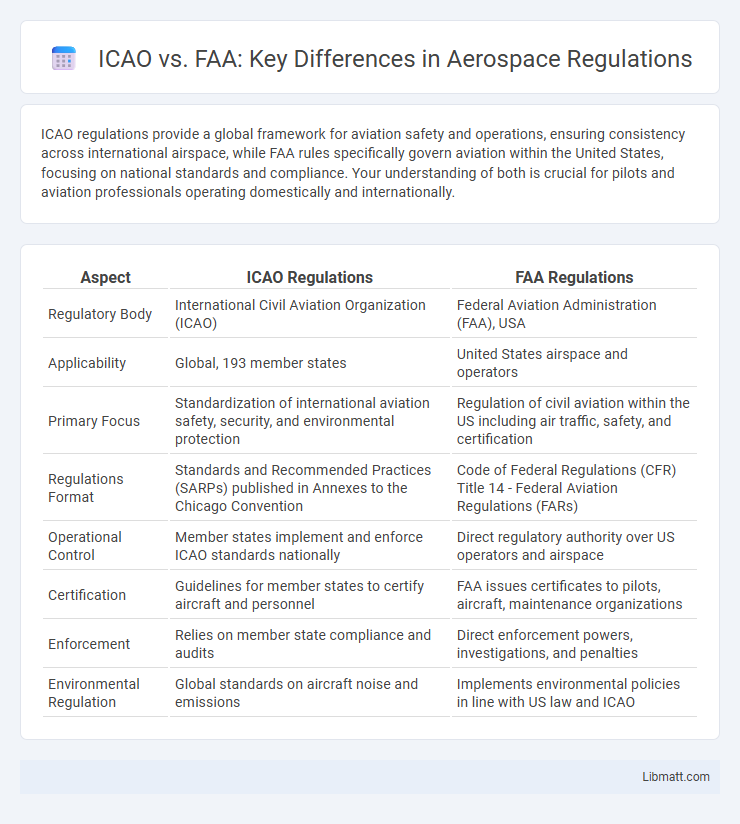
ICAO regulations provide a global framework for aviation safety and operations, ensuring consistency across international airspace, while FAA rules specifically govern aviation within the United States, focusing on national standards and compliance. Your understanding of both is crucial for pilots and aviation professionals operating domestically and internationally.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | ICAO Regulations | FAA Regulations |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Body | International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) | Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), USA |
| Applicability | Global, 193 member states | United States airspace and operators |
| Primary Focus | Standardization of international aviation safety, security, and environmental protection | Regulation of civil aviation within the US including air traffic, safety, and certification |
| Regulations Format | Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) published in Annexes to the Chicago Convention | Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 14 - Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs) |
| Operational Control | Member states implement and enforce ICAO standards nationally | Direct regulatory authority over US operators and airspace |
| Certification | Guidelines for member states to certify aircraft and personnel | FAA issues certificates to pilots, aircraft, maintenance organizations |
| Enforcement | Relies on member state compliance and audits | Direct enforcement powers, investigations, and penalties |
| Environmental Regulation | Global standards on aircraft noise and emissions | Implements environmental policies in line with US law and ICAO |
Introduction to ICAO and FAA
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) establishes global standards for aviation safety, security, efficiency, and environmental protection, serving as a specialized agency of the United Nations. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) oversees civil aviation within the United States, implementing regulations that align with ICAO standards while addressing national aviation system requirements. Both organizations play crucial roles in harmonizing international aviation protocols and ensuring safe air travel across different jurisdictions.
Organizational Structure: ICAO vs FAA
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) operates as a specialized United Nations agency, setting global aviation standards and policies through a council composed of member states, with a Secretariat responsible for implementation and coordination. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), a U.S. government agency under the Department of Transportation, manages civil aviation regulation, air traffic control, and safety oversight within the United States through a hierarchical structure including regional offices and specialized divisions. While ICAO provides international regulatory frameworks and recommendations, the FAA enforces and adapts aviation regulations domestically, reflecting distinct organizational scopes and operational jurisdictions.
Regulatory Scope and Jurisdiction
ICAO regulations establish international standards for aviation safety, security, and environmental protection, guiding member states worldwide through standardized protocols. FAA regulations govern civil aviation within the United States, enforcing rules tailored to domestic airspace, aircraft certification, and pilot licensing. Your operations must comply with FAA rules when flying in U.S. airspace, while ICAO standards influence global air navigation and cross-border aviation practices.
Key Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs)
ICAO's Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) establish international aviation safety, security, efficiency, and environmental protection benchmarks, creating a global framework for member states. The FAA's regulations, aligned with ICAO SARPs, provide specific operational and technical requirements for civil aviation within the United States. ICAO SARPs focus on harmonizing global aviation practices, while FAA regulations emphasize compliance enforcing U.S.-specific legal standards and procedures.
Certification and Licensing Requirements
ICAO certification and licensing requirements establish global standards for aviation safety, ensuring consistency across member states, while FAA regulations specifically govern certification within the United States, often incorporating more detailed procedural requirements. Both ICAO and FAA mandates emphasize pilot qualifications, aircraft airworthiness, and operational competency, but FAA licensing includes distinct categories and endorsements based on U.S. aviation needs. Understanding these frameworks is crucial for aligning Your aviation activities with international and domestic safety standards.
Airspace Management: Global vs National Approaches
ICAO's airspace management framework fosters global standardization and seamless international coordination, ensuring uniformity in procedures and safety standards across member states. In contrast, the FAA's approach emphasizes national sovereignty, tailoring regulations to U.S. airspace complexity while integrating with ICAO standards for international operations. The global vs. national dichotomy highlights ICAO's role in harmonizing cross-border airspace use versus the FAA's focus on optimizing airspace within U.S. jurisdiction.
Safety Oversight and Compliance
ICAO regulations establish a global framework for aviation safety oversight, emphasizing standardized compliance through State Safety Programs and universal auditing mechanisms like the Universal Safety Oversight Audit Program (USOAP). FAA regulations, while aligned with ICAO standards, implement detailed, country-specific safety oversight procedures, focusing on rigorous certification, continuous monitoring, and enforcement actions within the United States aviation system. Both entities prioritize compliance through systematic risk assessment, data-driven safety management systems, and strict adherence to international safety standards to enhance global aviation safety.
Environmental Regulations and Sustainability
ICAO environmental regulations emphasize global standards for aircraft emissions, noise reduction, and sustainable aviation fuels to address climate change on an international scale. The FAA focuses on implementing these standards within the U.S., promoting innovation in green technologies and incentivizing airlines to reduce their carbon footprint. Understanding these regulations helps you comply with evolving sustainability requirements and support eco-friendly aviation practices.
Differences in Operational Procedures
ICAO regulations emphasize global standardization of operational procedures, ensuring uniformity across international airspace, while FAA regulations are tailored to address specific national requirements and operational environments within the United States. Differences in pilot certification, air traffic control protocols, and flight planning procedures reflect the FAA's adaptation to domestic airspace complexities compared to ICAO's broader international framework. Your understanding of these distinctions is crucial for compliance and safety when operating or coordinating flights across both regulatory domains.
Harmonization and Global Impact
ICAO regulations serve as the global standard-setting framework, promoting harmonization across national aviation authorities, including the FAA, which adapts these standards to fit U.S. aviation operations. Harmonization between ICAO and FAA regulations enhances international flight safety, operational consistency, and reduces disparities in air navigation services. The global impact of this alignment facilitates seamless international air travel, bolstering global trade and connectivity within the aviation industry.
ICAO vs FAA Regulations Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com