Creosote treatment provides long-lasting protection for wood used in outdoor applications by penetrating deeply to resist moisture, fungi, and insects, making it ideal for railroad ties and utility poles. CCA treatment preserves wood using a mixture of chromium, copper, and arsenic chemicals to prevent decay and insect damage, commonly used for residential decks and playground equipment where appearance matters more than heavy-duty resistance.
Table of Comparison
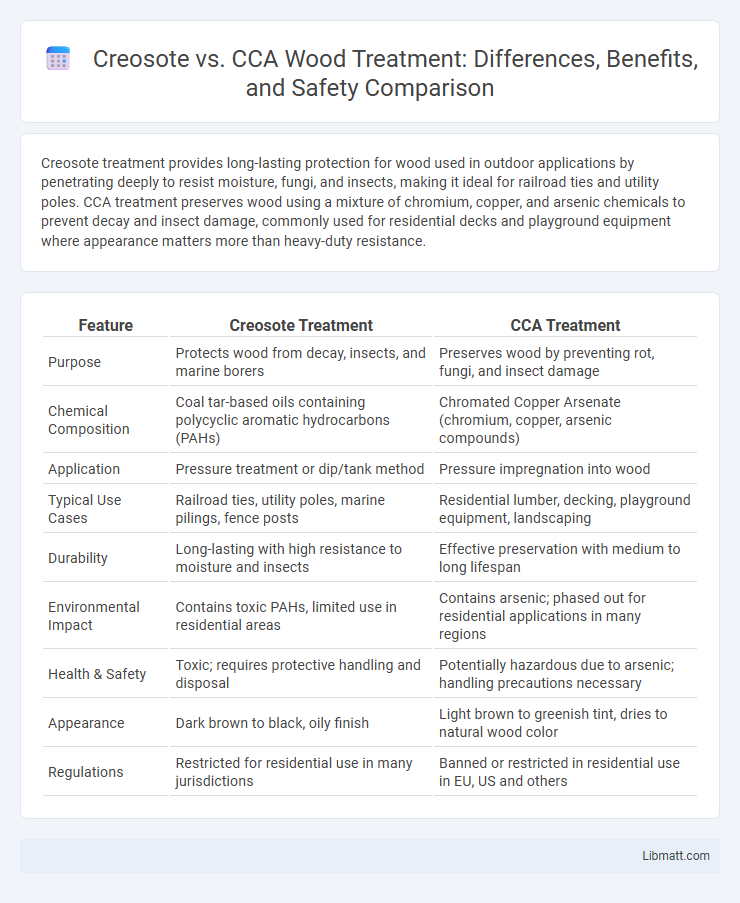
| Feature | Creosote Treatment | CCA Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects wood from decay, insects, and marine borers | Preserves wood by preventing rot, fungi, and insect damage |
| Chemical Composition | Coal tar-based oils containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) | Chromated Copper Arsenate (chromium, copper, arsenic compounds) |
| Application | Pressure treatment or dip/tank method | Pressure impregnation into wood |
| Typical Use Cases | Railroad ties, utility poles, marine pilings, fence posts | Residential lumber, decking, playground equipment, landscaping |
| Durability | Long-lasting with high resistance to moisture and insects | Effective preservation with medium to long lifespan |
| Environmental Impact | Contains toxic PAHs, limited use in residential areas | Contains arsenic; phased out for residential applications in many regions |
| Health & Safety | Toxic; requires protective handling and disposal | Potentially hazardous due to arsenic; handling precautions necessary |
| Appearance | Dark brown to black, oily finish | Light brown to greenish tint, dries to natural wood color |
| Regulations | Restricted for residential use in many jurisdictions | Banned or restricted in residential use in EU, US and others |
Overview of Wood Preservation Methods
Creosote and Chromated Copper Arsenate (CCA) are prominent wood preservation methods used to enhance durability and resistance to decay and insect damage. Creosote, derived from coal tar, is primarily used for outdoor applications like railroad ties and utility poles due to its deep penetration and waterproofing properties. CCA, a chemical preservative containing chromium, copper, and arsenic, provides effective protection against fungi and insects, commonly applied in residential and industrial wood products.
What is Creosote Treatment?
Creosote treatment is a wood preservation method that involves impregnating wood with a tar-like substance derived from coal tar distillation, offering durable protection against rot, fungi, and insect damage. Commonly used for railroad ties, utility poles, and marine pilings, creosote penetrates deeply into the wood fibers, enhancing longevity in outdoor and harsh environments. Understanding the benefits and potential environmental concerns of creosote treatment can help you make informed decisions about wood protection for your projects.
