-based logs to digital recording.
Compliance and Audit Risks
ELD (electronic logging device) systems ensure higher compliance accuracy by automatically recording hours of service (HOS), reducing risks associated with manual errors or falsified paper logbooks. Auditors prefer ELD data for its tamper-proof, real-time records, minimizing audit discrepancies and potential fines for violations. Your fleet's adherence to federal regulations improves significantly when using ELDs, lowering the risk of costly compliance audits and enhancing operational transparency.
Cost Comparison: ELDs vs Paper Logbooks
Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) typically involve higher upfront costs, including device purchase prices ranging from $200 to $800 and monthly service fees between $15 and $50. Paper logbooks, by contrast, have minimal initial expenses but may incur indirect costs such as fines from audit errors, increased labor for manual entries, and inefficiencies in compliance tracking. Over time, ELDs can reduce operational costs by improving accuracy, enabling real-time data management, and minimizing penalties associated with logbook violations.
Impact on Driver Productivity
ELDs (electronic logging devices) significantly enhance driver productivity by automating hours-of-service tracking, reducing manual input errors inherent in paper logbooks. This automation enables drivers to spend more time on the road and less on administrative tasks, improving route efficiency and compliance accuracy. Your workflow benefits from real-time data access and faster reporting, ultimately leading to optimized delivery schedules and reduced downtime.
Data Accessibility and Reporting
Electronic logging devices (ELDs) offer real-time data accessibility, enabling instant retrieval and automated reporting of driving hours through cloud-based platforms. Unlike paper logbooks, which require manual transcription and are prone to errors, ELDs generate accurate, easy-to-analyze reports that streamline compliance audits and enhance fleet management. Your ability to monitor driving patterns and ensure regulatory adherence improves significantly with the digital precision and accessibility of ELD data.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) enhance security by encrypting driver data and restricting unauthorized access, minimizing risks of tampering and falsification compared to traditional paper logbooks. Paper logbooks are vulnerable to physical damage, loss, and manual errors, posing significant privacy risks since sensitive information can be easily exposed or altered. Regulatory compliance with FMCSA mandates stringent data protection standards for ELDs, reinforcing privacy safeguards that paper records cannot consistently guarantee.
Future Trends in Logging Technology
Future trends in logging technology highlight a shift toward advanced Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) with enhanced real-time GPS tracking, automated hours-of-service (HOS) compliance, and cloud-based data integration for seamless fleet management. Machine learning algorithms and AI-powered analytics are increasingly used to optimize driver performance and predictive maintenance, surpassing the capabilities of traditional paper logbooks. Regulatory bodies continue to mandate digital record-keeping, driving widespread adoption of ELDs while reducing errors and improving operational efficiency in commercial trucking.
ELD (electronic logging device) vs paper logbooks Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com