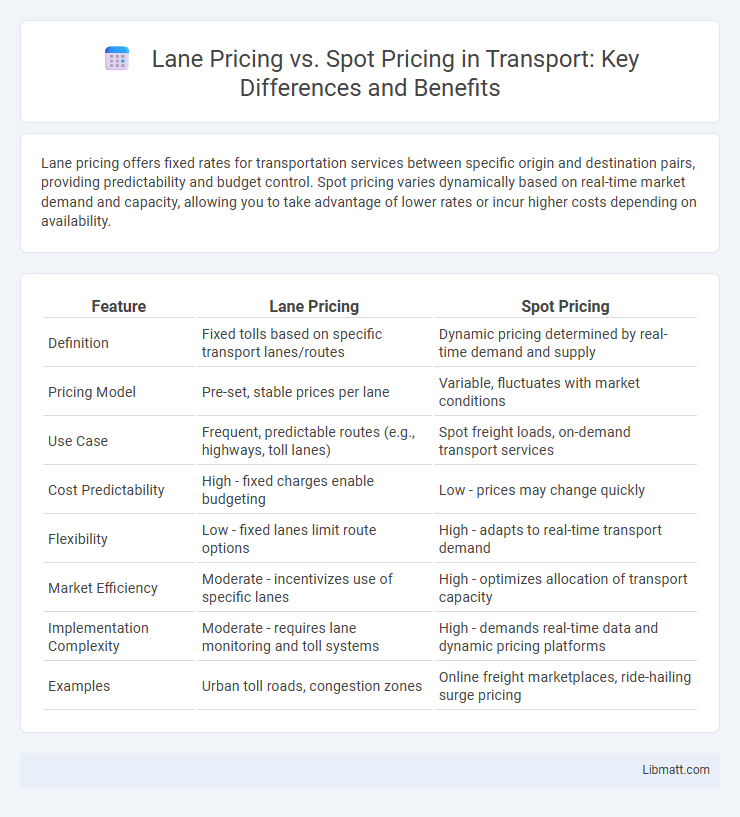
Lane pricing offers fixed rates for transportation services between specific origin and destination pairs, providing predictability and budget control. Spot pricing varies dynamically based on real-time market demand and capacity, allowing you to take advantage of lower rates or incur higher costs depending on availability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lane Pricing | Spot Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed tolls based on specific transport lanes/routes | Dynamic pricing determined by real-time demand and supply |
| Pricing Model | Pre-set, stable prices per lane | Variable, fluctuates with market conditions |
| Use Case | Frequent, predictable routes (e.g., highways, toll lanes) | Spot freight loads, on-demand transport services |
| Cost Predictability | High - fixed charges enable budgeting | Low - prices may change quickly |
| Flexibility | Low - fixed lanes limit route options | High - adapts to real-time transport demand |
| Market Efficiency | Moderate - incentivizes use of specific lanes | High - optimizes allocation of transport capacity |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate - requires lane monitoring and toll systems | High - demands real-time data and dynamic pricing platforms |
| Examples | Urban toll roads, congestion zones | Online freight marketplaces, ride-hailing surge pricing |
Understanding Lane Pricing and Spot Pricing
Lane pricing refers to a fixed rate established for transportation services between specific origin and destination points, enabling predictable budgeting for freight costs. Spot pricing fluctuates based on immediate market demand and capacity, offering flexibility but less predictable expenses. Understanding these pricing models helps you make informed decisions on cost efficiency and service reliability in logistics management.
Key Differences Between Lane and Spot Pricing
Lane pricing refers to negotiated, contract-based freight rates for specific origin-destination pairs, offering predictability and stability in logistics costs. Spot pricing fluctuates based on real-time market demand and capacity, resulting in variable rates that can be higher but offer flexibility for urgent shipments. Key differences include lane pricing's reliance on long-term agreements versus spot pricing's dynamic, market-driven nature, affecting cost certainty and shipment planning strategies.
How Lane Pricing Works in Freight Logistics
Lane pricing in freight logistics sets fixed rates based on specific routes between consistent origin and destination points, providing predictability and cost stability for shippers. This pricing model factors in historical data, volume commitments, and seasonal demand to establish lane-specific tariffs that optimize route efficiency and resource allocation. Unlike spot pricing, which fluctuates with real-time market conditions, lane pricing enables long-term contracts and strategic planning for transportation management.
The Dynamics of Spot Pricing in Transportation
Spot pricing in transportation fluctuates based on real-time market demand, capacity availability, and seasonal factors, offering flexibility but less predictability compared to lane pricing. Lane pricing sets fixed rates for specific routes, providing stability and easier budgeting for your logistics planning. Understanding spot pricing dynamics helps you optimize costs when urgent or variable shipping needs arise.
Benefits of Lane Pricing for Shippers and Carriers
Lane pricing offers shippers predictable transportation costs by establishing fixed rates for specific lanes, improving budget accuracy and cost control. Carriers benefit from lane pricing through optimized route planning and increased load consistency, leading to higher asset utilization and reduced empty miles. This pricing model fosters stronger shipper-carrier partnerships by aligning incentives and enhancing service reliability.
Advantages and Risks of Spot Pricing
Spot pricing offers the advantage of real-time market rate adaptation, enabling shippers to capitalize on lower costs during periods of low demand and increased capacity. This dynamic pricing model enhances flexibility and can lead to cost savings but carries the risk of price volatility, making budgeting and forecasting more challenging. Sudden spikes in spot rates during peak demand or capacity shortages may result in significantly higher expenses compared to fixed lane pricing contracts.
When to Choose Lane Pricing vs Spot Pricing
Choose lane pricing when you require stable, predictable shipping costs for consistent routes and volumes, enabling better budget management and long-term carrier relationships. Opt for spot pricing if your needs are irregular, time-sensitive, or vary greatly, allowing you to capitalize on market fluctuations and potentially lower rates for one-off shipments. Your decision should depend on shipment frequency, volume consistency, and the need for cost control versus flexibility.
Impact on Supply Chain Efficiency
Lane pricing enhances supply chain efficiency by providing predictable rates for specific shipping routes, enabling better budgeting and route optimization, which reduces delays and improves carrier utilization. Spot pricing offers flexibility in volatile markets, allowing shippers to quickly secure capacity during demand surges, but its unpredictability can lead to inconsistent costs and planning challenges. Combining lane pricing with spot market strategies can balance cost control and responsiveness, ultimately optimizing overall supply chain performance.
Cost Predictability and Budgeting Considerations
Lane pricing offers greater cost predictability by providing fixed rates for specific shipping routes, enabling precise budgeting and minimizing unexpected expenses. Spot pricing fluctuates based on real-time market demand and capacity, introducing variability that can complicate financial planning. Businesses prioritizing stable logistics budgets often prefer lane pricing to avoid the volatility inherent in spot market rates.
Future Trends in Lane and Spot Pricing
Future trends in lane and spot pricing indicate increased reliance on real-time data analytics and AI-driven algorithms to optimize freight costs and capacity utilization. Lane pricing is expected to become more dynamic, reflecting seasonal demand fluctuations and long-term contracts, while spot pricing will likely grow more volatile due to immediate market conditions and supply chain disruptions. Your logistics strategy can benefit from integrating predictive tools that balance both pricing models to improve cost efficiency and service reliability.
lane pricing vs spot pricing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com