Digital sampling converts sound into binary data for precise editing and easy manipulation, enabling you to replicate or alter audio with high fidelity. Physical sampling involves capturing actual sound waves through microphones or sensors, preserving the natural character and nuances of the original sound source.
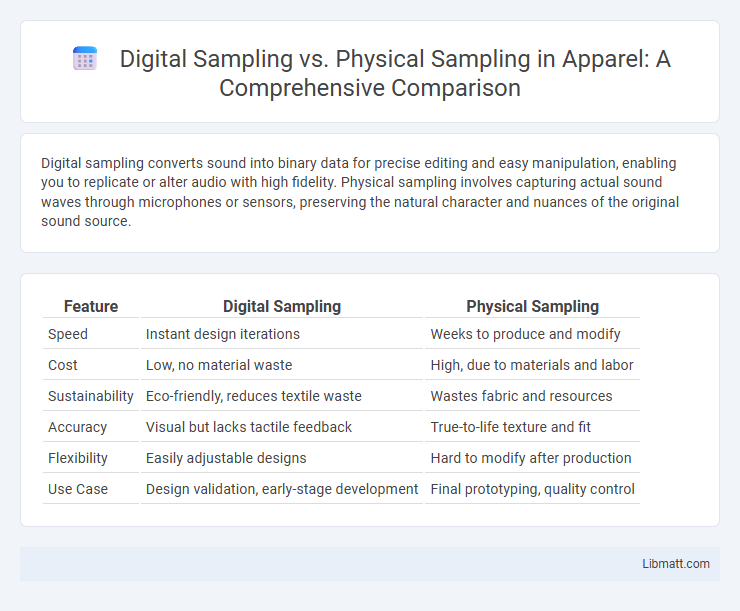
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Digital Sampling | Physical Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Instant design iterations | Weeks to produce and modify |
| Cost | Low, no material waste | High, due to materials and labor |
| Sustainability | Eco-friendly, reduces textile waste | Wastes fabric and resources |
| Accuracy | Visual but lacks tactile feedback | True-to-life texture and fit |
| Flexibility | Easily adjustable designs | Hard to modify after production |
| Use Case | Design validation, early-stage development | Final prototyping, quality control |
Introduction to Digital and Physical Sampling
Digital sampling captures audio signals by converting sound waves into binary data through analog-to-digital conversion, enabling precise editing and manipulation within digital audio workstations (DAWs). Physical sampling involves recording actual instruments or sounds in real acoustic environments using microphones, preserving the authentic timbre and spatial characteristics that digital methods may not fully replicate. Both techniques play pivotal roles in music production, with digital sampling offering flexibility and physical sampling providing organic sound quality.
Defining Digital Sampling
Digital sampling captures audio by converting sound waves into discrete numerical data, enabling precise manipulation and replication in digital audio workstations. Unlike physical sampling, which involves capturing sounds from tangible sources and analog equipment, digital sampling allows for instant editing, pitch shifting, and looping without degradation. This process underpins modern music production, sound design, and audio analysis by offering flexibility and high fidelity in sound reproduction.
Understanding Physical Sampling
Physical sampling involves capturing real-world sounds directly from instruments, environments, or objects using microphones and recording equipment, preserving the organic nuances and textures that digital sampling may not replicate accurately. This method enables musicians and producers to access authentic audio characteristics such as room acoustics, instrument resonance, and dynamic expression inherent in the original source. Understanding physical sampling is crucial for achieving high-quality, realistic sound reproduction in music production and sound design.
Core Differences Between Digital and Physical Sampling
Digital sampling captures sound waves through analog-to-digital conversion, creating editable, high-resolution audio files stored on computers, allowing precise manipulation of pitch, tempo, and effects. Physical sampling involves recording and reproducing sounds from tangible sources like vinyl records or drum machines, preserving the authentic analog warmth and texture. Your choice between digital and physical sampling depends on whether you prioritize flexibility and clarity or analog character and hands-on experience.
Advantages of Digital Sampling
Digital sampling offers precise and consistent sound reproduction, enabling musicians to manipulate audio with high fidelity and minimal degradation. This method provides extensive flexibility in editing, looping, and layering sounds, which enhances creative possibilities without the wear and tear experienced in physical sampling equipment. Your workflow benefits from the ease of storage, accessibility, and integration with software tools, making digital sampling a highly efficient and versatile choice.
Benefits of Physical Sampling
Physical sampling offers unparalleled sensory evaluation by allowing collectors and producers to experience the actual texture, aroma, and appearance of the product, leading to more accurate quality assessments. It enables firsthand verification of authenticity and condition, critical for industries like fashion, textiles, and food, where physical attributes directly impact consumer satisfaction. Furthermore, physical sampling facilitates tactile feedback and immediate experimentation, which digital simulations often cannot replicate with the same fidelity or precision.
Limitations of Digital Sampling
Digital sampling faces limitations such as finite bit depth and sample rate, which constrain audio resolution and frequency range, leading to potential loss of nuance and dynamic detail compared to physical sampling. It cannot fully capture the intricate sound variations and tactile interaction dynamics present in analog or acoustic sources, resulting in less authentic reproduction. Furthermore, digital artifacts like aliasing and quantization noise may degrade sound quality, highlighting the inherent challenges in purely digital audio representation.
Drawbacks of Physical Sampling
Physical sampling often faces limitations such as time-consuming setup, the high cost of acquiring and maintaining hardware, and the inability to easily manipulate or edit sounds once recorded. Environmental noise and inconsistencies during the recording process can degrade sample quality, affecting the accuracy and usability of the sound data. Storage and transportation of physical samples demand substantial space and can limit accessibility compared to digital counterparts.
Choosing the Right Sampling Method
Choosing the right sampling method depends on your project goals and resource availability. Digital sampling offers precision, flexibility, and ease of editing, making it ideal for electronic music production and sound design. Physical sampling captures authentic, organic sounds through real-world recordings, providing unique textures that enhance the realism of your work.
Future Trends in Sampling Technologies
Future trends in sampling technologies are shifting towards hybrid models that combine digital precision with the tactile authenticity of physical sampling, enhancing creative possibilities for producers. Advances in AI-driven algorithms are enabling more accurate and context-aware digital sampling, reducing the need for extensive physical libraries while maintaining sound fidelity. Your music production workflow will benefit from these innovations, offering faster, more flexible sampling options that adapt to evolving musical styles and production environments.
digital sampling vs physical sampling Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com