A dichroic filter selectively reflects specific wavelengths of light while allowing others to pass through, making it ideal for color separation and precise light control. Your choice of a neutral density filter reduces the overall intensity of light without altering its color balance, perfect for managing exposure in photography and videography.
Table of Comparison
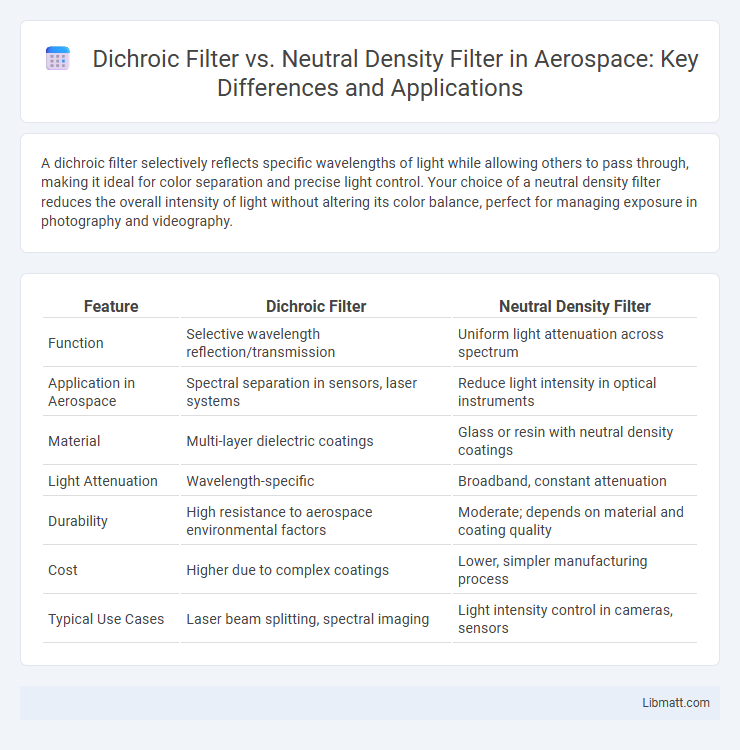
| Feature | Dichroic Filter | Neutral Density Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Selective wavelength reflection/transmission | Uniform light attenuation across spectrum |
| Application in Aerospace | Spectral separation in sensors, laser systems | Reduce light intensity in optical instruments |
| Material | Multi-layer dielectric coatings | Glass or resin with neutral density coatings |
| Light Attenuation | Wavelength-specific | Broadband, constant attenuation |
| Durability | High resistance to aerospace environmental factors | Moderate; depends on material and coating quality |
| Cost | Higher due to complex coatings | Lower, simpler manufacturing process |
| Typical Use Cases | Laser beam splitting, spectral imaging | Light intensity control in cameras, sensors |
Introduction to Optical Filters
Dichroic filters selectively reflect specific wavelengths while transmitting others, utilizing thin-film interference coatings for precise color separation. Neutral density filters uniformly reduce light intensity without altering color balance, making them ideal for controlling exposure in photography and optical instruments. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right optical filter for color management or light attenuation in various applications.
What is a Dichroic Filter?
A dichroic filter is an optical device designed to selectively transmit light within specific wavelength ranges while reflecting others, utilizing multi-layer thin-film coatings. Its precise wavelength selectivity enhances color separation and spectral filtering in applications such as photography, scientific instruments, and stage lighting. Unlike neutral density filters, which reduce overall light intensity without altering color balance, dichroic filters manipulate the spectral composition of light for enhanced color accuracy and contrast.
What is a Neutral Density (ND) Filter?
A Neutral Density (ND) filter is a photographic lens filter that reduces the amount of light entering the camera sensor without affecting color balance, allowing for greater control over exposure settings. It enables longer shutter speeds and wider apertures in bright conditions, useful for motion blur effects and shallow depth of field. Unlike dichroic filters, which selectively reflect and transmit specific wavelengths for color manipulation, ND filters provide uniform attenuation across the visible spectrum.
Key Differences Between Dichroic and ND Filters
Dichroic filters selectively reflect and transmit specific wavelengths of light using thin-film coatings, enabling precise color separation and high spectral efficiency, while neutral density (ND) filters uniformly reduce light intensity across all wavelengths without altering color balance. Dichroic filters are ideal for applications requiring sharp wavelength discrimination in scientific instrumentation and multi-spectral imaging, whereas ND filters are commonly used in photography and videography to control exposure and depth of field without affecting color rendition. The primary distinction lies in their spectral behavior: dichroic filters manipulate light based on wavelength-specific reflection/transmission properties, whereas ND filters attenuate light intensity evenly across the visible spectrum.
How Dichroic Filters Work: Principles and Applications
Dichroic filters operate by selectively reflecting certain wavelengths of light while transmitting others through interference coatings, enabling precise color separation. These filters leverage multiple thin-film layers that cause constructive and destructive interference, resulting in high-efficiency spectral filtering used in applications like fluorescence microscopy, stage lighting, and optical instruments. Your optical system benefits from dichroic filters when accurate wavelength discrimination and minimal light loss are essential.
How Neutral Density Filters Work: Principles and Applications
Neutral density (ND) filters reduce the intensity of all wavelengths of light equally without altering color balance, allowing you to control exposure by limiting the amount of light reaching the camera sensor. By uniformly attenuating light, ND filters enable longer shutter speeds and wider apertures, essential for techniques like motion blur or shallow depth of field in bright conditions. Unlike dichroic filters that selectively reflect and transmit specific wavelengths, ND filters maintain natural color fidelity, making them ideal for photography and videography requiring precise exposure control without color shifts.
Advantages of Dichroic Filters
Dichroic filters offer superior color accuracy and higher durability compared to neutral density filters due to their thin-film interference coating, which selectively reflects specific wavelengths while transmitting others with minimal light absorption. This results in less heat buildup and longer lifespan, making them ideal for precision color applications and environments requiring stable optical performance. Your imaging or lighting setup can benefit from enhanced color fidelity and reduced thermal effects when using dichroic filters over traditional neutral density filters.
Advantages of ND Filters
Neutral density (ND) filters offer precise control over light intensity without altering color balance, making them ideal for long exposure photography and reducing glare. They enable photographers to use wider apertures or slower shutter speeds in bright conditions, enhancing creative flexibility. ND filters also maintain image quality by minimizing chromatic aberrations and preserving true color fidelity compared to dichroic filters.
Choosing Between Dichroic and ND Filters: Use Cases
Dichroic filters excel in applications requiring precise wavelength separation and minimal light absorption, ideal for scientific imaging and color enhancement. Neutral density filters reduce overall light intensity without altering color balance, making them perfect for controlling exposure in photography and videography. You should select a dichroic filter for color-specific tasks and an ND filter for managing light levels evenly across all wavelengths.
Conclusion: Which Filter is Right for Your Needs?
Dichroic filters excel in applications requiring precise color separation and minimal light loss, making them ideal for advanced imaging and projection systems. Neutral density filters are better suited for controlling light intensity without altering color balance, benefiting photography and videography in bright conditions. Choosing the right filter depends on whether color fidelity or light attenuation is the priority in your specific optical setup.
dichroic filter vs neutral density filter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com