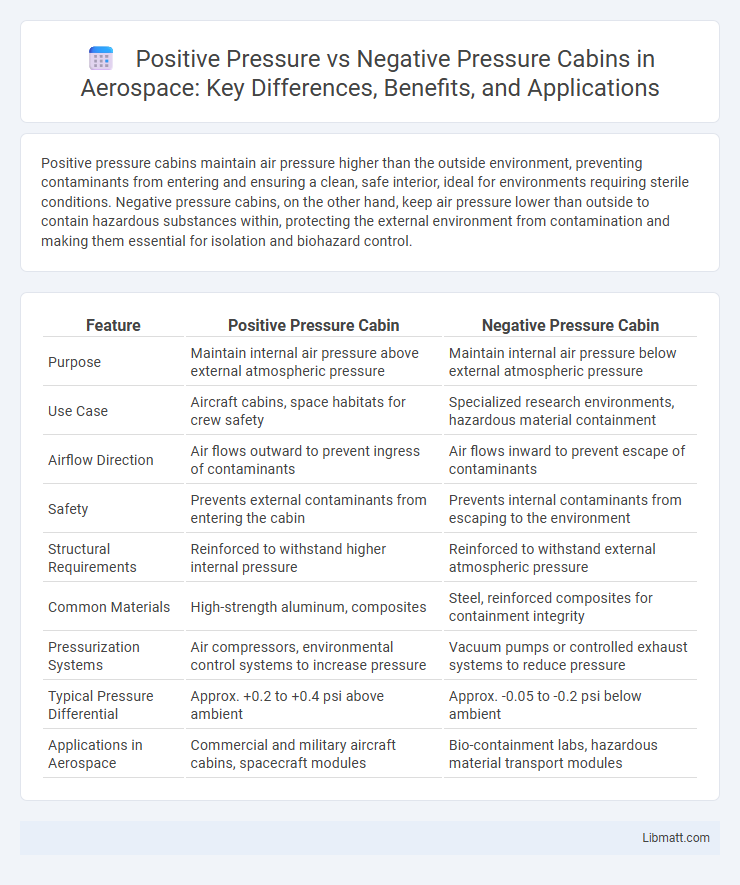
Positive pressure cabins maintain air pressure higher than the outside environment, preventing contaminants from entering and ensuring a clean, safe interior, ideal for environments requiring sterile conditions. Negative pressure cabins, on the other hand, keep air pressure lower than outside to contain hazardous substances within, protecting the external environment from contamination and making them essential for isolation and biohazard control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Positive Pressure Cabin | Negative Pressure Cabin |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Maintain internal air pressure above external atmospheric pressure | Maintain internal air pressure below external atmospheric pressure |
| Use Case | Aircraft cabins, space habitats for crew safety | Specialized research environments, hazardous material containment |
| Airflow Direction | Air flows outward to prevent ingress of contaminants | Air flows inward to prevent escape of contaminants |
| Safety | Prevents external contaminants from entering the cabin | Prevents internal contaminants from escaping to the environment |
| Structural Requirements | Reinforced to withstand higher internal pressure | Reinforced to withstand external atmospheric pressure |
| Common Materials | High-strength aluminum, composites | Steel, reinforced composites for containment integrity |
| Pressurization Systems | Air compressors, environmental control systems to increase pressure | Vacuum pumps or controlled exhaust systems to reduce pressure |
| Typical Pressure Differential | Approx. +0.2 to +0.4 psi above ambient | Approx. -0.05 to -0.2 psi below ambient |
| Applications in Aerospace | Commercial and military aircraft cabins, spacecraft modules | Bio-containment labs, hazardous material transport modules |
Introduction to Pressure Cabins
Positive pressure cabins maintain an internal pressure higher than the external environment, ensuring contaminants are kept out and providing a safer and more controlled atmosphere for occupants. Negative pressure cabins operate with a lower internal pressure than the outside, effectively containing hazardous substances within the cabin to prevent contamination of surrounding areas. Both pressure cabin types are critical in medical, laboratory, and industrial applications where air quality control and contamination prevention are paramount.
