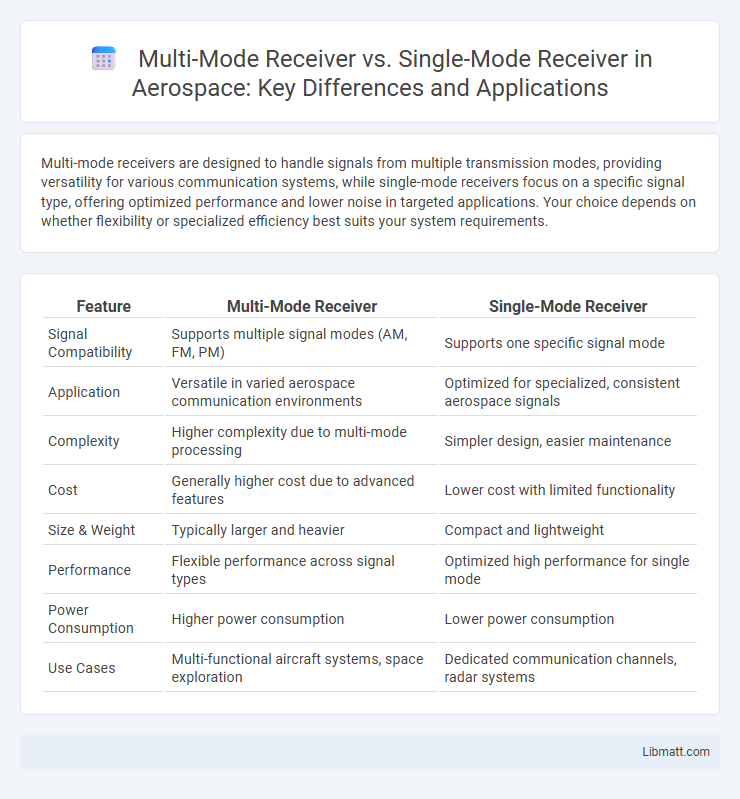
Multi-mode receivers are designed to handle signals from multiple transmission modes, providing versatility for various communication systems, while single-mode receivers focus on a specific signal type, offering optimized performance and lower noise in targeted applications. Your choice depends on whether flexibility or specialized efficiency best suits your system requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Multi-Mode Receiver | Single-Mode Receiver |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Compatibility | Supports multiple signal modes (AM, FM, PM) | Supports one specific signal mode |
| Application | Versatile in varied aerospace communication environments | Optimized for specialized, consistent aerospace signals |
| Complexity | Higher complexity due to multi-mode processing | Simpler design, easier maintenance |
| Cost | Generally higher cost due to advanced features | Lower cost with limited functionality |
| Size & Weight | Typically larger and heavier | Compact and lightweight |
| Performance | Flexible performance across signal types | Optimized high performance for single mode |
| Power Consumption | Higher power consumption | Lower power consumption |
| Use Cases | Multi-functional aircraft systems, space exploration | Dedicated communication channels, radar systems |
Introduction to Multi-Mode and Single-Mode Receivers
Multi-mode receivers are designed to handle multiple optical modes, enabling efficient signal processing in short-distance fiber optic communications due to their larger core diameter and higher modal dispersion tolerance. Single-mode receivers operate with a single optical mode, offering higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances by minimizing modal dispersion through their smaller core diameter. Choosing between multi-mode and single-mode receivers depends on specific network requirements such as distance, data rate, and cost considerations.
Key Definitions and Technologies
Multi-mode receivers use multiple optical modes to transmit data, suitable for short-distance communication with LED light sources, while single-mode receivers utilize a single light mode, enabling long-distance transmission with laser diodes. Multi-mode fiber has a larger core diameter (typically 50-62.5 microns) compared to the smaller core (around 8-10 microns) of single-mode fiber, affecting bandwidth and distance capabilities. Your choice depends on the required range and data rate, as single-mode receivers support higher bandwidth and longer distances whereas multi-mode receivers offer cost-effective solutions for shorter links.
Core Differences Between Multi-Mode and Single-Mode Receivers
Multi-mode receivers utilize larger core fibers, typically 50 or 62.5 microns, allowing multiple light modes to propagate simultaneously, which suits shorter-distance data transmission. Single-mode receivers use smaller core fibers around 9 microns, supporting a single light mode for higher bandwidth and longer-distance communication, making them ideal for telecommunications and high-speed networks. Your choice between these receivers depends on distance requirements, bandwidth needs, and cost considerations in your optical fiber system.
Performance and Functionality Comparison
Multi-mode receivers support multiple signal types, offering versatile functionality suitable for diverse communication environments, while single-mode receivers are optimized for one specific signal, ensuring higher sensitivity and lower noise. Multi-mode receivers may experience slightly reduced performance in signal clarity and processing speed compared to single-mode receivers, which deliver more precise and reliable signal reception. Your choice depends on whether flexibility or optimized performance is the priority in your communication system.
Applications in Modern Communication Systems
Multi-mode receivers are ideal for short to medium distance communication in modern systems such as local area networks (LANs) and data centers due to their cost-effectiveness and high bandwidth support over multimode fibers. Single-mode receivers excel in long-distance applications, including telecommunications and high-speed internet backbone infrastructure, by providing low signal attenuation and minimal modal dispersion on single-mode fibers. Understanding your communication system's distance and bandwidth requirements ensures optimal receiver choice, enhancing performance and reliability.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Multi-mode receivers generally cost less upfront due to lower component precision, making them a budget-friendly option for short-distance communication needs. Single-mode receivers involve higher expenses from advanced laser sources and precision alignment, justifying their investment for long-distance and high-bandwidth applications. Your choice between these options should balance initial costs with performance requirements and future scalability.
Integration and Compatibility Factors
Multi-mode receivers offer broader integration flexibility with diverse optical systems, supporting various fiber types and wavelengths, enhancing compatibility in mixed-network environments. Single-mode receivers provide higher precision and longer-distance capabilities but require stricter alignment and are optimized for specific wavelengths, limiting cross-compatibility. Selecting between them depends on system requirements for integration ease, network infrastructure, and desired performance metrics.
Maintenance and Reliability Aspects
Multi-mode receivers typically require more frequent maintenance due to modal dispersion and alignment sensitivity, which can impact their long-term reliability in complex network environments. Single-mode receivers offer greater stability and lower signal attenuation, resulting in enhanced reliability and reduced upkeep for your optical communication systems. Choosing a single-mode receiver can minimize maintenance efforts and extend the overall lifespan of your network equipment.
Future Trends in Receiver Technology
Future trends in receiver technology emphasize increased integration of multi-mode receivers to support diverse communication standards such as 5G, Wi-Fi 6, and IoT networks, improving compatibility and performance in complex environments. Multi-mode receivers offer superior flexibility, allowing seamless switching between single-mode signals and multiple frequency bands, which enhances signal reliability and device efficiency. Your network infrastructure will benefit from these advancements by enabling higher data rates, lower latency, and enhanced connectivity across varied applications.
Choosing the Right Receiver for Your Needs
Selecting the right optical fiber receiver depends on your network requirements and distance constraints, with multi-mode receivers suited for shorter distances up to 2 kilometers and offering cost-effective solutions. Single-mode receivers support longer distances exceeding 10 kilometers with high bandwidth capacity, ideal for long-haul and high-performance applications. Consider factors like fiber type compatibility, transmission distance, and data rate demands when choosing between multi-mode and single-mode receivers to optimize network efficiency and cost.
multi-mode receiver vs single-mode receiver Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com