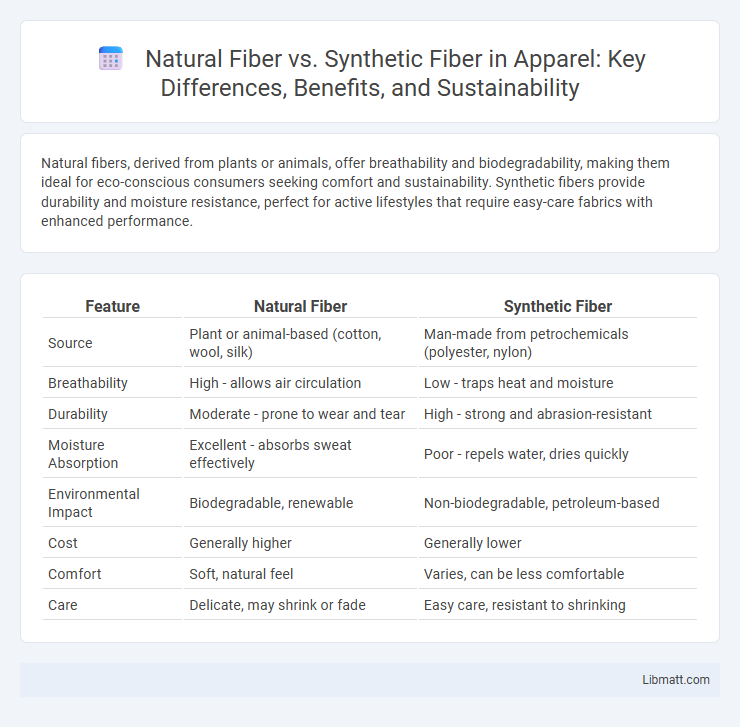
Natural fibers, derived from plants or animals, offer breathability and biodegradability, making them ideal for eco-conscious consumers seeking comfort and sustainability. Synthetic fibers provide durability and moisture resistance, perfect for active lifestyles that require easy-care fabrics with enhanced performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Fiber | Synthetic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant or animal-based (cotton, wool, silk) | Man-made from petrochemicals (polyester, nylon) |
| Breathability | High - allows air circulation | Low - traps heat and moisture |
| Durability | Moderate - prone to wear and tear | High - strong and abrasion-resistant |
| Moisture Absorption | Excellent - absorbs sweat effectively | Poor - repels water, dries quickly |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Comfort | Soft, natural feel | Varies, can be less comfortable |
| Care | Delicate, may shrink or fade | Easy care, resistant to shrinking |
Introduction to Natural and Synthetic Fibers
Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and silk originate from plants and animals, offering biodegradability and breathability that enhance comfort and environmental sustainability. Synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic are human-made from petrochemicals, providing durability, elasticity, and resistance to moisture and wrinkles. Understanding the fundamental differences in origin and properties between natural and synthetic fibers informs their selection for diverse textile applications.
Defining Natural Fibers: Sources and Types
Natural fibers originate from plants, animals, or minerals, offering biodegradable and sustainable textile options. Common plant-based fibers include cotton, flax, and hemp, while animal-derived fibers encompass wool, silk, and alpaca. Each type of natural fiber presents unique properties such as breathability, moisture absorption, and strength, making them essential in eco-friendly fabric production.
Understanding Synthetic Fibers: Creation and Varieties
Synthetic fibers are man-made materials produced through chemical processes, primarily derived from petrochemicals such as petroleum, coal, or natural gas. Common varieties include polyester, nylon, acrylic, and spandex, each designed for specific properties like durability, elasticity, or moisture resistance. Your choice between synthetic and natural fibers can significantly impact fabric performance, sustainability, and comfort.
Environmental Impact: Natural vs Synthetic Fibers
Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and hemp are biodegradable and have a lower environmental footprint compared to synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon, which are derived from petrochemicals and contribute significantly to microplastic pollution. Natural fibers require less energy-intensive production processes and decompose more easily, reducing landfill waste and soil contamination. Your choice of natural fibers supports sustainability by minimizing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing the accumulation of non-biodegradable materials in ecosystems.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and linen offer breathability and comfort but generally have lower durability and shorter lifespan compared to synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic, which are engineered for strength and resistance to wear and tear. Synthetic fibers resist moisture, mildew, and UV damage better, making them ideal for outdoor and heavy-use applications, while natural fibers may degrade faster when exposed to environmental stressors. Your choice depends on the desired balance between comfort and the need for long-lasting, resilient fabric.
Comfort and Breathability: Fiber Performance in Wear
Natural fibers like cotton, wool, and linen offer superior comfort and breathability due to their ability to absorb moisture and allow air circulation, keeping your skin dry and cool during wear. Synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon often retain heat and moisture, leading to reduced breathability and potential discomfort in prolonged use. Choosing natural fibers enhances fiber performance by promoting temperature regulation and moisture management for optimal wear comfort.
Cost Analysis: Natural vs Synthetic Fiber Products
Natural fiber products generally have higher upfront costs due to labor-intensive harvesting and processing, but they offer biodegradability and sustainability advantages. Synthetic fibers, often produced from petrochemicals, tend to be more affordable and widely available, making them popular for budget-conscious consumers. Your choice depends on valuing environmental impact versus immediate expenses in the cost-benefit analysis.
Applications in Fashion and Industry
Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and silk are highly favored in fashion for their breathability, biodegradability, and comfort, making them ideal for everyday wear and luxury garments. Synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic dominate industrial applications due to their durability, resistance to chemicals, and cost-effectiveness, widely used in automotive textiles, geotextiles, and protective clothing. Your choice between natural and synthetic fibers impacts garment performance, environmental sustainability, and end-use functionality in both fashion and industrial sectors.
Sustainability and Eco-friendly Alternatives
Natural fibers such as cotton, hemp, and jute offer superior sustainability compared to synthetic fibers, as they are biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, reducing environmental impact. Synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon are petroleum-based, contribute to microplastic pollution, and pose challenges in waste management due to their non-biodegradable nature. Choosing natural fiber products supports eco-friendly alternatives that minimize carbon footprint and promote sustainable textile production for your environmentally conscious lifestyle.
Choosing the Right Fiber: Key Factors to Consider
Choosing the right fiber involves evaluating factors such as durability, environmental impact, and comfort. Natural fibers like cotton and wool offer breathability and biodegradability but may require more care and have lower resistance to wear compared to synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon, which provide enhanced strength and moisture-wicking properties. Cost-effectiveness and intended use, including climate and activity level, also play critical roles in determining the optimal fiber choice for textiles and apparel.
Natural Fiber vs Synthetic Fiber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com