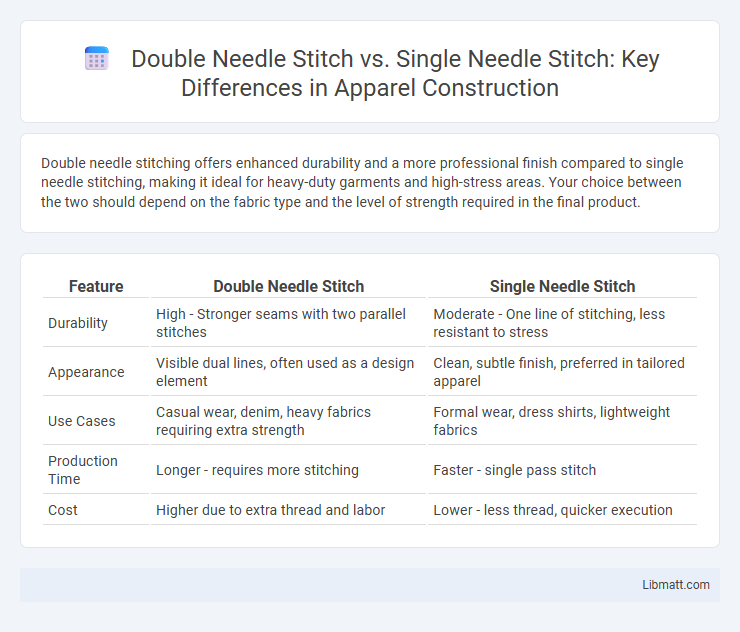
Double needle stitching offers enhanced durability and a more professional finish compared to single needle stitching, making it ideal for heavy-duty garments and high-stress areas. Your choice between the two should depend on the fabric type and the level of strength required in the final product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Double Needle Stitch | Single Needle Stitch |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High - Stronger seams with two parallel stitches | Moderate - One line of stitching, less resistant to stress |
| Appearance | Visible dual lines, often used as a design element | Clean, subtle finish, preferred in tailored apparel |
| Use Cases | Casual wear, denim, heavy fabrics requiring extra strength | Formal wear, dress shirts, lightweight fabrics |
| Production Time | Longer - requires more stitching | Faster - single pass stitch |
| Cost | Higher due to extra thread and labor | Lower - less thread, quicker execution |
Introduction to Double Needle vs Single Needle Stitch
Double needle stitch involves two parallel rows of stitching, enhancing garment durability and providing a clean, professional finish ideal for high-stress areas. Single needle stitch uses one row of stitching, offering a more refined and less bulky seam preferred for detailed or delicate fabrics. Understanding the differences in strength, appearance, and application is crucial for selecting the appropriate stitching method in apparel manufacturing.
Understanding Stitch Construction
Double needle stitch features two parallel rows of stitching, providing enhanced durability and a clean, symmetrical appearance ideal for high-stress areas like seams on denim jeans. Single needle stitch consists of one row of stitches, offering a refined, minimalist look with greater precision useful for detailed garment construction. Both stitch types use lockstitch techniques, but double needle stitching increases strength by distributing tension across two rows, reducing the risk of seam failure.
Appearance and Finish Differences
Double needle stitch features two parallel rows of stitching, providing a more durable and professional appearance, while single needle stitch has only one row, offering a cleaner but less reinforced finish. The double needle stitch creates a thicker seam that resists wear and adds visual depth, ideal for heavy-duty garments or visible areas. Your chosen stitch type affects not only the look but also the garment's strength and longevity.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Double needle stitch offers superior durability and strength compared to single needle stitch due to its two parallel rows of stitching, which distribute stress more evenly across the fabric. This technique is commonly used in high-stress areas of garments like jeans and workwear, enhancing resistance to wear and tear. Single needle stitch, while cleaner and more precise, provides less reinforcement, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Flexibility and Comfort in Wear
Double needle stitch provides enhanced durability and flexibility, making it ideal for garments requiring frequent movement and stretch. Single needle stitch offers a cleaner, more tailored appearance but with less give, which may limit comfort during extended wear. Your choice ultimately depends on whether you prioritize flexibility and long-term wear resistance or a sleek, refined finish.
Applications in Garment Production
Double needle stitch offers enhanced durability and is commonly used in high-stress areas of garments such as seams in jeans, activewear, and outerwear, providing reinforced strength and longevity. Single needle stitch is preferred for its precision and clean finish, often utilized in tailored garments, dress shirts, and delicate fabrics where appearance and fine detailing are crucial. Your choice between these stitches impacts the garment's durability and aesthetic, depending on whether reinforcement or a sleek look is prioritized during production.
Cost and Production Efficiency
Double needle stitch requires more thread and sewing time than single needle stitch, increasing overall production costs. Single needle stitch offers faster assembly with reduced labor input, enhancing production efficiency for high-volume manufacturing. While double needle stitch provides stronger seams ideal for durability, single needle stitch remains the cost-effective choice for rapid garment production.
Common Fabrics for Each Stitch Type
Single needle stitch is typically used for lightweight to medium-weight fabrics such as cotton, linen, and polyester blends, providing a clean and durable seam ideal for casual shirts and dresses. Double needle stitch is commonly employed on heavier or stretch fabrics like denim, knits, and fleece, offering reinforced strength and flexibility essential for activewear and denim jeans. Your choice between these stitch types should align with the fabric's weight and intended garment use to ensure optimal durability and appearance.
Pros and Cons of Double Needle Stitch
Double needle stitch offers enhanced durability and professional appearance, making it ideal for heavy-duty fabrics and garments requiring reinforced seams. However, it requires specialized machines and can increase production time and cost compared to single needle stitching. Single needle stitch, while faster and more cost-effective, may lack the strength and aesthetic finish provided by double needle stitch.
Pros and Cons of Single Needle Stitch
Single needle stitch offers superior durability and a cleaner, more professional finish compared to double needle stitch, making it ideal for high-quality garment construction. It allows for greater precision and less bulk, which improves comfort and appearance but may be less strong in heavy-duty applications. Your choice depends on the balance between aesthetic appeal and the required strength of the garment's seams.
Double Needle Stitch vs Single Needle Stitch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com