A moisture meter directly measures the moisture content within materials such as wood or drywall, providing precise readings essential for construction, restoration, or woodworking projects. Your choice depends on whether you need to assess surface or internal moisture levels, as a hygrometer measures ambient humidity in the air rather than material moisture.
Table of Comparison
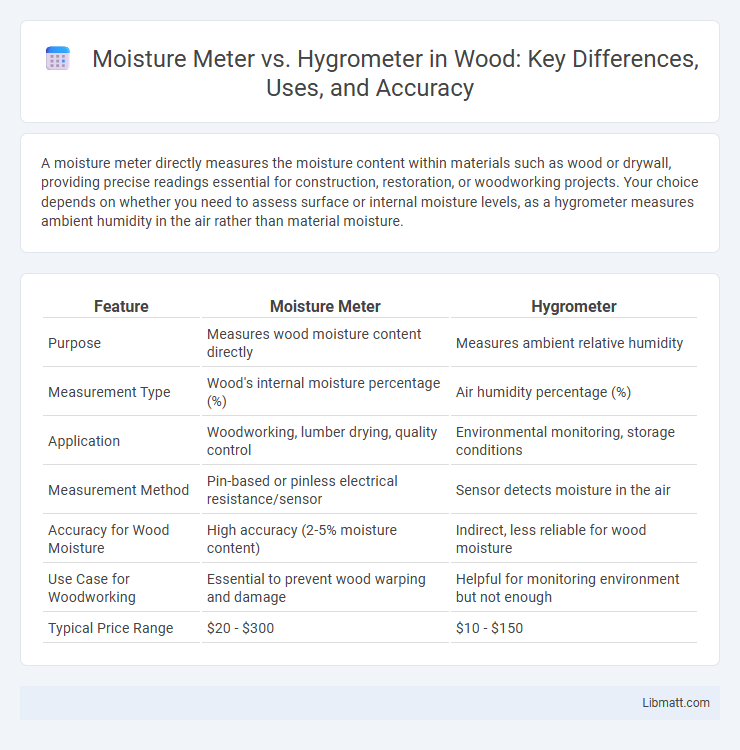
| Feature | Moisture Meter | Hygrometer |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures wood moisture content directly | Measures ambient relative humidity |
| Measurement Type | Wood's internal moisture percentage (%) | Air humidity percentage (%) |
| Application | Woodworking, lumber drying, quality control | Environmental monitoring, storage conditions |
| Measurement Method | Pin-based or pinless electrical resistance/sensor | Sensor detects moisture in the air |
| Accuracy for Wood Moisture | High accuracy (2-5% moisture content) | Indirect, less reliable for wood moisture |
| Use Case for Woodworking | Essential to prevent wood warping and damage | Helpful for monitoring environment but not enough |
| Typical Price Range | $20 - $300 | $10 - $150 |
Introduction to Moisture Meters and Hygrometers
Moisture meters and hygrometers are essential tools for measuring moisture levels but serve distinct purposes: moisture meters detect moisture content within materials like wood or drywall, while hygrometers measure the humidity in the surrounding air. Accurate readings from moisture meters help prevent structural damage and mold growth, making them crucial in construction, woodworking, and restoration projects. Understanding the difference between these devices allows you to select the right tool for monitoring and maintaining optimal moisture conditions in your environment.
Key Differences Between Moisture Meters and Hygrometers
Moisture meters measure the actual moisture content within materials such as wood, concrete, or soil by penetrating their surfaces, providing precise localized readings essential for construction or agriculture. Hygrometers assess the relative humidity in the air, indicating the percentage of water vapor present, which is crucial for indoor climate control and weather forecasting. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate tool for monitoring moisture levels in specific environments or materials.
How Moisture Meters Work
Moisture meters measure the water content in materials by using electrical resistance or capacitance sensors to detect moisture levels. These devices send a small electrical current through the material, and higher moisture increases conductivity, which the meter translates into a moisture percentage. Unlike hygrometers that measure humidity in the air, moisture meters provide direct readings of moisture within substances like wood, concrete, or soil.
How Hygrometers Function
Hygrometers measure humidity by detecting the amount of water vapor in the air using sensors such as capacitive, resistive, or thermal conductivity elements that change electrical properties based on moisture levels. Capacitive hygrometers use a moisture-sensitive polymer film that alters its capacitance with varying humidity, while resistive types detect changes in electrical resistance of a hygroscopic material. Thermal conductivity hygrometers assess humidity by comparing heat conductance between dry and moist air, providing accurate readings for environmental monitoring.
Common Applications for Moisture Meters
Moisture meters are primarily used in construction, woodworking, and agriculture to measure the moisture content in materials like wood, concrete, and soil, ensuring optimal conditions for structural integrity and crop health. These devices provide precise moisture readings that help prevent issues such as mold growth, wood rot, and improper drying. You can rely on moisture meters to make informed decisions during building inspections, moisture control, and quality assurance processes.
Typical Uses for Hygrometers
Hygrometers are commonly used to measure relative humidity in indoor environments, essential for maintaining optimal air quality in homes, museums, and greenhouses. They help monitor climate conditions to prevent mold growth and protect sensitive materials or plants. Industrial applications also rely on hygrometers to ensure proper humidity levels in manufacturing and storage facilities.
Accuracy and Reliability: Moisture Meter vs Hygrometer
Moisture meters provide direct and highly accurate readings of moisture content within materials, making them essential for construction and woodworking where precise moisture levels are critical. Hygrometers measure relative humidity in the air, offering reliable data for monitoring environmental conditions but can be less accurate for assessing moisture inside objects. Your choice between a moisture meter and hygrometer depends on whether you need to measure internal material moisture or ambient humidity for optimal accuracy and reliability.
Pros and Cons of Moisture Meters
Moisture meters offer precise, localized measurements of moisture content in materials like wood and drywall, making them essential for construction and restoration projects. Their pros include quick, non-destructive readings and portability, but cons involve limited scope, as they cannot measure ambient humidity or provide comprehensive environmental data like hygrometers. Understanding your project's needs helps determine if a moisture meter aligns with your moisture assessment requirements or if a broader tool like a hygrometer is more suitable.
Advantages and Limitations of Hygrometers
Hygrometers offer precise measurement of air humidity, essential for monitoring indoor climate and preventing mold growth, with advantages including real-time readings and ease of use. However, their limitations involve sensitivity to temperature fluctuations and less accuracy in very low or high humidity ranges compared to specialized moisture meters. While hygrometers excel in ambient humidity detection, they may not provide reliable moisture content in materials, necessitating moisture meters for construction or agriculture applications.
Choosing the Right Device for Your Needs
Selecting the right device depends on whether you need to measure moisture content in materials or the humidity level in the air. A moisture meter is ideal for detecting water levels inside wood, drywall, or concrete, essential for construction and restoration projects. In contrast, a hygrometer measures ambient humidity, crucial for climate control in homes, greenhouses, and industrial settings.
Moisture meter vs Hygrometer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com