What is CCA (Chromated Copper Arsenate) Treatment?
CCA (Chromated Copper Arsenate) treatment is a wood preservation method that uses a chemical mixture of chromium, copper, and arsenic to protect timber from rot, decay, and insect damage. This treatment penetrates deep into the wood fibers, providing long-lasting durability and resistance, especially in outdoor and ground-contact applications. Understanding CCA treatment helps you make informed decisions about wood safety and environmental impact in construction or landscaping projects.
Chemical Composition: Creosote vs CCA
Creosote is a complex mixture of phenolic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and heterocyclic organic compounds derived from the distillation of coal tar, providing high water repellency and insecticidal properties. Chromated Copper Arsenate (CCA) consists primarily of chromium, copper, and arsenic salts, which work together to impart fungicidal, insecticidal, and anti-weathering properties by penetrating wood fibers. While creosote acts mainly as a preservative through its hydrophobic chemicals, CCA preserves wood through chemical fixation and metal ion toxicity mechanisms.
Effectiveness Against Fungi, Insects, and Decay
Creosote provides strong protection against fungi, insects, and decay due to its deep penetration and water-repellent properties, making it highly effective for outdoor applications like railroad ties and utility poles. CCA treatment offers broad-spectrum effectiveness as a preservative, preventing fungal growth, insect infestation, and wood decay by using a copper-based chemical formulation. When choosing between the two, your specific exposure conditions and environmental concerns will determine which treatment ensures optimal long-term durability and protection.
Environmental Impact and Toxicity
Creosote treatment involves wood preservation using coal tar derivatives, which release harmful polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) posing significant environmental risks and toxicity to aquatic life. In contrast, Chromated Copper Arsenate (CCA) treatment incorporates chromium, copper, and arsenic compounds that can leach into soil and groundwater, contributing to heavy metal contamination and long-term ecological hazards. Your choice of wood treatment should consider these toxicological effects and environmental persistence, with CCA banned or restricted in many regions due to its carcinogenic potential.
Safety Considerations for Handling and Use
Creosote, a petroleum-based wood preservative, poses significant health risks due to its carcinogenic compounds and requires careful handling with protective gear to prevent skin contact and inhalation. CCA (Chromated Copper Arsenate) contains arsenic, chromium, and copper, necessitating precautions to avoid exposure through skin contact or dust, as these metals are toxic and potentially carcinogenic. Both treatments mandate strict adherence to safety guidelines, including using gloves, masks, and ensuring proper ventilation to minimize risks during application and maintenance.
Typical Applications and Industry Usage
Creosote treatment is commonly used for heavy-duty applications such as railroad ties, utility poles, and marine pilings due to its excellent water resistance and long-lasting protection against fungi and insects. CCA (Chromated Copper Arsenate) treatment is widely applied in residential construction, including decking, fencing, and playground equipment, valued for its effectiveness in preventing wood decay and insect damage while maintaining structural integrity. Your choice between creosote and CCA depends on the specific industry requirements and environmental regulations associated with the treated wood's intended use.
Longevity and Performance Comparison
Creosote-treated wood offers superior longevity, often lasting over 30 years in ground contact due to its deep penetration and water-resistant properties. CCA (Chromated Copper Arsenate) treatment provides strong protection against decay and insects, typically extending wood's lifespan up to 20-25 years, but may degrade faster in extreme weather conditions. Both treatments enhance durability, yet creosote excels in outdoor applications requiring prolonged resistance to moisture and fungal decay.
Regulatory Standards and Restrictions
Creosote-treated wood faces stringent EPA regulations due to its classification as a hazardous material, limiting its use primarily to industrial applications such as railroad ties and utility poles, whereas CCA (chromated copper arsenate) treatment is regulated under the EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act but allowed for residential use with specific application restrictions. Regulatory standards mandate that creosote must not be used in residential construction due to its carcinogenic components, while CCA-treated wood, once widely used in decks and playgrounds, is now restricted for residential applications, especially where direct human contact occurs, under EPA and state-level guidelines. Both treatments require compliance with disposal and handling protocols to prevent environmental contamination and human health risks, reflecting evolving regulatory efforts to balance efficacy with safety.
Creosote vs CCA treatment Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com