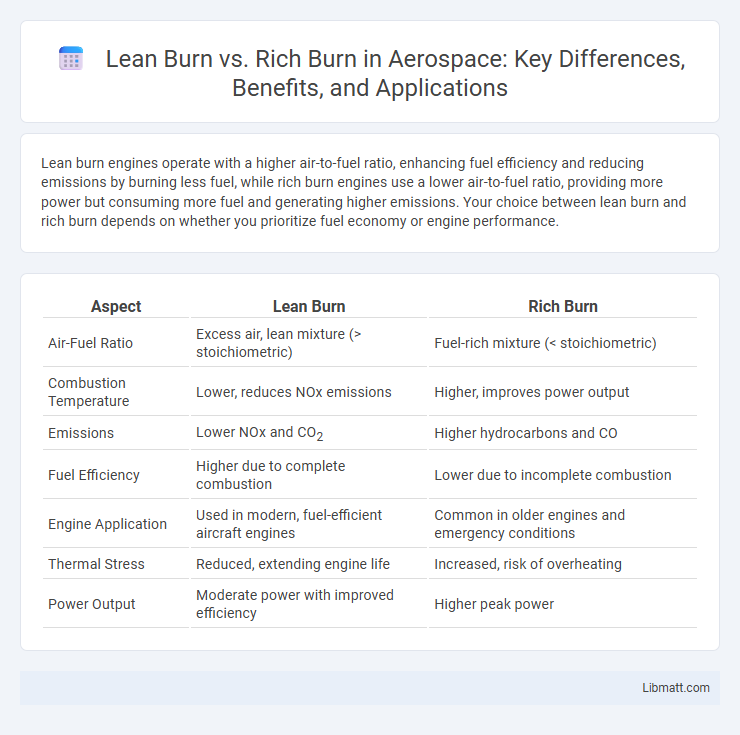
Lean burn engines operate with a higher air-to-fuel ratio, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions by burning less fuel, while rich burn engines use a lower air-to-fuel ratio, providing more power but consuming more fuel and generating higher emissions. Your choice between lean burn and rich burn depends on whether you prioritize fuel economy or engine performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lean Burn | Rich Burn |
|---|---|---|
| Air-Fuel Ratio | Excess air, lean mixture (> stoichiometric) | Fuel-rich mixture (< stoichiometric) |
| Combustion Temperature | Lower, reduces NOx emissions | Higher, improves power output |
| Emissions | Lower NOx and CO2 | Higher hydrocarbons and CO |
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher due to complete combustion | Lower due to incomplete combustion |
| Engine Application | Used in modern, fuel-efficient aircraft engines | Common in older engines and emergency conditions |
| Thermal Stress | Reduced, extending engine life | Increased, risk of overheating |
| Power Output | Moderate power with improved efficiency | Higher peak power |
Introduction to Lean Burn and Rich Burn
Lean burn and rich burn refer to different air-to-fuel ratios used in internal combustion engines, where lean burn operates with excess air and less fuel, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Rich burn mixes contain more fuel relative to air, producing higher power output but with increased fuel consumption and pollutant production. Understanding these combustion strategies is essential for optimizing engine performance and meeting environmental regulations.
What is Lean Burn?
Lean burn refers to an engine operating with a fuel-air mixture containing more air than the stoichiometric ratio, typically resulting in improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. This combustion method promotes lower temperatures, minimizing nitrogen oxide (NOx) formation while maintaining engine performance. Your vehicle benefits from lean burn technology by achieving better mileage and cleaner exhaust gases compared to rich burn conditions.
What is Rich Burn?
Rich burn refers to an engine combustion process where the air-fuel mixture contains a higher proportion of fuel than the stoichiometric ratio, resulting in incomplete combustion. This method produces more power and improved throttle response but at the cost of increased fuel consumption and higher emissions. Your engine running rich burn will typically emit more pollutants like carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons compared to lean burn conditions.
Key Differences Between Lean Burn and Rich Burn
Lean burn engines operate with a higher air-to-fuel ratio, resulting in more efficient fuel consumption and reduced emissions, while rich burn engines use a lower air-to-fuel ratio that produces more power but increases fuel consumption and pollutant output. Lean burn combustion promotes cooler engine temperatures and improved fuel economy, whereas rich burn combustion generates higher temperatures and more complete combustion of fuel. Key differences revolve around efficiency, emissions, engine temperature, and power output, with lean burn favoring environmental benefits and rich burn optimizing performance.
Fuel Efficiency: Lean vs Rich Burn
Lean burn engines operate with an excess of air relative to fuel, improving fuel efficiency by promoting more complete combustion and reducing fuel consumption. Rich burn engines use a higher fuel-to-air ratio, resulting in more fuel consumption and lower efficiency but typically providing increased power output. Optimizing fuel efficiency often favors lean burn technology due to its ability to minimize fuel usage and emissions.
Emission Levels and Environmental Impact
Lean burn engines operate with excess air, resulting in lower emissions of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) due to more complete combustion, which significantly reduces environmental pollutants. Rich burn engines use a fuel-rich mixture that generates higher levels of CO and HC emissions but typically produce lower nitrogen oxides (NOx) compared to lean burn engines. The environmental impact of lean burn technology is generally more favorable as it minimizes greenhouse gases and toxic emissions, contributing to improved air quality and reduced ecological harm.
Performance and Power Output Comparison
Lean burn engines improve fuel efficiency by operating with excess air, which reduces fuel consumption and lowers emissions but may result in slightly lower power output due to less fuel being combusted. Rich burn engines deliver higher power output as they use a fuel-rich mixture, allowing for more energy release per combustion cycle, ideal for performance-focused applications but at the cost of increased fuel consumption and emissions. Your choice between lean and rich burn should balance the need for maximum power against fuel economy and environmental considerations.
Applications in Engines and Industries
Lean burn engines operate with excess air, reducing fuel consumption and emissions, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace applications where fuel efficiency and lower NOx emissions are critical. Rich burn engines run with excess fuel, producing higher power output and better performance under heavy load, commonly used in industrial gas turbines and high-performance racing engines. Industries such as power generation and manufacturing often choose rich burn systems for stability and power, while lean burn configurations dominate in sectors prioritizing environmental compliance and fuel economy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
Lean burn engines improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by using excess air during combustion, resulting in lower fuel consumption and decreased carbon monoxide output. However, they often produce higher nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and may suffer from rougher engine operation at low loads. Rich burn engines generate more power with a richer fuel mixture, offering better cold-start performance and lower NOx levels, but they consume more fuel and emit higher levels of carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Lean Burn and Rich Burn
Choosing between lean burn and rich burn depends on your engine's performance goals and fuel efficiency preferences. Lean burn engines optimize fuel consumption and emissions by using a higher air-to-fuel ratio, while rich burn engines prioritize power and responsiveness with a lower air-to-fuel ratio. Your ideal choice balances efficiency and output according to specific driving demands and environmental considerations.
Lean burn vs Rich burn Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com