Air tight joinery provides superior insulation and energy efficiency by preventing drafts and moisture infiltration, making it ideal for maintaining comfortable indoor environments. Open joinery, while offering better ventilation and aesthetic appeal, may compromise thermal performance and increase the risk of air leakage in your building.
Table of Comparison
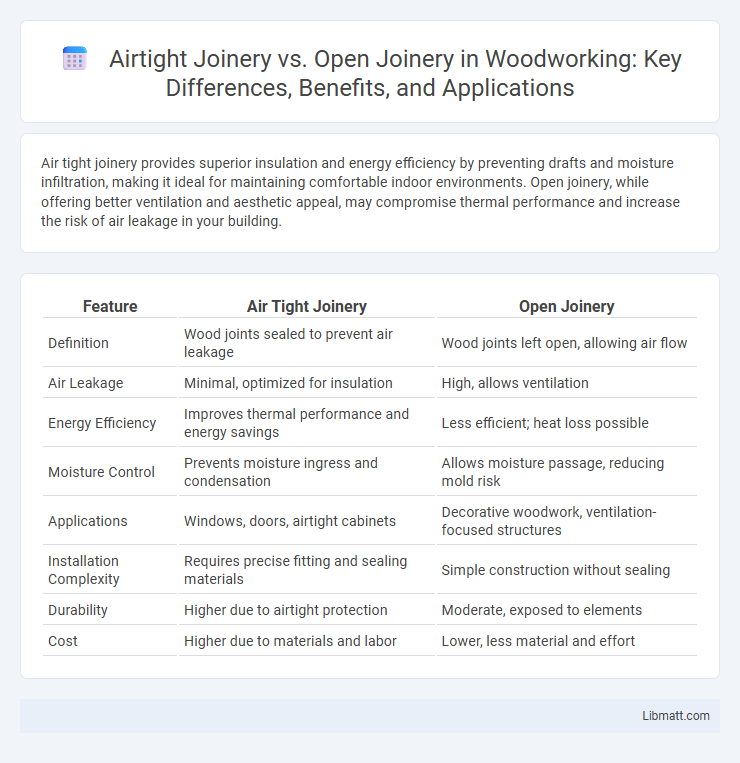
| Feature | Air Tight Joinery | Open Joinery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wood joints sealed to prevent air leakage | Wood joints left open, allowing air flow |
| Air Leakage | Minimal, optimized for insulation | High, allows ventilation |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves thermal performance and energy savings | Less efficient; heat loss possible |
| Moisture Control | Prevents moisture ingress and condensation | Allows moisture passage, reducing mold risk |
| Applications | Windows, doors, airtight cabinets | Decorative woodwork, ventilation-focused structures |
| Installation Complexity | Requires precise fitting and sealing materials | Simple construction without sealing |
| Durability | Higher due to airtight protection | Moderate, exposed to elements |
| Cost | Higher due to materials and labor | Lower, less material and effort |
Introduction: Defining Air Tight and Open Joinery
Air tight joinery involves sealing joints to prevent air leakage, enhancing energy efficiency and indoor climate control in buildings. Open joinery allows natural airflow through joints, promoting ventilation but potentially compromising insulation performance. Choosing between air tight and open joinery depends on balancing energy conservation with ventilation needs.
Key Differences Between Air Tight and Open Joinery
Air tight joinery creates a sealed connection that prevents air leakage, improving insulation and energy efficiency in buildings. Open joinery allows airflow through joints, which can lead to drafts but may be beneficial for ventilation in certain constructions. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize airtightness for heating and cooling efficiency or ventilation for moisture control and air circulation.
Performance in Energy Efficiency
Air tight joinery significantly enhances energy efficiency by minimizing air leakage and preventing heat loss through windows and doors, leading to lower heating and cooling costs. Open joinery, with gaps and poor sealing, allows drafts and moisture infiltration, reducing insulation effectiveness and increasing energy consumption. Your choice of air tight joinery can contribute to a more sustainable, cost-effective building envelope with improved indoor comfort.
Impacts on Indoor Air Quality
Air tight joinery significantly enhances indoor air quality by minimizing air leakage and preventing the infiltration of pollutants, dust, and allergens from outside. In contrast, open joinery allows uncontrolled airflow, which can introduce humidity and contaminants, leading to poor air quality and potential health issues. Properly sealed joinery supports energy efficiency by maintaining consistent ventilation through mechanical systems while protecting indoor environments from external pollutants.
Moisture Control and Durability
Air tight joinery significantly enhances moisture control by preventing water vapor infiltration, reducing the risk of mold growth and structural damage in your building. Open joinery, while allowing some natural ventilation, increases the potential for moisture accumulation and can compromise durability over time due to prolonged exposure to damp conditions. Choosing air tight joinery ensures long-term protection and stability of your structure by maintaining a controlled internal environment.
Aesthetic Considerations in Joinery Choices
Air tight joinery offers sleek, seamless lines that enhance modern, minimalist aesthetics by eliminating visible gaps and joints. Open joinery, characterized by exposed joints and intentional gaps, creates a handcrafted, rustic appeal that highlights craftsmanship and detail. Your design preference will influence whether you prioritize the clean precision of airtight joinery or the textured warmth of open joinery in your space.
Installation Process Comparison
Air tight joinery requires precise sealing techniques during installation to prevent air leakage, often involving high-quality gaskets, sealants, and meticulous fitting. Open joinery allows for simpler installation with less emphasis on airtightness, as gaps and ventilation are part of the design, reducing the need for specialized sealing materials. Your choice affects installation complexity, time, and the overall energy efficiency of the building envelope.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Type
Air tight joinery demands regular inspections and sealing to prevent air leakage and maintain energy efficiency, often requiring weatherstripping replacement and caulking touch-ups. Open joinery, while allowing natural ventilation, typically experiences fewer maintenance issues related to air seals but may require more frequent cleaning to address dust and debris accumulation in exposed gaps. Choosing between air tight and open joinery hinges on balancing the need for controlled indoor environments against simpler upkeep routines.
Cost Analysis: Air Tight vs Open Joinery
Air tight joinery typically incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized seals and precision installation required to ensure minimal air leakage. Open joinery has lower initial expenses but may result in increased long-term costs from energy loss, moisture damage, and maintenance needs. Evaluating overall value, air tight joinery offers better energy efficiency and durability, offsetting its higher installation cost over time.
Choosing the Right Joinery for Your Project
Choosing the right joinery for your project depends on factors such as desired durability, weather resistance, and energy efficiency. Air tight joinery provides superior insulation and prevents drafts, making it ideal for energy-conscious buildings, while open joinery allows better ventilation but may compromise thermal performance. Your selection should balance the need for airtightness with the functional and aesthetic requirements of the space.
Air tight joinery vs open joinery Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com