White birch features smooth, white bark that peels in thin layers and thrives in cooler climates, making it ideal for ornamental use and paper production. Yellow birch displays a shiny, bronze-yellow bark with a slightly sweet scent and is valued for its strong, hard wood used in furniture and flooring.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | White Birch | Yellow Birch |
|---|---|---|
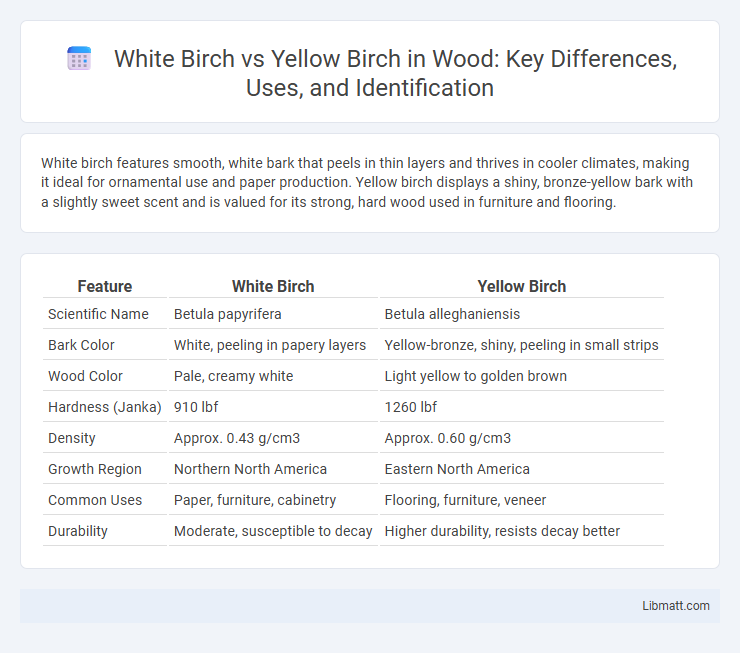
| Scientific Name | Betula papyrifera | Betula alleghaniensis |
| Bark Color | White, peeling in papery layers | Yellow-bronze, shiny, peeling in small strips |
| Wood Color | Pale, creamy white | Light yellow to golden brown |
| Hardness (Janka) | 910 lbf | 1260 lbf |
| Density | Approx. 0.43 g/cm3 | Approx. 0.60 g/cm3 |
| Growth Region | Northern North America | Eastern North America |
| Common Uses | Paper, furniture, cabinetry | Flooring, furniture, veneer |
| Durability | Moderate, susceptible to decay | Higher durability, resists decay better |
Introduction to White Birch and Yellow Birch
White birch and yellow birch are two distinct species native to North America, each valued for their unique wood properties and ecological roles. White birch, known scientifically as Betula papyrifera, features smooth, white bark and is commonly used for paper production and furniture-making due to its lightweight yet durable wood. Yellow birch, or Betula alleghaniensis, displays yellowish-brown bark with a curled, peeling texture and is prized for its hard, heavy wood ideal for flooring and cabinetry.
Botanical Classification and Identification
White birch (Betula papyrifera) and yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis) both belong to the Betulaceae family but differ in bark characteristics and habitat. White birch is identified by its distinctive white, peeling bark and grows primarily in northern North American forests, while yellow birch features shiny, bronze-yellow bark with horizontal lenticels and thrives in cooler, moist environments. Leaf shape and catkin structures also aid in distinguishing these two birch species.
Geographic Distribution and Habitat
White birch primarily thrives in the cooler climates of northeastern North America, favoring well-drained, sandy soils often found in mixed hardwood forests. Yellow birch is commonly found in similar regions but prefers moist, rich soils near streams and swamps, thriving in both northern and mountainous areas. Understanding these habitat preferences helps you select the ideal birch species for your landscape based on local environmental conditions.
Distinctive Bark Characteristics
White birch features smooth, white bark that peels in thin, papery layers, giving it a striking, clean appearance often used for decorative purposes. Yellow birch bark has a more golden or bronze hue with a shiny, slightly peeling surface that emits a spicy fragrance when scratched. Your choice between white and yellow birch can be guided by these distinctive bark traits, which also indicate different growth environments and wood uses.
Leaf Shape and Seasonal Changes
White birch leaves are typically triangular with serrated edges, turning vibrant yellow in the fall, while yellow birch leaves have more ovate, finely toothed margins and also shift to golden-yellow hues. Seasonal changes reveal white birch leaves often display more intense and uniform coloration, in contrast to the yellow birch, whose foliage may have varied tones and a slightly delayed color change. Your ability to identify these trees benefits from observing the distinct leaf shapes alongside the timing and vibrancy of their autumn transformation.
Growth Patterns and Lifespan
White birch (Betula papyrifera) grows quickly, reaching maturity within 30 to 40 years, and typically lives around 80 to 140 years. Yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis) has a slower growth rate, taking 50 to 70 years to mature, but boasts a longer lifespan, often exceeding 150 years. Understanding these growth patterns allows you to select the species best suited to your landscape's timeline and longevity needs.
Wood Properties and Commercial Uses
White birch features fine-grained, light-colored wood that is moderately strong and easy to work with, making it ideal for furniture, plywood, and veneer applications. Yellow birch wood is harder, heavier, and more durable with a warm tone, commonly used in cabinetry, flooring, and millwork due to its high resistance to abrasion. Your choice depends on the desired strength, appearance, and specific commercial application requirements for these birch species.
Ecological Roles and Wildlife Value
White birch (Betula papyrifera) supports diverse wildlife by providing essential food sources such as seeds and catkins for birds and small mammals, and serves as a habitat for various insects that are crucial in forest food webs. Yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis) plays a vital ecological role in its native northern hardwood forests by stabilizing soil and offering browse for deer and moose, while also hosting numerous insect species that contribute to ecosystem health. Both birch species promote biodiversity and sustain complex terrestrial ecosystems through their interactions with flora and fauna.
Landscape and Ornamental Applications
White birch (Betula papyrifera) offers a striking white bark and graceful form that enhances landscape aesthetics, making it a popular choice for ornamental planting in residential and public gardens. Yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis) features a durable, bronze-yellow bark and adapts well to moist, cool environments, providing unique texture and color contrast in landscape design. Your selection between white birch and yellow birch will depend on site conditions and desired visual impact, with both trees delivering significant ornamental value.
Key Differences: White Birch vs. Yellow Birch
White birch (Betula papyrifera) features smooth, white bark that peels in horizontal strips and thrives in cooler climates, while yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis) displays bronze-yellow bark with a metallic sheen and prefers moist, well-drained soils. White birch wood is lighter and softer, commonly used for pulpwood and decorative veneer, whereas yellow birch wood is denser and harder, valued in furniture making and flooring. Differences in leaf shape also assist identification: white birch leaves are triangular with double-toothed edges, while yellow birch leaves are ovate with single-toothed margins.
White birch vs yellow birch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com