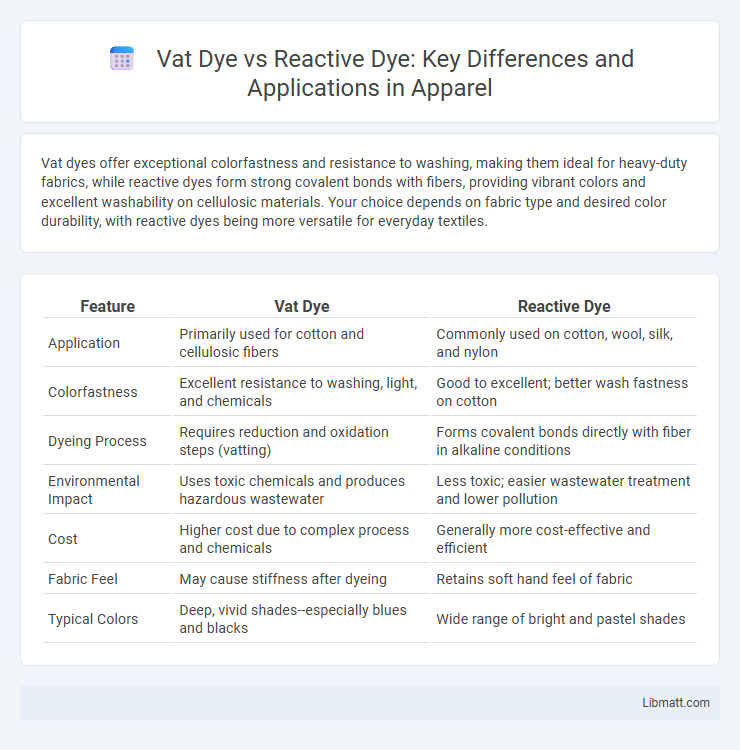
Vat dyes offer exceptional colorfastness and resistance to washing, making them ideal for heavy-duty fabrics, while reactive dyes form strong covalent bonds with fibers, providing vibrant colors and excellent washability on cellulosic materials. Your choice depends on fabric type and desired color durability, with reactive dyes being more versatile for everyday textiles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vat Dye | Reactive Dye |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Primarily used for cotton and cellulosic fibers | Commonly used on cotton, wool, silk, and nylon |
| Colorfastness | Excellent resistance to washing, light, and chemicals | Good to excellent; better wash fastness on cotton |
| Dyeing Process | Requires reduction and oxidation steps (vatting) | Forms covalent bonds directly with fiber in alkaline conditions |
| Environmental Impact | Uses toxic chemicals and produces hazardous wastewater | Less toxic; easier wastewater treatment and lower pollution |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex process and chemicals | Generally more cost-effective and efficient |
| Fabric Feel | May cause stiffness after dyeing | Retains soft hand feel of fabric |
| Typical Colors | Deep, vivid shades--especially blues and blacks | Wide range of bright and pastel shades |
Introduction to Vat Dyes and Reactive Dyes
Vat dyes are insoluble pigments that require a chemical reduction process to become soluble for fabric dyeing, providing excellent colorfastness on cotton and other cellulose fibers. Reactive dyes form covalent bonds with fiber molecules, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting colors primarily used for cellulose textiles such as cotton and linen. The choice between vat and reactive dyes depends on the desired color durability, fabric type, and application method.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Vat dyes are characterized by their insoluble, large, polycyclic aromatic structures, which require reduction in an alkaline solution to become soluble and bond with fibers. Reactive dyes contain functional groups like halogens or vinyl sulfone that chemically react with cellulose fibers, forming covalent bonds through nucleophilic substitution or addition reactions. Understanding the chemical composition and structure of these dyes helps you select the appropriate dye type for fabric compatibility and desired fastness properties.
Dyeing Process Comparison
Vat dyeing involves a complex reduction-oxidation process where the dye is first reduced to a soluble form, absorbed by the fabric, and then oxidized to its insoluble form, providing excellent colorfastness and durability. Reactive dyeing attaches dye molecules covalently to the fiber, typically requiring alkaline conditions and fixation through heat or time, resulting in vibrant colors ideal for cellulose fibers like cotton. Your choice between vat and reactive dyes depends on the required durability, fabric type, and specific application needs in the dyeing process.
Color Fastness Properties
Vat dyes exhibit exceptional color fastness properties, including high resistance to washing, light, and chemicals, making them ideal for fabrics exposed to harsh conditions. Reactive dyes also offer good color fastness, particularly to washing and light, due to their strong covalent bonding with cellulose fibers in cotton and other plant-based textiles. However, vat dyes generally outperform reactive dyes in terms of longevity and durability, especially on cellulosic fibers.
Application Methods and Techniques
Vat dyes require a reduction process to become soluble before application, commonly used in padding, batch, or continuous dyeing techniques suitable for cellulose fibers. Reactive dyes form covalent bonds with fibers through direct application methods like exhaust, continuous, or printing techniques, offering vibrant colors and excellent wash fastness. Your choice between vat and reactive dyes influences the dyeing equipment and process control needed to achieve desired color results on textiles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vat dyes exhibit high colorfastness but involve hazardous chemicals and generate toxic effluents, posing significant environmental challenges. Reactive dyes offer better ecological profiles with lower water pollution and less chemical usage due to covalent bonding with fibers, enhancing sustainability in textile processing. Sustainable dyeing practices increasingly favor reactive dyes, utilizing advanced wastewater treatment and reduced resource consumption to minimize environmental impact.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Vat dyes typically have higher initial costs due to their complex application process and specialized equipment requirements, but they offer superior colorfastness and durability, making them cost-effective for long-term use in industrial textile production. Reactive dyes, while generally less expensive and easier to apply on cellulose fibers like cotton, may require additional treatments to achieve similar wash fastness, potentially increasing overall expenditure. Choosing between vat and reactive dyes depends on balancing upfront costs with desired product longevity and color quality in economic assessments.
Fabric Compatibility
Vat dyes are primarily compatible with cellulose fibers such as cotton and flax due to their insoluble nature and need for reduction and oxidation processes. Reactive dyes offer broader fabric compatibility, bonding chemically with cellulose, wool, silk, and nylon, providing vibrant colors and good wash fastness. Fabric selection depends on the dye's chemical affinity, with reactive dyes favored for versatility across diverse textiles.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Vat dyes offer excellent colorfastness and resistance to washing, making them ideal for heavy-duty fabrics, but their complex application process and use of harsh chemicals can be time-consuming and environmentally challenging. Reactive dyes provide vibrant colors with better fixation on cotton and other cellulosic fibers, allowing for simpler application and lower water usage, though they tend to have lower wash fastness compared to vat dyes. Understanding the balance between durability and application ease helps you choose the right dye for your textile projects.
Choosing Between Vat Dye and Reactive Dye
Choosing between vat dye and reactive dye depends on your fabric type and desired durability; vat dyes excel on cotton and provide excellent wash and light fastness, making them ideal for long-lasting color. Reactive dyes chemically bond with cellulose fibers, offering bright, vivid colors and suitability for a wide range of fabrics, including cotton and blends, while ensuring easy application and softer hand feel. Your decision should consider the end-use, cost, and environmental impact, with reactive dyes often preferred for faster processing and vat dyes favored for superior color fastness.
Vat dye vs reactive dye Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com