FJ core plywood offers superior dimensional stability and fewer voids due to its finger-jointed laminated strips, making it ideal for applications requiring strength and smooth finishes. Your choice between FJ core and solid core plywood depends on the balance you need between cost efficiency and maximum resistance to warping or delamination.
Table of Comparison
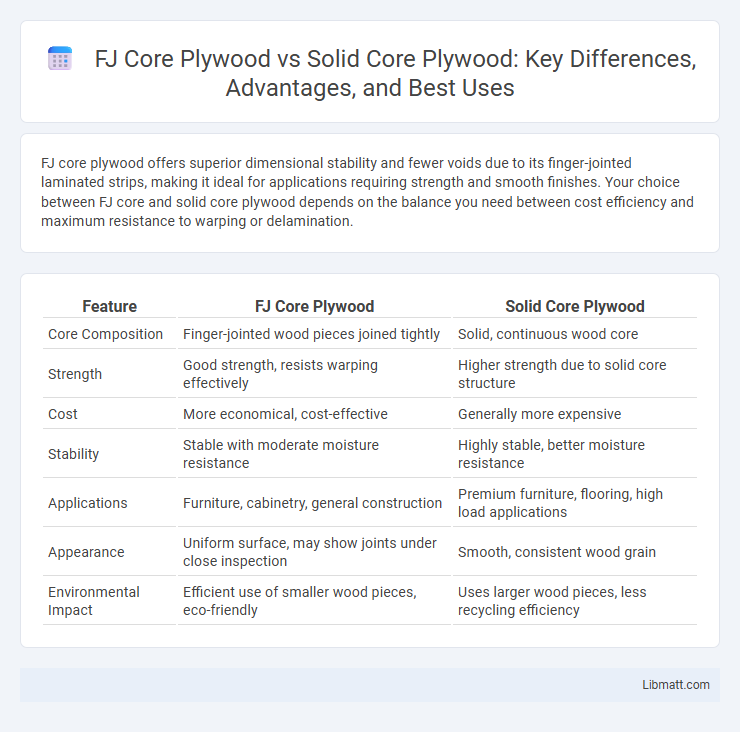
| Feature | FJ Core Plywood | Solid Core Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Core Composition | Finger-jointed wood pieces joined tightly | Solid, continuous wood core |
| Strength | Good strength, resists warping effectively | Higher strength due to solid core structure |
| Cost | More economical, cost-effective | Generally more expensive |
| Stability | Stable with moderate moisture resistance | Highly stable, better moisture resistance |
| Applications | Furniture, cabinetry, general construction | Premium furniture, flooring, high load applications |
| Appearance | Uniform surface, may show joints under close inspection | Smooth, consistent wood grain |
| Environmental Impact | Efficient use of smaller wood pieces, eco-friendly | Uses larger wood pieces, less recycling efficiency |
Introduction to FJ Core Plywood and Solid Core Plywood
FJ core plywood features finger-jointed strips of wood laminated together to create a strong, stable core with minimal voids, enhancing durability and resistance to warping. Solid core plywood consists of a single, continuous wood core, offering superior weight and density for applications demanding extra strength and a smooth finish. Your choice between FJ core and solid core plywood depends on the project's structural needs and desired surface quality.
Definition and Composition of FJ Core Plywood
FJ core plywood features finger-jointed veneer strips meticulously glued together to form a stable, cohesive core, enhancing dimensional stability and reducing warping compared to solid core plywood made from a single, continuous piece of wood. This engineered composition provides superior strength and uniformity, ideal for applications requiring consistent thickness and reduced defects. Your choice of FJ core plywood ensures reliable performance in furniture and cabinetry, where precise finish and structural integrity are critical.
Definition and Composition of Solid Core Plywood
Solid core plywood consists of a core layer made from solid wood strips, veneer, or fiberboard, providing enhanced strength and impact resistance compared to FJ core plywood, which uses finger-jointed wood pieces. The solid core's dense and uniform composition reduces voids and improves load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as flooring and furniture. This construction ensures better dimensional stability and durability, especially in environments prone to moisture and heavy wear.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
FJ core plywood is manufactured by finger jointing shorter wood pieces to create long, uniform core layers that improve stability and reduce warping. Solid core plywood consists of a single solid wood slab as its core, providing greater strength but often resulting in heavier panels. The finger jointing process in FJ core plywood enhances material efficiency and uniformity, while solid core plywood relies on natural wood integrity and density for durability.
Strength and Durability Differences
FJ core plywood features finger-jointed veneer strips, providing consistent strength and reduced warping, making it ideal for applications requiring uniform stability. Solid core plywood, constructed with a solid, continuous core layer, offers superior durability and impact resistance, excelling in heavy-duty or high-stress environments. Understanding these strength and durability differences helps you choose the right plywood type for structural integrity and long-lasting performance.
Cost and Price Comparison
FJ core plywood generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to solid core plywood due to its laminated finger-jointed core, which uses smaller wood pieces that reduce material waste and manufacturing expenses. Solid core plywood, composed of a single solid wood or composite core, usually commands a higher price reflecting its enhanced strength and durability. You can expect FJ core plywood to provide significant savings for projects where budget constraints are important without heavily compromising on quality.
Common Applications and Uses
FJ core plywood is commonly used in furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, and interior paneling due to its smooth surface and stability, making it ideal for visible finishes. Solid core plywood is preferred for structural applications, flooring, and exterior projects because of its enhanced strength and durability. Both types serve distinct purposes, with FJ core prioritizing aesthetics and solid core emphasizing robustness in construction.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
FJ core plywood, made with finger-jointed wood pieces, often utilizes smaller, faster-growing timber, reducing deforestation and promoting sustainable forestry practices compared to solid core plywood, which uses larger timber sections. The production of FJ core plywood generates less waste and supports resource efficiency, making it a greener choice for environmentally conscious projects. Your decision to choose FJ core plywood supports reduced environmental impact without compromising on strength or durability.
Pros and Cons of FJ Core Plywood
FJ core plywood is made by finger-jointing small wood pieces to create a stable core, offering better dimensional stability and resistance to warping compared to solid core plywood. Its consistent quality and strength make it ideal for furniture and cabinetry, but the visible finger joints may affect aesthetics in applications where a smooth core surface is needed. You benefit from cost efficiency and improved environmental sustainability, though FJ core plywood may be less suitable for heavy structural uses compared to solid core plywood's uniform, solid interior.
Pros and Cons of Solid Core Plywood
Solid core plywood offers superior strength, durability, and excellent sound insulation compared to FJ core plywood, making it ideal for heavy-duty furniture and flooring applications. However, it tends to be heavier, more expensive, and less dimensionally stable, which can lead to potential warping and increased transportation costs. The consistent density of solid core plywood also provides better screw holding capacity but may require more effort for cutting and machining.
FJ core plywood vs solid core plywood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com