Wood dye penetrates deeper into the wood fibers, offering vibrant color without obscuring the grain, while wood stain primarily sits on the surface, enhancing the wood's natural texture with pigment and protective elements. Choosing between wood dye and wood stain depends on your desired appearance and how much you want to emphasize the wood's grain.
Table of Comparison
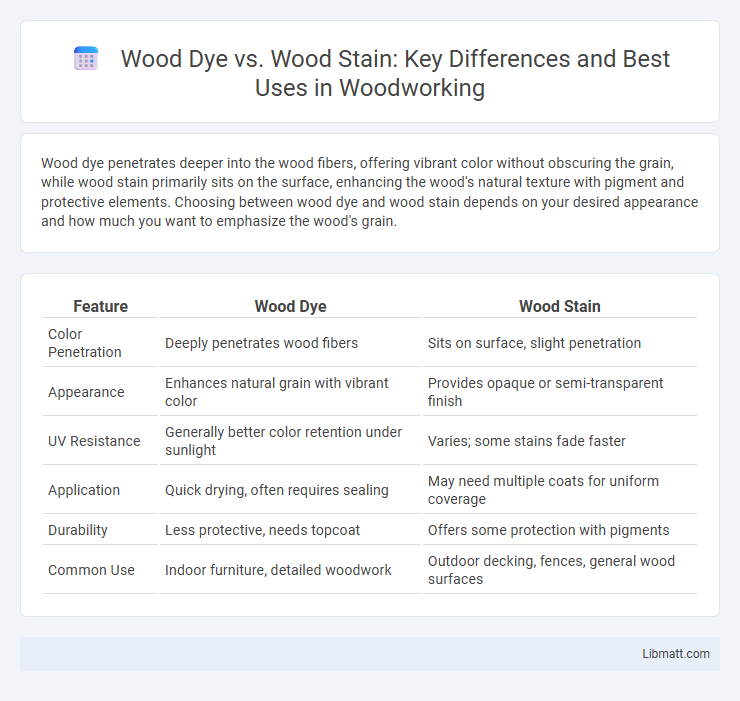
| Feature | Wood Dye | Wood Stain |
|---|---|---|
| Color Penetration | Deeply penetrates wood fibers | Sits on surface, slight penetration |
| Appearance | Enhances natural grain with vibrant color | Provides opaque or semi-transparent finish |
| UV Resistance | Generally better color retention under sunlight | Varies; some stains fade faster |
| Application | Quick drying, often requires sealing | May need multiple coats for uniform coverage |
| Durability | Less protective, needs topcoat | Offers some protection with pigments |
| Common Use | Indoor furniture, detailed woodwork | Outdoor decking, fences, general wood surfaces |
Introduction to Wood Dye and Wood Stain
Wood dye penetrates deeply into wood fibers, offering vibrant, uniform color enhanced by its molecular absorption properties, ideal for highlighting wood grain without surface film. Wood stain combines pigment particles suspended in a binder, providing surface color that sits atop the wood, delivering both color and protection while accentuating texture. Understanding the chemical composition and application methods of wood dye versus wood stain allows for informed choices based on desired aesthetic effects and durability requirements.
Key Differences Between Wood Dye and Wood Stain
Wood dye penetrates deeply into the wood fibers, enhancing the natural grain with vibrant, translucent color, while wood stain sits mainly on the surface, providing a pigmented layer that can mask imperfections. Your choice depends on desired color intensity and wood type, as dyes offer more vivid hues but less protection, whereas stains add color and a layer of protective finish. Understanding these differences ensures you select the right product to achieve the perfect blend of aesthetics and durability for your woodworking project.
Composition and Ingredients Comparison
Wood dye primarily consists of soluble colorants such as aniline or acid dyes that penetrate deeply into the wood fibers, offering vibrant and transparent coloration without obscuring the grain. Wood stain, in contrast, combines pigments or dyes suspended in a binder like oil, water, or lacquer, providing both color and surface protection by sitting atop the wood. Understanding these compositional differences helps you choose the right product for your woodworking project based on desired color intensity and finish durability.
Application Methods for Wood Dye vs Stain
Wood dye penetrates deeply into the wood fibers, requiring application methods such as brushing, spraying, or wiping with a cloth for even absorption and vibrant color. Wood stain sits more on the surface and often demands brushing or wiping on thicker layers, followed by wiping off excess to achieve the desired shade. Your choice between dye and stain will determine your application technique to ensure consistent color and finish quality.
Color Penetration and Grain Enhancement
Wood dye penetrates deeply into the wood fibers, offering vibrant color saturation without obscuring the natural grain patterns, making it ideal for highlighting the wood's intrinsic beauty. Wood stain primarily sits on the surface or slightly penetrates, enhancing the grain texture by emphasizing its contrast and depth through pigment particles. Both options provide unique color penetration levels and grain enhancement effects, with dye delivering uniform color and stain emphasizing texture variations.
Durability and Fading Over Time
Wood dye penetrates deeper into the wood fibers, offering vibrant color but tends to fade faster when exposed to UV light and weather elements. Wood stain forms a thinner, surface-level layer that provides better protection against moisture and sun damage, contributing to longer-lasting durability and color stability. Your choice between wood dye and wood stain should consider how much exposure to sunlight and outdoor conditions the wood will endure over time.
Suitable Wood Types for Dyes and Stains
Wood dyes penetrate deeper into hardwoods like maple, cherry, and oak, enhancing natural grain patterns with vibrant, uniform color, making them ideal for fine furniture and detailed woodworking. Wood stains work well on softwoods such as pine, cedar, and fir, partially settling on the surface to add rich color while highlighting texture and knots. Your choice between dye and stain should consider wood species and desired finish intensity for optimal results.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wood Dye
Wood dye penetrates deeply into wood pores, enhancing natural grain patterns with vibrant color and providing a uniform finish, unlike wood stain which often sits on the surface creating a thicker layer. You benefit from wood dye's faster drying time and greater color intensity, but it lacks the protective qualities and UV resistance that stains offer. The main disadvantage of wood dye is its susceptibility to fading and less durability in outdoor conditions compared to wood stain.
Pros and Cons of Wood Stain
Wood stain enhances the natural grain of wood while providing moderate protection against moisture and UV damage, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and decks. It penetrates the wood surface deeply, which helps prevent peeling and flaking but requires regular maintenance to retain its appearance. However, wood stain offers limited color options compared to wood dye and may not achieve the vibrant or uniform hues that dyes can provide.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Wood Project
Choosing between wood dye and wood stain depends on the desired finish and wood type; wood dyes penetrate deeply for vibrant, even color, while stains add pigment and highlight grain texture. Wood dye suits projects needing rich, uniform color without obscuring the wood's natural patterns, ideal for hardwoods and fine furniture. Stains offer better surface protection and enhance wood grain, making them perfect for outdoor projects or surfaces requiring durability and a varied finish.
Wood dye vs Wood stain Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com