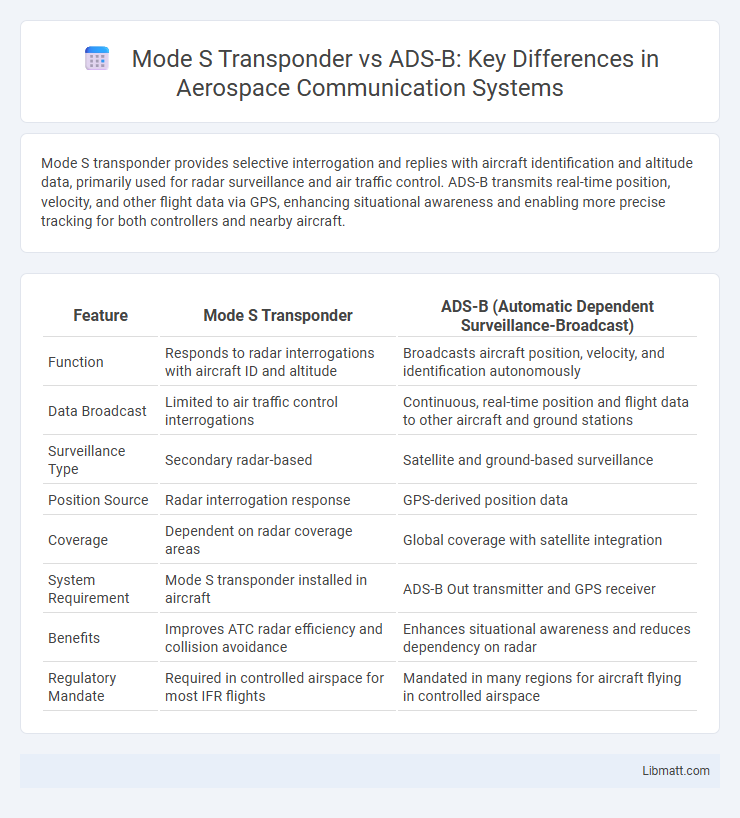
Mode S transponder provides selective interrogation and replies with aircraft identification and altitude data, primarily used for radar surveillance and air traffic control. ADS-B transmits real-time position, velocity, and other flight data via GPS, enhancing situational awareness and enabling more precise tracking for both controllers and nearby aircraft.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mode S Transponder | ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Responds to radar interrogations with aircraft ID and altitude | Broadcasts aircraft position, velocity, and identification autonomously |
| Data Broadcast | Limited to air traffic control interrogations | Continuous, real-time position and flight data to other aircraft and ground stations |
| Surveillance Type | Secondary radar-based | Satellite and ground-based surveillance |
| Position Source | Radar interrogation response | GPS-derived position data |
| Coverage | Dependent on radar coverage areas | Global coverage with satellite integration |
| System Requirement | Mode S transponder installed in aircraft | ADS-B Out transmitter and GPS receiver |
| Benefits | Improves ATC radar efficiency and collision avoidance | Enhances situational awareness and reduces dependency on radar |
| Regulatory Mandate | Required in controlled airspace for most IFR flights | Mandated in many regions for aircraft flying in controlled airspace |
Introduction to Mode S Transponder and ADS-B
Mode S transponder enables aircraft identification and selective interrogation by radar systems, improving air traffic control precision through unique 24-bit addresses and enhanced data exchange. ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) provides real-time aircraft position, velocity, and identification by broadcasting GPS-derived data to ground stations and other aircraft, enhancing situational awareness and safety. Both systems are critical for modern surveillance but differ in operational methods: Mode S relies on radar interrogation while ADS-B depends on autonomous broadcasting.
How Mode S Transponders Work
Mode S transponders communicate with air traffic control radar by responding to specific interrogation signals with a unique aircraft identification code and altitude information. They operate by using selective addressing, allowing controllers to target individual aircraft for more precise tracking and reducing radio frequency congestion. Your aircraft's Mode S transponder improves situational awareness and collision avoidance through this data exchange, forming the foundation for advanced surveillance systems like ADS-B.
