CNC routing uses rotating cutting tools to shape materials such as wood, plastic, and metal, offering deep cuts and smooth edges ideal for detailed 3D parts. Laser cutting employs a focused laser beam to precisely cut or engrave thin materials, providing sharp, clean edges with minimal heat impact perfect for intricate designs and fine details.
Table of Comparison
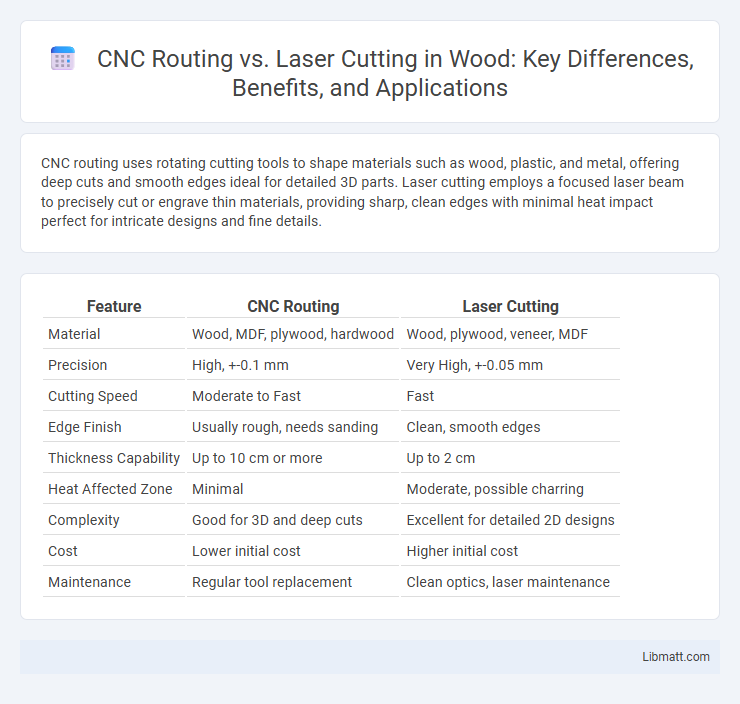
| Feature | CNC Routing | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Wood, MDF, plywood, hardwood | Wood, plywood, veneer, MDF |
| Precision | High, +-0.1 mm | Very High, +-0.05 mm |
| Cutting Speed | Moderate to Fast | Fast |
| Edge Finish | Usually rough, needs sanding | Clean, smooth edges |
| Thickness Capability | Up to 10 cm or more | Up to 2 cm |
| Heat Affected Zone | Minimal | Moderate, possible charring |
| Complexity | Good for 3D and deep cuts | Excellent for detailed 2D designs |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Maintenance | Regular tool replacement | Clean optics, laser maintenance |
Introduction to CNC Routing and Laser Cutting
CNC routing uses rotary cutting tools to carve, shape, and engrave materials like wood, plastic, and metal with high precision, making it ideal for thicker and more rigid materials. Laser cutting employs a focused laser beam to cut or etch materials such as acrylic, fabric, and thin metals, offering unparalleled accuracy and smooth edges. Understanding the strengths of your project materials helps you choose between CNC routing's versatility and laser cutting's fine detail.
How CNC Routing Works
CNC routing operates by using computer-controlled rotating cutting tools to carve or shape materials such as wood, plastic, and metal with high precision. The machine follows a programmed digital design, moving the router bit along multiple axes to execute complex cuts, engravings, and profiles. Unlike laser cutting, CNC routing physically removes material through mechanical cutting, allowing for greater depth and versatility across various thicknesses.
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting works by directing a high-powered laser beam onto materials, which melts, burns, or vaporizes the targeted area with extreme precision. The process is controlled by computer numerical control (CNC) systems that guide the laser to create intricate designs and clean edges on a variety of materials like metal, wood, and plastic. Your projects benefit from the speed, accuracy, and minimal material waste that laser cutting technology provides, making it ideal for detailed and complex cutting tasks.
Materials Suitable for CNC Routing
CNC routing is highly effective for cutting and shaping a wide range of materials including wood, plastic, composites, and soft metals such as aluminum and brass. It excels in handling thicker and denser materials that require precise carving, drilling, or milling operations. This versatility makes CNC routing ideal for applications in woodworking, signage, and manufacturing industries.
Materials Suitable for Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is highly effective for materials such as wood, acrylic, plastics, leather, fabric, paper, and thin metals like stainless steel and aluminum. This technology excels in precision and clean edges, making it ideal for intricate designs and delicate stock. Unlike CNC routing, laser cutting cannot efficiently process thick metals or dense hardwoods due to limited material penetration and potential heat distortion.
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
CNC routing offers high precision with typical tolerances around +-0.005 inches, suitable for detailed wood, plastic, and metal work, while laser cutting achieves superior accuracy with tolerances as tight as +-0.001 inches, enabling intricate cuts on thin materials like sheet metal and acrylic. Laser cutting produces cleaner edges with minimal kerf width, enhancing detail clarity compared to CNC routing's wider tool paths. Your choice depends on the material thickness and the level of precision needed, with laser cutting preferred for ultra-fine details and CNC routing for robust, thicker projects.
Speed and Efficiency Differences
CNC routing offers high-speed material removal, excelling in cutting thicker materials like wood and plastics with consistent efficiency. Laser cutting provides superior precision and faster processing for thin sheets and intricate designs, minimizing waste and reducing setup time. Your choice depends on the balance between speed on heavy-duty projects and the need for detailed, fast cuts in fine materials.
Design Flexibility and Limitations
CNC routing offers high design flexibility with the ability to create complex 3D shapes, deep cuts, and varied material thicknesses, making it ideal for woodworking, plastics, and metals. Laser cutting excels in precision and detail, delivering fine, intricate cuts and engravings primarily on thinner materials, but struggles with thickness and certain reflective or heat-sensitive materials. Both technologies have limitations: CNC routing faces restrictions in extremely fine detail due to tool diameter, while laser cutting is limited by material thickness and potential heat distortion.
Cost Analysis: CNC Routing vs Laser Cutting
CNC routing typically involves higher initial equipment costs but offers lower operational expenses for thick materials, making it cost-effective for large-scale production. Laser cutting often carries lower startup costs and excels in precision work with minimal material waste, yet its higher maintenance and energy consumption increase operational costs. Evaluating project volume, material type, and precision requirements is essential for determining the most economical choice between CNC routing and laser cutting.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
CNC routing excels in cutting thick materials like wood, plastic, and metal, providing precise three-dimensional shapes with high durability and smooth finishes. Laser cutting offers superior detail for thin materials such as acrylic, rubber, and fabric, enabling intricate designs with minimal material waste and fast processing times. Selecting the right method depends on material type, thickness, desired precision, and project complexity to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
CNC routing vs Laser cutting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com