Heat setting stabilizes yarn or fabric by applying heat to lock in shape and prevent shrinkage, while calendering enhances surface smoothness and sheen through mechanical pressing between heated rollers. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize dimensional stability or a polished, glossy finish for the textile.
Table of Comparison
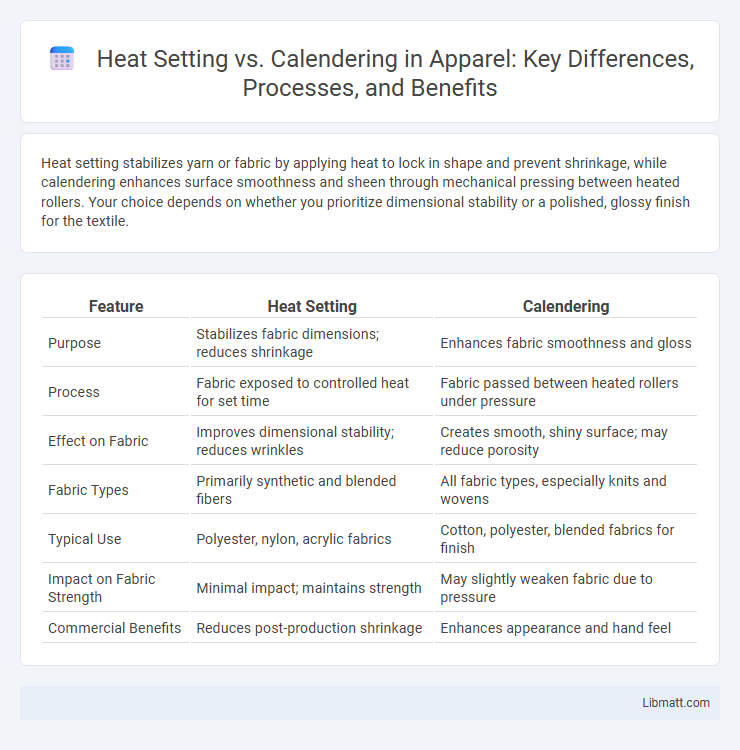
| Feature | Heat Setting | Calendering |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Stabilizes fabric dimensions; reduces shrinkage | Enhances fabric smoothness and gloss |
| Process | Fabric exposed to controlled heat for set time | Fabric passed between heated rollers under pressure |
| Effect on Fabric | Improves dimensional stability; reduces wrinkles | Creates smooth, shiny surface; may reduce porosity |
| Fabric Types | Primarily synthetic and blended fibers | All fabric types, especially knits and wovens |
| Typical Use | Polyester, nylon, acrylic fabrics | Cotton, polyester, blended fabrics for finish |
| Impact on Fabric Strength | Minimal impact; maintains strength | May slightly weaken fabric due to pressure |
| Commercial Benefits | Reduces post-production shrinkage | Enhances appearance and hand feel |
Introduction to Heat Setting and Calendering
Heat setting is a thermal process used to stabilize fibers and fabrics by exposing them to controlled heat, improving dimensional stability and resistance to shrinkage. Calendering involves passing fabric through heated rollers to enhance surface smoothness, sheen, and texture, often used in textile finishing. Both techniques optimize fabric performance but serve distinct purposes--heat setting for molecular stability and calendering for aesthetic enhancement.
What is Heat Setting?
Heat setting is a thermal process used to stabilize synthetic fibers like polyester by exposing them to high temperatures, which locks in their shape and dimensions. This method improves fabric durability, reduces shrinkage, and enhances wrinkle resistance, making it essential for producing high-quality textiles. Your fabric's performance and longevity significantly benefit from proper heat setting, ensuring consistent texture and dimensional stability.
What is Calendering?
Calendering is a mechanical process used in textile manufacturing where fabric or yarn passes between heated rollers to smooth, compress, and enhance surface finish. This technique improves fabric density, gloss, and texture, making materials more uniform and visually appealing. Calendering differs from heat setting, which primarily stabilizes synthetic fibers through controlled heat exposure to lock in shape and dimensions.
Key Differences Between Heat Setting and Calendering
Heat setting stabilizes synthetic fibers by heating them to a specific temperature, locking in shape and dimensional stability, while calendering involves passing fabrics through heated rollers to enhance smoothness, sheen, and fabric density. Heat setting primarily targets fiber performance and shrinkage control, whereas calendering modifies the fabric surface for aesthetic and tactile improvements. The processes differ in application stage, with heat setting applied post-fiber extrusion and calendering performed after fabric formation.
The Science Behind Heat Setting
Heat setting involves exposing fibers to controlled heat to stabilize their dimensions and improve fabric stability by altering the molecular structure, which reduces shrinkage and distortion. This process induces crystallization within synthetic fibers like polyester, enhancing tensile strength and wrinkle resistance through thermally-induced molecular rearrangement. Unlike calendering, which mechanically compresses fabric surfaces for smoothness and sheen, heat setting chemically fixes fiber morphology at a molecular level, producing long-lasting shape retention.
The Process of Calendering Explained
Calendering is a manufacturing process where fabric or other materials pass through a series of heated rollers to smooth, compress, or add gloss to the surface. This technique enhances material texture and appearance by applying controlled pressure and heat, resulting in a uniform finish that improves durability and aesthetic appeal. Your products benefit from calendering through improved fabric strength and a polished, professional look that heat setting alone cannot achieve.
Advantages of Heat Setting
Heat setting enhances dimensional stability and improves wrinkle resistance in synthetic fabrics by applying controlled heat and tension during processing. This process also increases fabric strength and maintains shape retention, which is essential for high-performance textiles. Compared to calendering, heat setting provides longer-lasting structural improvements without compromising fabric softness.
Benefits of Calendering
Calendering enhances fabric quality by producing a smooth, glossy surface that improves visual appeal and tactile softness. This process increases fabric density and uniformity, resulting in improved durability and resistance to abrasion. Your textiles benefit from enhanced dimensional stability and an overall premium finish that boosts market value.
Choosing Between Heat Setting and Calendering
Choosing between heat setting and calendering depends on your fabric's end-use requirements, such as dimensional stability and surface smoothness. Heat setting stabilizes synthetic fibers by applying controlled heat and tension, preventing shrinkage and distortion, while calendering uses pressure and heat to produce a smooth, glossy finish on the fabric surface. Understanding these processes enables you to optimize fabric performance and aesthetics for your specific textile application.
Conclusion: Heat Setting vs Calendering
Heat setting stabilizes synthetic fibers by applying controlled heat to lock in dimensional stability and reduce shrinkage, essential for maintaining fabric shape during use. Calendering enhances fabric surface properties, such as smoothness, luster, and thickness, by passing material through heated rollers under pressure, improving aesthetic appeal and hand feel. Choosing between heat setting and calendering depends on desired outcomes--durability and dimensional control versus surface finish and texture enhancement in textile processing.
Heat Setting vs Calendering Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com