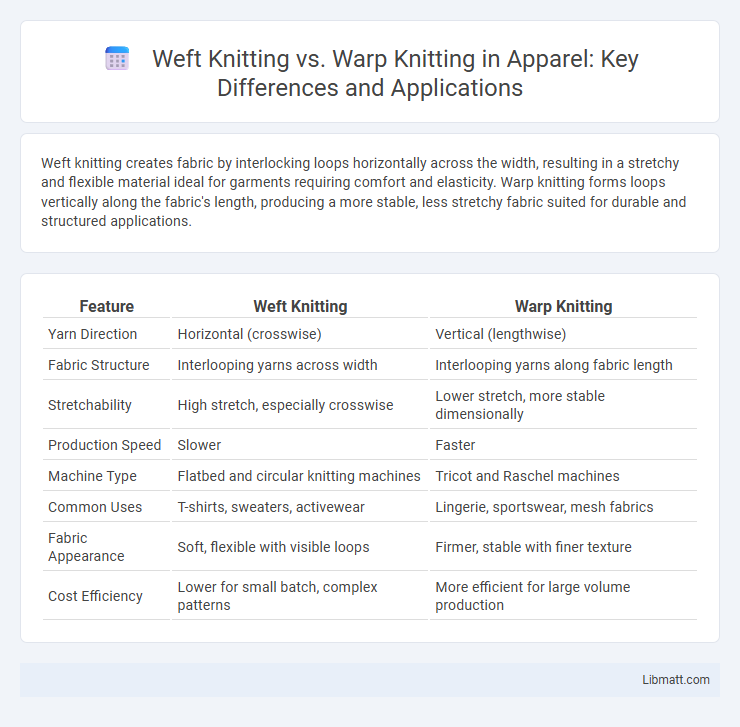
Weft knitting creates fabric by interlocking loops horizontally across the width, resulting in a stretchy and flexible material ideal for garments requiring comfort and elasticity. Warp knitting forms loops vertically along the fabric's length, producing a more stable, less stretchy fabric suited for durable and structured applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Weft Knitting | Warp Knitting |
|---|---|---|
| Yarn Direction | Horizontal (crosswise) | Vertical (lengthwise) |
| Fabric Structure | Interlooping yarns across width | Interlooping yarns along fabric length |
| Stretchability | High stretch, especially crosswise | Lower stretch, more stable dimensionally |
| Production Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Machine Type | Flatbed and circular knitting machines | Tricot and Raschel machines |
| Common Uses | T-shirts, sweaters, activewear | Lingerie, sportswear, mesh fabrics |
| Fabric Appearance | Soft, flexible with visible loops | Firmer, stable with finer texture |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower for small batch, complex patterns | More efficient for large volume production |
Introduction to Weft and Warp Knitting
Weft knitting involves creating fabric by interlocking loops horizontally across the width, making it highly stretchable and suitable for garments requiring flexibility. Warp knitting forms loops vertically along the fabric's length, resulting in more stable and less elastic textiles ideal for industrial and technical applications. Understanding the basic loop formation in weft and warp knitting highlights their distinct structural qualities and use cases in textile manufacturing.
Fundamental Differences Between Weft and Warp Knitting
Weft knitting involves interlocking loops horizontally across the fabric, creating a flexible and stretchable material ideal for garments that require comfort and elasticity. Warp knitting, by contrast, forms loops vertically along the length of the fabric, producing a more stable and less stretchy textile suited for durable applications such as sportswear and lingerie. Your choice between weft and warp knitting directly influences fabric performance characteristics like elasticity, strength, and texture based on loop orientation and knitting technique.
Yarn Pathways: Weft vs. Warp Knitting Techniques
Weft knitting involves yarns that run horizontally, interlooping across the fabric width, allowing flexibility and stretch, commonly found in t-shirts and sweaters. Warp knitting features yarns that run vertically, creating loops along the fabric length with higher speed and stability, ideal for industrial applications such as lingerie and automotive textiles. The distinct yarn pathways in weft and warp knitting directly influence fabric characteristics like elasticity, strength, and production efficiency.
Machine Types Used in Weft and Warp Knitting
Weft knitting primarily uses circular and flat knitting machines, which produce fabric by interlooping yarns horizontally, offering flexibility and versatility for various textile applications. Warp knitting employs machines like tricot and raschel knitting machines, designed to create fabric by interlooping yarns vertically for enhanced strength and stability, commonly used in technical textiles and lingerie. The distinct machine types in weft and warp knitting optimize production efficiency and fabric characteristics specific to their structural differences.
Fabric Structure and Characteristics
Weft knitting produces fabrics with horizontal loops intermeshed across the width, resulting in greater elasticity and softness ideal for stretchable garments like T-shirts and sweaters. Warp knitting forms vertical loops along the fabric's length, creating a stable, less stretchy structure often used in lingerie and sportswear for durability and shape retention. Understanding these fabric characteristics helps you choose the right knit for your apparel needs based on flexibility and strength.
Common Applications and End Uses
Weft knitting is commonly used in producing garments like T-shirts, sweaters, and socks due to its flexibility and stretchability, making it ideal for comfortable everyday wear. Warp knitting finds applications in lingerie, sportswear, and technical textiles where durability and stability are crucial. Your choice between weft and warp knitting depends on the specific performance requirements and end-use functionality of the fabric.
Strengths and Limitations of Weft Knitting
Weft knitting offers excellent elasticity and comfort, making it ideal for garments requiring stretch and flexibility, such as t-shirts and activewear. However, its structure tends to be less stable and durable compared to warp knitting, with a higher susceptibility to runs and deformation under stress. While weft knitting allows for easy fabric shaping and diverse stitch patterns, it is limited in producing high-strength technical textiles where dimensional stability is crucial.
Strengths and Limitations of Warp Knitting
Warp knitting offers superior fabric stability and resistance to runs compared to weft knitting due to its vertical loop structure, making it ideal for industrial applications and durable textiles. This method enables faster production speeds and the creation of complex, multi-layered fabrics but is limited in stretchability and design flexibility compared to weft knitting. Warp knit fabrics typically exhibit higher dimensional stability and reduced elongation, which restricts their use in garments requiring significant elasticity or drape.
Cost and Production Efficiency Comparison
Weft knitting generally offers lower production costs due to simpler machinery and faster setup times, making it ideal for small to medium runs. Warp knitting, while requiring higher initial investment and more complex equipment, excels in production efficiency for large-scale manufacturing with consistent fabric quality. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints against volume demands and fabric specifications.
Choosing Between Weft and Warp Knitting: Key Considerations
Choosing between weft knitting and warp knitting depends on fabric stretch, production speed, and application requirements. Weft knitting offers greater elasticity, making it ideal for garments requiring flexibility, while warp knitting provides higher dimensional stability and faster manufacturing suitable for industrial textiles. Evaluating factors such as desired texture, durability, and end-use performance is essential to determine the optimal knitting method.
Weft Knitting vs Warp Knitting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com