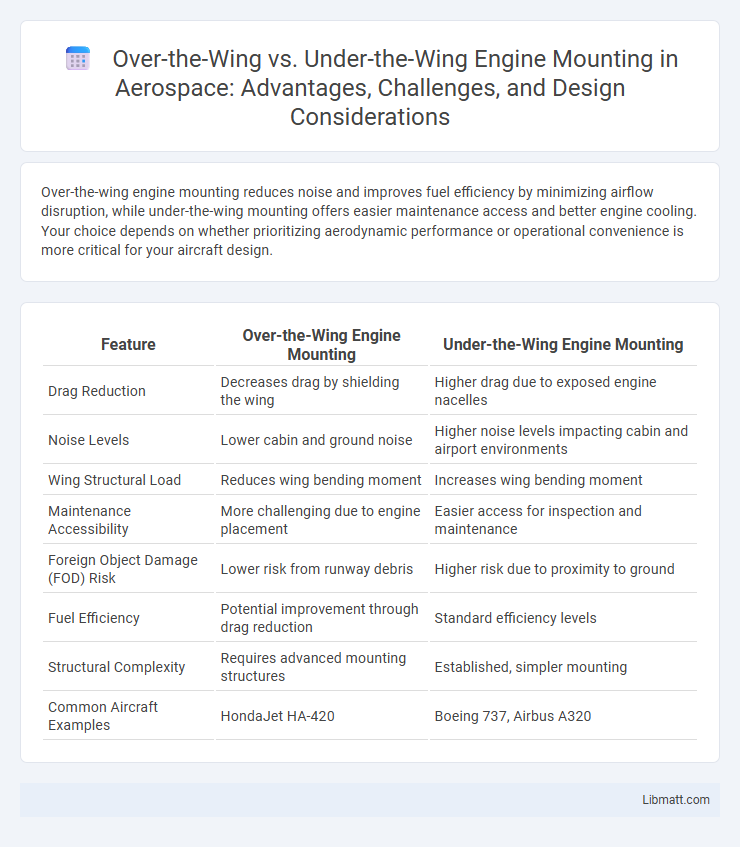
Over-the-wing engine mounting reduces noise and improves fuel efficiency by minimizing airflow disruption, while under-the-wing mounting offers easier maintenance access and better engine cooling. Your choice depends on whether prioritizing aerodynamic performance or operational convenience is more critical for your aircraft design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Over-the-Wing Engine Mounting | Under-the-Wing Engine Mounting |
|---|---|---|
| Drag Reduction | Decreases drag by shielding the wing | Higher drag due to exposed engine nacelles |
| Noise Levels | Lower cabin and ground noise | Higher noise levels impacting cabin and airport environments |
| Wing Structural Load | Reduces wing bending moment | Increases wing bending moment |
| Maintenance Accessibility | More challenging due to engine placement | Easier access for inspection and maintenance |
| Foreign Object Damage (FOD) Risk | Lower risk from runway debris | Higher risk due to proximity to ground |
| Fuel Efficiency | Potential improvement through drag reduction | Standard efficiency levels |
| Structural Complexity | Requires advanced mounting structures | Established, simpler mounting |
| Common Aircraft Examples | HondaJet HA-420 | Boeing 737, Airbus A320 |
Introduction to Engine Mounting Configurations
Over-the-wing engine mounting positions engines above the wing, reducing cabin noise and improving fuel efficiency by optimizing airflow around the wing structure. Under-the-wing mounting places engines below the wing, enhancing structural efficiency by allowing direct load transfer to the wing spar and facilitating easier maintenance access. Each configuration influences aircraft aerodynamics, structural design, and operational performance, making the choice critical for specific aircraft models and mission profiles.
Historical Development of Engine Placement
The historical development of engine placement evolved from early under-the-wing mounts, favored for stability and ease of maintenance, to innovative over-the-wing designs aimed at noise reduction and improved aerodynamics. Over-the-wing engines gained prominence with experimental aircraft and regional jets, enhancing fuel efficiency while minimizing ground debris ingestion. Your understanding of these advancements highlights how engineering priorities shifted towards optimizing performance and operational efficiency in modern aircraft design.
Over-the-Wing Engine Mounting: Overview
Over-the-wing engine mounting places the engines above the aircraft's wings, improving ground clearance and reducing foreign object damage risk during takeoff and landing. This design enhances aerodynamic efficiency by minimizing wing structural stress and can lower noise levels inside the cabin. Your aircraft benefits from improved maintenance accessibility and potentially increased fuel efficiency compared to conventional under-the-wing configurations.
Under-the-Wing Engine Mounting: Overview
Under-the-wing engine mounting is the most common aircraft engine configuration, where engines are attached beneath the wings via pylons. This design enhances aerodynamic efficiency by reducing drag and allows easier maintenance access due to the engines' lower position. Your aircraft benefits from improved fuel efficiency and quieter operation, as the wing structure provides noise shielding and reduces engine vibration transmission.
Aerodynamic Impacts of Engine Location
Over-the-wing engine mounting reduces wing bending moments, enhancing structural efficiency and potentially lowering maintenance costs by decreasing wing fatigue. Under-the-wing engines improve aerodynamic lift distribution and reduce interference drag, boosting overall fuel efficiency during cruise. Your choice between these configurations affects the aircraft's drag profile and fuel consumption, directly influencing operational performance.
Noise and Vibration Considerations
Over-the-wing engine mounting significantly reduces cabin noise and vibrations by shielding the fuselage from direct engine sound waves, enhancing passenger comfort. Under-the-wing installations often transmit higher vibration levels to the airframe due to closer structural attachment, which can increase cabin noise. Your aircraft's operational environment and noise certification requirements play a crucial role in determining the optimal engine mounting configuration for noise and vibration control.
Maintenance and Accessibility Factors
Over-the-wing engine mounting improves ground-level accessibility, simplifying routine maintenance tasks by reducing the need for tall scaffolding or heavy lifting equipment. Under-the-wing engines, though more common, often require larger support structures and increased downtime for inspections due to their lower placement. Maintenance crews benefit from the reduced risk of foreign object damage with over-the-wing configurations, enhancing inspection efficiency and turnaround times.
Fuel Efficiency and Performance Implications
Over-the-wing engine mounting often reduces wing bending moments, allowing for lighter wing structures that enhance fuel efficiency by decreasing overall aircraft weight. This configuration can also improve aerodynamic performance by mitigating wing interference drag and optimizing airflow, leading to better fuel consumption rates. Under-the-wing mounts typically provide easier maintenance access and proven structural reliability but may induce higher drag and weight penalties affecting performance efficiency.
Safety and Emergency Procedures
Over-the-wing engine mounting enhances safety by reducing the risk of foreign object damage during takeoff and landing, while facilitating easier access for emergency evacuations due to improved wing clearance. Under-the-wing engines, though traditional, offer straightforward inspection and maintenance but may increase risk of debris ingestion and complicate emergency egress in wing-adjacent areas. Your aircraft's safety protocols should align with the engine position to optimize emergency response efficiency and passenger protection.
Future Trends in Engine Mounting Technologies
Future trends in engine mounting technologies emphasize aerodynamic efficiency, noise reduction, and ease of maintenance. Over-the-wing engine mounting is gaining attention for its potential to decrease noise pollution and improve fuel efficiency by optimizing airflow around the engine nacelle. Your choice between over-the-wing and under-the-wing mounting will increasingly depend on advanced materials, lightweight composites, and integration with hybrid-electric propulsion systems.
Over-the-wing vs Under-the-wing engine mounting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com