Pressure treated wood is infused with chemical preservatives under high pressure to resist rot, insects, and decay, making it ideal for outdoor projects exposed to moisture. Heat treated wood undergoes controlled heating to reduce moisture and kill pests without chemicals, enhancing stability and eco-friendliness, but it may not offer the same level of protection in highly damp environments as pressure treated wood.
Table of Comparison
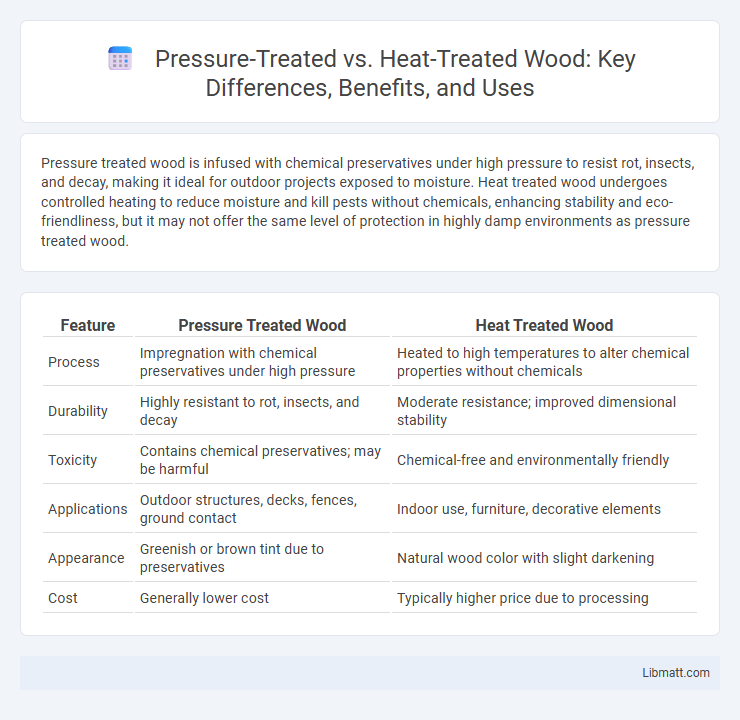
| Feature | Pressure Treated Wood | Heat Treated Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Impregnation with chemical preservatives under high pressure | Heated to high temperatures to alter chemical properties without chemicals |
| Durability | Highly resistant to rot, insects, and decay | Moderate resistance; improved dimensional stability |
| Toxicity | Contains chemical preservatives; may be harmful | Chemical-free and environmentally friendly |
| Applications | Outdoor structures, decks, fences, ground contact | Indoor use, furniture, decorative elements |
| Appearance | Greenish or brown tint due to preservatives | Natural wood color with slight darkening |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher price due to processing |
Introduction to Pressure Treated and Heat Treated Wood
Pressure treated wood undergoes a chemical infusion process that protects it from rot, insects, and decay, making it ideal for outdoor applications like decks and fences. Heat treated wood is exposed to high temperatures that alter its cellular structure, enhancing durability and resistance without the use of chemicals, often preferred for indoor use or eco-friendly projects. Understanding these treatments helps you select the right wood for durability and environmental impact in your construction or woodworking projects.
What is Pressure Treated Wood?
Pressure treated wood is lumber infused with chemical preservatives under high pressure to protect against rot, decay, and insect damage. This process extends the wood's durability, making it ideal for outdoor construction projects such as decks, fences, and utility poles. The chemicals used in pressure treating are designed to penetrate deep into the wood fibers, enhancing resistance to moisture and environmental exposure.
What is Heat Treated Wood?
Heat treated wood is lumber that has been exposed to high temperatures, typically between 160degC and 220degC, to remove moisture and pests without the use of chemicals. This process enhances the wood's durability, stability, and resistance to decay, making it an eco-friendly alternative to pressure treated wood. Your choice of heat treated wood supports sustainable construction while providing improved dimensional stability and reduced risk of warping.
Key Differences Between Pressure Treated and Heat Treated Wood
Pressure treated wood is infused with chemical preservatives under high pressure to resist rot, insects, and fungal growth, making it ideal for outdoor applications exposed to moisture. Heat treated wood undergoes a high-temperature drying process that reduces moisture content and enhances dimensional stability without adding chemicals, often used for indoor purposes or pallets. Your choice depends on whether durability against environmental factors or chemical-free treatment is a priority for your wood project.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Pressure treated wood undergoes chemical infusion to resist rot, insects, and moisture, significantly enhancing its durability and longevity for outdoor applications. Heat treated wood is dried at high temperatures to remove moisture and pests, increasing stability and resistance to decay but typically offers a shorter lifespan compared to pressure treated wood. Choosing the right treatment depends on your project's exposure to harsh environmental conditions and desired longevity.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Pressure-treated wood often contains chemical preservatives like chromated copper arsenate (CCA), which can leach into soil and water, posing environmental and health risks including toxicity to plants, animals, and humans. Heat-treated wood avoids the use of chemicals by using high temperatures to eradicate pests, making it a more eco-friendly and non-toxic option suitable for sensitive applications such as playgrounds and food packaging. Choosing heat-treated wood reduces the potential for harmful chemical exposure and supports sustainable forestry practices with lower environmental impact.
Common Applications of Pressure Treated Wood
Pressure treated wood is predominantly used in outdoor construction projects such as decks, fences, and playground equipment due to its resistance to moisture, decay, and insect damage. It is also commonly applied in landscaping, retaining walls, and utility poles where long-term durability against environmental factors is critical. Unlike heat treated wood, which is primarily used for indoor or specialized applications, pressure treated wood ensures structural integrity in exposed conditions.
Typical Uses of Heat Treated Wood
Heat treated wood is commonly used in applications requiring enhanced durability and stability, such as flooring, decking, and outdoor furniture. Its improved resistance to moisture and insects makes it ideal for garden structures, window frames, and saunas. Unlike pressure treated wood, heat treated wood is preferred for indoor uses due to its non-toxic, chemical-free treatment process.
Cost Comparison and Economic Factors
Pressure treated wood generally costs less upfront compared to heat treated wood due to its widespread availability and faster processing times. Heat treated wood can have higher initial expenses driven by energy-intensive treatment and specialized equipment, but it often offers greater durability and resistance, potentially lowering long-term maintenance costs. Your decision should weigh immediate budget constraints against anticipated lifespan and performance to find the most cost-effective solution for your project.
Choosing the Right Treatment for Your Project
Pressure-treated wood offers enhanced resistance to moisture, insects, and decay, making it ideal for outdoor projects such as decks, fences, and landscaping. Heat-treated wood undergoes a chemical-free thermal modification process that improves dimensional stability and durability, suited for indoor applications like flooring and furniture where environmental impact is a concern. Selecting between pressure-treated and heat-treated wood depends on exposure conditions, desired longevity, and specific project requirements.
Pressure treated vs heat treated Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com