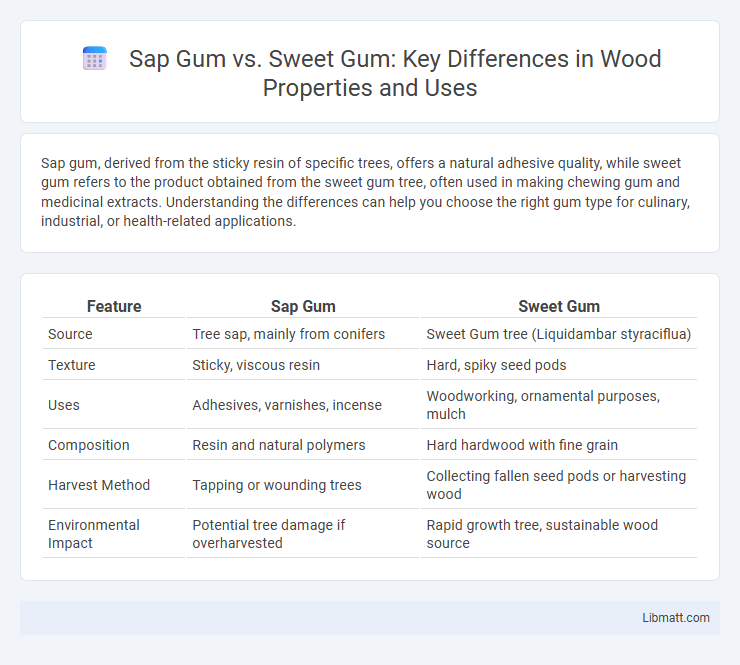
Sap gum, derived from the sticky resin of specific trees, offers a natural adhesive quality, while sweet gum refers to the product obtained from the sweet gum tree, often used in making chewing gum and medicinal extracts. Understanding the differences can help you choose the right gum type for culinary, industrial, or health-related applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sap Gum | Sweet Gum |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Tree sap, mainly from conifers | Sweet Gum tree (Liquidambar styraciflua) |
| Texture | Sticky, viscous resin | Hard, spiky seed pods |
| Uses | Adhesives, varnishes, incense | Woodworking, ornamental purposes, mulch |
| Composition | Resin and natural polymers | Hard hardwood with fine grain |
| Harvest Method | Tapping or wounding trees | Collecting fallen seed pods or harvesting wood |
| Environmental Impact | Potential tree damage if overharvested | Rapid growth tree, sustainable wood source |
Introduction: Sap Gum vs Sweet Gum
Sap gum, primarily harvested from the sap of certain pine trees like the longleaf and slash pine, is valued for its adhesive and emulsifying properties in food and industrial applications. Sweet gum refers to the resin extracted from the sweetgum tree (Liquidambar styraciflua), known for its aromatic qualities and uses in traditional medicine and fragrance industries. Both gums are natural resins but differ significantly in botanical origin, chemical composition, and commercial applications.
Botanical Overview of Sap Gum and Sweet Gum
Sap gum, commonly derived from Acacia trees, is a natural exudate rich in polysaccharides used extensively in food and pharmaceutical industries for its emulsifying and stabilizing properties. Sweet gum, sourced from Liquidambar styraciflua, produces a resinous latex valued for its aromatic qualities and traditional medicinal uses. Your understanding of these gums benefits from recognizing their distinct botanical origins, chemical compositions, and applications.
Geographic Distribution and Habitats
Sap gum primarily grows in the southeastern United States, thriving in well-drained, sandy soils typical of pine forests and coastal plains. Sweet gum is widespread across the eastern United States, from Connecticut to Florida and west to Texas, favoring moist, fertile soils along riverbanks and bottomlands. Differences in their geographic distribution reflect each species' adaptability to distinct soil moisture and regional climate conditions.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Sap gum is a sticky, viscous substance exuded from certain trees, typically amber or yellowish in color, with a glossy, syrup-like texture. Sweet gum refers to the spiky, star-shaped seed pods and the wood of the Liquidambar styraciflua tree, featuring a rough, woody exterior and a distinctive sweet-smelling resin. Physically, sap gum is a fluid, resinous secretion, whereas sweet gum denotes both the hard, spiny fruit and the aromatic hardwood of the sweet gum tree.
Wood Properties: Sap Gum vs Sweet Gum
Sap gum wood is generally softer and less dense than sweet gum wood, making it easier to work with but less durable for heavy structural applications. Sweet gum wood offers a harder, more resilient grain structure with better shock resistance, ideal for furniture, flooring, and cabinetry. Your choice between the two depends on whether you prioritize ease of machining or long-term strength and wear resistance.
Uses and Applications in Industry
Sap gum, commonly derived from trees like spruce and fir, is extensively used in the food industry as a stabilizer, thickener, and emulsifier in products such as ice cream, candy, and soft drinks due to its excellent adhesive and gelling properties. Sweet gum, harvested from Liquidambar trees, finds applications primarily in the manufacture of chewing gum base, adhesives, and certain pharmaceuticals, valued for its natural resinous components and aromatic qualities. The industrial preference for sap gum lies in its superior solubility and viscosity control, while sweet gum's resin is prized for its elasticity and flavor-enhancing characteristics.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Wood Type
Sap gum wood offers high resin content that enhances its durability and water resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications, but its sticky surface can complicate finishing processes. Sweet gum wood is valued for its attractive grain and smooth texture, offering excellent workability and a cost-effective option for furniture and cabinetry; however, it tends to be less resistant to decay and moisture compared to sap gum. Both wood types provide unique aesthetic and functional benefits, with sap gum excelling in durability and sweet gum favored for visual appeal and ease of use.
Identification Tips for Sap Gum and Sweet Gum
Sap gum can be identified by its sticky, resinous exudate that oozes from wounds or cuts on the tree's bark, often leaving a shiny, amber-colored residue. Sweet gum trees are recognized by their star-shaped leaves and spiky, spherical seed pods, with the bark appearing deeply furrowed and grayish-brown. You can distinguish sap gum by its gum production, while sweet gum is noted for its distinctive leaf shape and hard seed balls.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sap gum, derived primarily from the Sweetgum tree (Liquidambar styraciflua), demonstrates a moderate environmental impact due to its natural extraction process, which minimally harms trees and supports sustainable harvesting. Sweet gum trees contribute to ecosystem stability by providing habitat and improving soil quality while their resin extraction promotes carbon sequestration over the trees' lifespan. Compared to synthetic alternatives, sap gum from sweet gum trees offers a biodegradable, renewable resource with reduced carbon footprint, making it a more sustainable choice in various industrial applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Sap Gum and Sweet Gum
Choosing between sap gum and sweet gum depends on your specific needs for flavor and texture; sap gum offers a mild, less sticky chew with natural resin properties, while sweet gum provides a stronger, sweeter taste accompanied by a more elastic texture. Your preference for sweetness intensity and gum consistency will guide the optimal choice for enjoyment or culinary use. Considering factors like flavor profile, stickiness, and natural ingredients ensures you select the gum that best complements your taste and application.
Sap gum vs sweet gum Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com