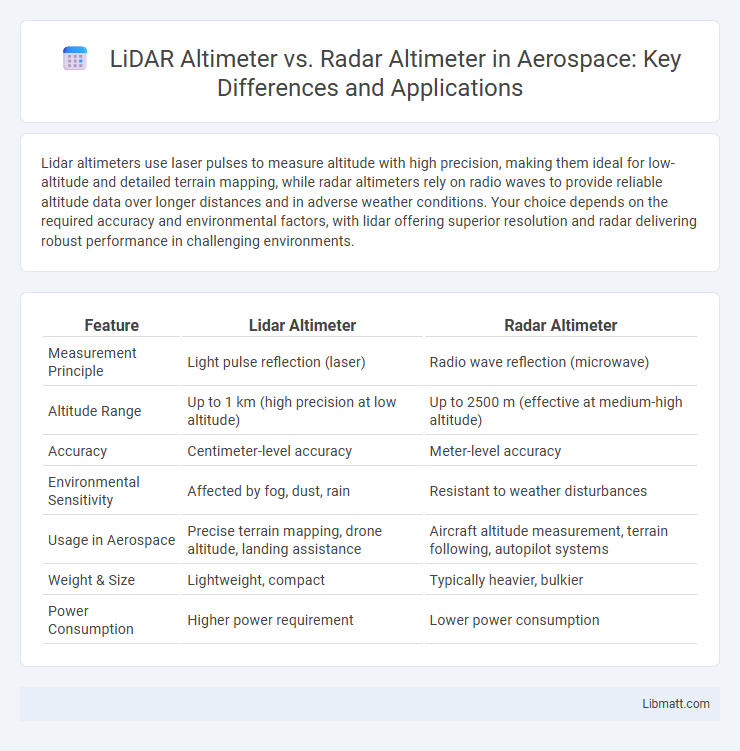
Lidar altimeters use laser pulses to measure altitude with high precision, making them ideal for low-altitude and detailed terrain mapping, while radar altimeters rely on radio waves to provide reliable altitude data over longer distances and in adverse weather conditions. Your choice depends on the required accuracy and environmental factors, with lidar offering superior resolution and radar delivering robust performance in challenging environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lidar Altimeter | Radar Altimeter |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Light pulse reflection (laser) | Radio wave reflection (microwave) |
| Altitude Range | Up to 1 km (high precision at low altitude) | Up to 2500 m (effective at medium-high altitude) |
| Accuracy | Centimeter-level accuracy | Meter-level accuracy |
| Environmental Sensitivity | Affected by fog, dust, rain | Resistant to weather disturbances |
| Usage in Aerospace | Precise terrain mapping, drone altitude, landing assistance | Aircraft altitude measurement, terrain following, autopilot systems |
| Weight & Size | Lightweight, compact | Typically heavier, bulkier |
| Power Consumption | Higher power requirement | Lower power consumption |
Introduction to Altimetry Technologies
Lidar altimeters use laser pulses to measure altitude by calculating the time it takes for light to reflect off surfaces, providing high-resolution and precise terrain mapping. Radar altimeters emit radio waves and measure the return time, offering reliable altitude data in various weather conditions and over diverse surfaces. Both technologies play crucial roles in aviation, remote sensing, and autonomous navigation by delivering accurate altitude measurements tailored to specific operational needs.
What is a Lidar Altimeter?
A Lidar altimeter measures altitude by emitting laser pulses toward the ground and calculating the time it takes for the reflected light to return, providing highly accurate elevation data. Unlike radar altimeters that use radio waves, Lidar offers finer resolution and is effective for detailed terrain mapping, especially in environments with minimal atmospheric interference. Your choice between Lidar and radar altimeters depends on specific application needs such as precision, range, and environmental conditions.
What is a Radar Altimeter?
A Radar Altimeter measures altitude by emitting radio waves and calculating the time it takes for the waves to reflect off the ground and return. Unlike Lidar altimeters that use laser light, Radar altimeters operate effectively in various weather conditions, including fog and rain, providing reliable altitude data for your aircraft or vehicle. This technology is essential for precise low-altitude navigation and landing systems.
Core Working Principles Compared
Lidar altimeters measure altitude by emitting laser pulses and calculating the time taken for the reflected light to return, enabling high-resolution terrain mapping due to shorter wavelengths. Radar altimeters transmit radio waves and assess altitude through the time delay of the reflected signals, offering reliable performance in various weather conditions with longer wavelengths. The core difference lies in Lidar's use of light waves for precise, short-range detection, while Radar employs radio waves for broader, weather-resistant altitude measurements.
Accuracy and Precision Differences
Lidar altimeters use laser pulses to measure altitude, providing higher accuracy and precision by detecting smaller surface details with centimeter-level resolution. Radar altimeters operate using radio waves, offering reliable altitude readings with meter-level accuracy but less sensitivity to fine topographic variations. Your choice depends on the required precision for applications such as autonomous vehicles or aircraft navigation, where lidar excels in detailed mapping and radar ensures robust performance in adverse weather.
Applications in Various Industries
Lidar altimeters provide high-resolution altitude measurements crucial for autonomous vehicles, drones, and precision agriculture by enabling accurate terrain mapping and obstacle detection. Radar altimeters, known for their ability to operate reliably in adverse weather conditions, are extensively used in aviation for landing systems and automotive safety features such as adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance. Both technologies serve industries like aerospace, defense, and environmental monitoring, with Lidar excelling in detailed surface profiling and Radar ensuring dependable altitude data in all weather scenarios.
Advantages of Lidar Altimeters
Lidar altimeters offer higher resolution and accuracy by using laser pulses to measure altitude, making them ideal for detailed terrain mapping and precise navigation. They provide better performance in low-altitude flights and complex environments due to their shorter wavelength and finer spatial resolution compared to radar altimeters. Lidar systems are also less affected by electromagnetic interference, enhancing reliability in challenging conditions.
Advantages of Radar Altimeters
Radar altimeters offer precise altitude measurements even in adverse weather conditions, such as fog, rain, or dust, thanks to their radio wave technology that penetrates atmospheric obstacles. Their long-range capability and high reliability are essential for aviation safety, enabling accurate low-altitude readings critical during landing approaches. Your aircraft benefits from the consistent performance of radar altimeters, ensuring accurate terrain awareness and enhancing overall flight safety.
Limitations and Challenges
Lidar altimeters face limitations such as reduced performance in adverse weather conditions like fog, rain, or snow, which scatter laser signals and degrade accuracy. Radar altimeters encounter challenges with signal interference and multipath reflections, leading to potential measurement errors over complex terrain. Your choice between the two depends on the application's environmental factors and required measurement precision.
Choosing the Right Altimeter for Your Needs
Lidar altimeters provide high-resolution, precise altitude measurements using laser light, making them ideal for applications requiring detailed terrain mapping and obstacle detection. Radar altimeters operate effectively in adverse weather conditions and offer reliable altitude readings over water or uneven surfaces, suitable for aviation and marine navigation. Selecting the right altimeter depends on factors like environmental conditions, required accuracy, and application-specific needs, with lidar favored for precision and radar preferred for robustness.
Lidar altimeter vs Radar altimeter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com