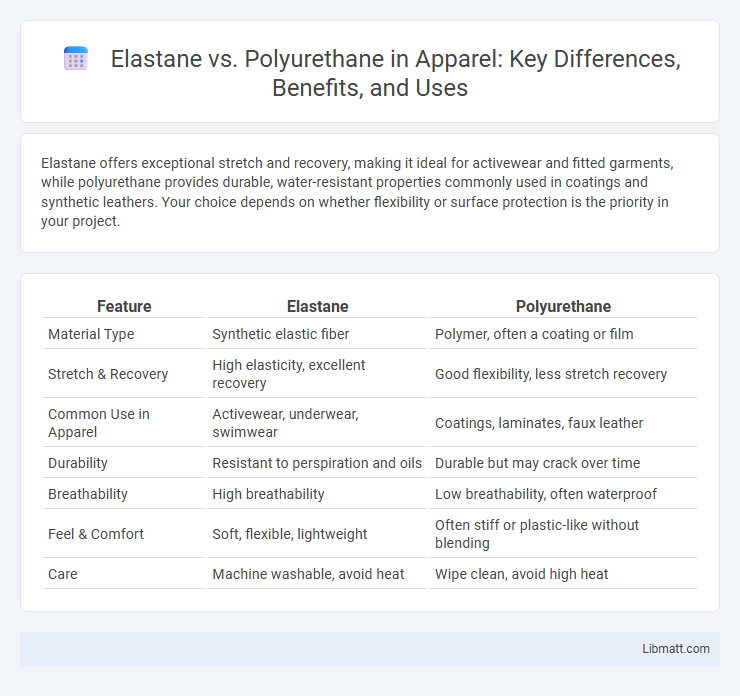
Elastane offers exceptional stretch and recovery, making it ideal for activewear and fitted garments, while polyurethane provides durable, water-resistant properties commonly used in coatings and synthetic leathers. Your choice depends on whether flexibility or surface protection is the priority in your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elastane | Polyurethane |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic elastic fiber | Polymer, often a coating or film |
| Stretch & Recovery | High elasticity, excellent recovery | Good flexibility, less stretch recovery |
| Common Use in Apparel | Activewear, underwear, swimwear | Coatings, laminates, faux leather |
| Durability | Resistant to perspiration and oils | Durable but may crack over time |
| Breathability | High breathability | Low breathability, often waterproof |
| Feel & Comfort | Soft, flexible, lightweight | Often stiff or plastic-like without blending |
| Care | Machine washable, avoid heat | Wipe clean, avoid high heat |
Introduction to Elastane and Polyurethane
Elastane, also known as spandex or Lycra, is a synthetic fiber renowned for its exceptional elasticity and ability to stretch up to five times its original length, making it a popular choice in textile manufacturing for activewear and form-fitting garments. Polyurethane is a versatile polymer used in a wide range of applications including coatings, adhesives, and flexible foams, valued for its durability, abrasion resistance, and waterproof properties. While elastane primarily serves as a stretchable fabric component, polyurethane functions as both a protective coating and structural material, contributing significantly to comfort and performance in clothing and industrial products.
Chemical Composition: Elastane vs Polyurethane
Elastane is a synthetic fiber composed of long-chain polymers called polyurethane, created through a chemical reaction between diisocyanates and polyols. Polyurethane, as a versatile polymer, can exist in various forms including flexible foams, rigid plastics, and elastomeric fibers like elastane. Elastane's chemical structure specifically features segmented polyurethane chains that provide exceptional elasticity and durability compared to generic polyurethane materials.
Production Process Differences
Elastane is produced through a polyaddition reaction between diisocyanates and polyols, resulting in long, elastic polymer chains primarily used in textiles for stretchability. In contrast, polyurethane encompasses a broader category of polymers formed by reacting polyols with diisocyanates but can be tailored for flexible foams, coatings, adhesives, or rigid plastics. Your choice between elastane and polyurethane depends on the desired elasticity and manufacturing complexity, as elastane requires precise control over chain length and crystallinity in fiber production.
Physical Properties Comparison
Elastane offers exceptional elasticity with a stretch ratio of up to 600%, making it ideal for flexible and form-fitting garments. Polyurethane features high abrasion resistance and durability, often used in coatings and synthetic leather due to its toughness and resistance to water and chemicals. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize stretch and comfort (elastane) or strength and resilience (polyurethane).
Key Applications in Textiles and Beyond
Elastane excels in activewear, swimwear, and hosiery due to its exceptional stretch and recovery properties, providing comfort and fit for dynamic movement. Polyurethane, often used in coatings, adhesives, and synthetic leather, offers durability, water resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for outerwear and upholstery applications. Your choice between elastane and polyurethane depends on the balance you need between elasticity and protective surface qualities in textiles and other material uses.
Durability and Performance Analysis
Elastane offers superior elasticity and breathability, making it highly durable for activewear and stretch garments, while polyurethane provides excellent water resistance and abrasion protection ideal for outerwear and protective gear. The performance of elastane excels in flexibility and recovery after stretching, whereas polyurethane stands out for its toughness and resistance to environmental factors like moisture and chemicals. Both materials are engineered for durability, but elastane suits dynamic movement applications, and polyurethane is preferred for long-lasting barrier protection.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Elastane, commonly used in stretchable textiles, poses sustainability challenges due to its synthetic origin and non-biodegradability, contributing to microplastic pollution. Polyurethane, often applied in coatings and foams, varies in environmental impact depending on production methods, with bio-based alternatives offering reduced carbon footprints. Your choice between these materials can influence environmental outcomes, emphasizing the importance of selecting sustainably sourced or recycled options to minimize ecological harm.
Cost and Market Availability
Elastane is generally more cost-effective and widely available in global textile markets due to its extensive use in apparel manufacturing, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious producers. Polyurethane, while more expensive, offers superior versatility and durability, leading to niche applications primarily in high-performance or specialized products. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with the material properties needed for your specific project.
Consumer Preferences and Industry Trends
Consumers favor elastane for its superior stretch and comfort in activewear and casual clothing, while polyurethane is preferred in performance gear and outerwear for its durability and waterproof properties. Industry trends reveal a shift towards sustainable alternatives, with manufacturers blending elastane with recycled fibers or developing bio-based polyurethane to reduce environmental impact. Your choice between these materials depends on the balance of flexibility, durability, and eco-friendliness required for the intended use.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Elastane and Polyurethane
Elastane offers exceptional elasticity and breathability, making it ideal for activewear and garments requiring stretch and comfort. Polyurethane provides superior durability and water resistance, commonly used in coatings and outerwear for protection and longevity. Your choice depends on prioritizing flexibility and comfort with elastane or durability and weather resistance with polyurethane.
Elastane vs polyurethane Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com