Overview of ADS-B Technology
ADS-B technology uses GPS signals to broadcast real-time aircraft position, velocity, and identification data automatically to ground stations and other aircraft, enhancing situational awareness and traffic tracking. Unlike the Mode S transponder, which relies on radar interrogation and responds with limited data, ADS-B continuously transmits detailed, accurate information without the need for radar. Your aircraft equipped with ADS-B benefits from improved safety, better air traffic management, and compliance with modern aviation regulations worldwide.
Key Differences Between Mode S and ADS-B
Mode S transponders transmit radar data by replying to radar interrogations with unique aircraft identification and altitude information, while ADS-B continuously broadcasts precise GPS-derived position, velocity, and other flight data to ground stations and nearby aircraft. ADS-B provides more comprehensive situational awareness and enables real-time traffic and weather updates, enhancing safety and efficiency compared to Mode S's radar-dependent system. Your aircraft's compliance with ADS-B mandates and its integration with modern air traffic management systems make understanding these differences crucial for navigation and communication.
Advantages of Mode S Transponders
Mode S transponders provide enhanced aircraft identification and selective interrogation capabilities, allowing air traffic control to efficiently manage traffic and reduce radar clutter. These transponders support data link communication for more accurate aircraft position reporting compared to traditional radar systems. Your aircraft benefits from improved situational awareness and compatibility with existing radar infrastructure, ensuring reliable tracking in diverse airspace environments.
Advantages of ADS-B Systems
ADS-B systems provide enhanced situational awareness by broadcasting real-time aircraft position and velocity data without relying on radar infrastructure, leading to improved air traffic management efficiency. Unlike Mode S transponders, ADS-B offers greater accuracy and coverage, especially in remote or oceanic regions where radar is limited. Your ability to receive precise traffic information and weather updates directly improves flight safety and operational decision-making.
Regulatory Requirements for Mode S and ADS-B
Mode S transponders are mandated by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) for controlled airspace operations, requiring aircraft to transmit unique 24-bit addresses for identification and altitude reporting. ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) mandates, enforced by the FAA and EASA, require aircraft to broadcast precise GPS-based position, velocity, and identification data to enhance situational awareness and traffic management. Regulatory frameworks like FAA's 14 CFR Part 91.225 and EASA's Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/947 specify ADS-B Out equipment requirements, phasing in compliance timelines to improve aviation safety and efficiency globally.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Mode S transponders generally have lower upfront costs and simpler installation compared to ADS-B systems, making them a more budget-friendly option for many pilots. ADS-B Out units often require additional avionics upgrades and professional installation due to regulatory compliance and integration with GPS capabilities. Your choice may depend on balancing immediate expenses against long-term benefits from ADS-B's enhanced traffic awareness and airspace access.
Operational Impacts in Modern Airspace
Mode S transponders provide selective interrogation and reporting capabilities essential for radar-based surveillance, supporting controlled airspace operations and collision avoidance systems. ADS-B enhances situational awareness by broadcasting precise aircraft position and velocity data via satellite and ground stations, enabling real-time tracking in areas lacking radar coverage. The integration of Mode S and ADS-B technologies improves operational efficiency, reduces controller workload, and increases airspace capacity in modern air traffic management systems.
Future Trends in Aircraft Surveillance Technology
Future trends in aircraft surveillance technology emphasize the shift from Mode S transponders to ADS-B systems, which provide more accurate and real-time positional data. ADS-B enhances situational awareness with satellite-based tracking, enabling improved traffic management and safety in increasingly crowded airspace. Your aircraft's integration of ADS-B technology ensures compliance with evolving international regulations and supports next-generation air traffic control systems.
mode S transponder vs ADS-B Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com