What is a Positive Pressure Cabin?
A positive pressure cabin maintains higher air pressure inside than outside, preventing contaminants, dust, and airborne pathogens from entering the enclosed space. Your safety and comfort are enhanced as clean, filtered air is continuously supplied, creating a controlled environment crucial in medical facilities, aircraft, and cleanrooms. This system effectively blocks external pollutants by ensuring airflow moves outward through any gaps or openings.
What is a Negative Pressure Cabin?
A negative pressure cabin is an environment where the air pressure inside is lower than the surrounding atmosphere, preventing contaminants from escaping when doors or windows are opened. This setup is commonly used in medical isolation rooms, biosafety labs, and quarantine areas to contain airborne pathogens and protect external environments. Controlled airflow systems maintain the negative pressure differential, ensuring that potentially hazardous air remains confined within the cabin.
Key Differences Between Positive and Negative Pressure Cabins
Positive pressure cabins maintain an internal environment where air pressure is higher than the outside, preventing contaminants from entering and ensuring a sterile atmosphere, commonly used in cleanrooms and operating theaters. Negative pressure cabins create a lower internal pressure compared to the surrounding environment, effectively containing harmful pathogens or hazardous substances within the space, essential for isolation rooms and biosafety labs. The key difference lies in airflow direction and pressure gradient, with positive pressure pushing contaminants out while negative pressure pulls them in to protect external environments.
Applications of Positive Pressure Cabins
Positive pressure cabins are primarily used in environments requiring contamination control, such as operating rooms, cleanrooms, and pharmaceutical manufacturing, where maintaining sterile and particle-free air is critical. These cabins prevent airborne contaminants from entering by ensuring air pressure inside the space remains higher than outside, protecting both personnel and sensitive equipment. Your workspace benefits from positive pressure cabins in industries like healthcare, aerospace, and electronics, where maintaining a contaminant-free environment is essential for product quality and safety.
Applications of Negative Pressure Cabins
Negative pressure cabins are widely used in applications requiring contamination control and infection prevention, such as isolation rooms in hospitals and biosafety laboratories. These cabins maintain air pressure lower than the surrounding environment to prevent airborne contaminants from escaping, protecting both personnel and sensitive equipment. Your safety in medical or industrial settings benefits significantly from the containment capabilities of negative pressure cabins.
Advantages of Positive Pressure Cabins
Positive pressure cabins maintain a higher air pressure inside compared to the outside environment, effectively preventing contaminants and hazardous particles from entering the space. This advantage ensures a safer and more controlled environment for personnel, especially in medical, industrial, or cleanroom applications. Your health and work efficiency benefit from the reduced risk of exposure to airborne pathogens or pollutants.
Advantages of Negative Pressure Cabins
Negative pressure cabins enhance safety by preventing airborne contaminants from escaping, making them ideal for isolation in medical and laboratory environments. These cabins maintain lower internal air pressure relative to the surrounding area, effectively containing pathogens and reducing cross-contamination risks. Their design supports better infection control in hospitals, cleanrooms, and quarantine facilities, promoting a safer environment for both occupants and staff.
Choosing the Right Pressure Cabin for Your Needs
Choosing the right pressure cabin depends on your specific operational requirements and environmental conditions. Positive pressure cabins maintain an internal environment by preventing contaminants from entering, ideal for cleanrooms and hazardous material handling, while negative pressure cabins contain airborne pollutants within, perfect for infection control or hazardous isolation. Understanding your need for contamination control or containment helps you select the most effective pressure system to ensure safety and operational efficiency.
Future Trends in Pressure Cabin Technology
Future trends in pressure cabin technology indicate a shift toward adaptive pressure systems capable of dynamically adjusting between positive and negative pressures based on real-time environmental and physiological data. Innovations in smart materials and sensor integration will enhance cabin pressure regulation for improved occupant safety and comfort, particularly in aerospace and medical applications. Emerging energy-efficient technologies aim to reduce the power consumption of pressure control systems while maintaining precise atmospheric conditions inside cabins.
positive pressure cabin vs negative pressure cabin Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com