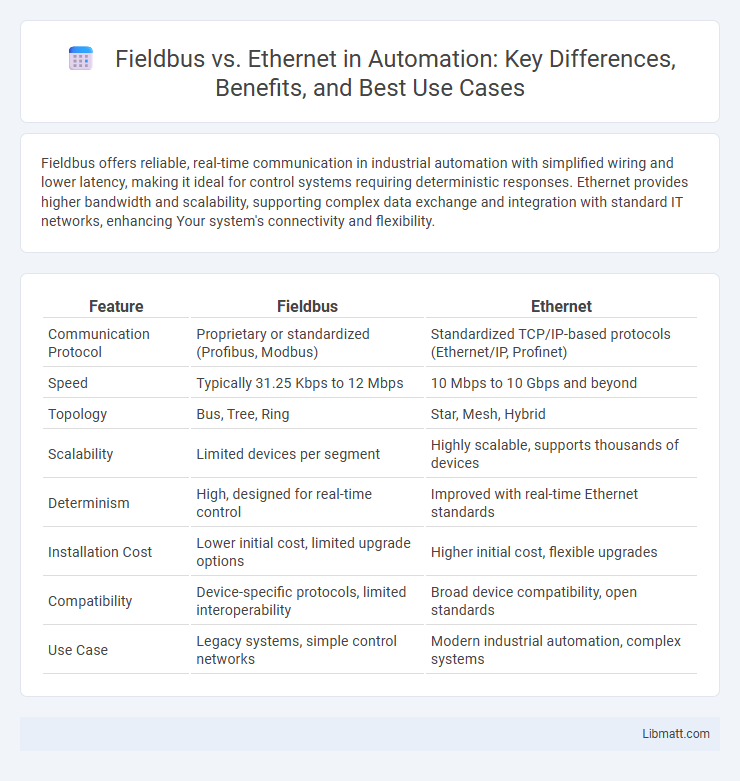
Fieldbus offers reliable, real-time communication in industrial automation with simplified wiring and lower latency, making it ideal for control systems requiring deterministic responses. Ethernet provides higher bandwidth and scalability, supporting complex data exchange and integration with standard IT networks, enhancing Your system's connectivity and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fieldbus | Ethernet |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Protocol | Proprietary or standardized (Profibus, Modbus) | Standardized TCP/IP-based protocols (Ethernet/IP, Profinet) |
| Speed | Typically 31.25 Kbps to 12 Mbps | 10 Mbps to 10 Gbps and beyond |
| Topology | Bus, Tree, Ring | Star, Mesh, Hybrid |
| Scalability | Limited devices per segment | Highly scalable, supports thousands of devices |
| Determinism | High, designed for real-time control | Improved with real-time Ethernet standards |
| Installation Cost | Lower initial cost, limited upgrade options | Higher initial cost, flexible upgrades |
| Compatibility | Device-specific protocols, limited interoperability | Broad device compatibility, open standards |
| Use Case | Legacy systems, simple control networks | Modern industrial automation, complex systems |
Introduction to Fieldbus and Ethernet
Fieldbus and Ethernet are industrial communication protocols designed to connect automation devices and control systems efficiently. Fieldbus operates as a real-time, deterministic network widely used in process automation for reliable device-level communication, while Ethernet provides high-speed data transfer and broad compatibility with IT infrastructure. Your choice between Fieldbus and Ethernet depends on factors like system complexity, required data speed, and integration needs.
Key Differences Between Fieldbus and Ethernet
Fieldbus systems use serial communication protocols designed for real-time, deterministic industrial automation, providing reliable control over short distances with lower bandwidth. Ethernet offers higher data transfer speeds and greater network flexibility with TCP/IP protocols, enabling integration of industrial devices with enterprise IT systems. Your choice depends on whether priority is real-time control and simplicity (Fieldbus) or scalability and high-speed communication (Ethernet).
Communication Protocols Overview
Fieldbus and Ethernet represent distinct industrial communication protocols designed for data exchange in automation systems. Fieldbus protocols such as Profibus, DeviceNet, and Foundation Fieldbus operate on determinism and real-time control principles, optimizing performance for sensor and actuator communications within constrained networks. Ethernet protocols, including EtherNet/IP and Profinet, provide high-speed, scalable, and flexible networking options suited for integration with enterprise IT systems and broader automation environments, offering seamless data handling for complex industrial operations. Your choice between these protocols depends on network requirements, device compatibility, and system architecture.
Network Topologies and Architectures
Fieldbus networks typically employ bus or tree topologies allowing straightforward device connections with deterministic communication ideal for real-time industrial automation. Ethernet networks use star or hierarchical topologies supporting high-speed data transfer and flexible architectures that scale from small local area networks to extensive enterprise systems. The deterministic control of Fieldbus contrasts with Ethernet's adaptability, making each suited to different layers of industrial network hierarchies.
Speed and Data Transmission Rates
Ethernet offers significantly higher speeds and data transmission rates compared to traditional Fieldbus systems, with standard Ethernet supporting up to 1 Gbps and advanced variations reaching 10 Gbps or more. Fieldbus protocols typically operate at lower speeds, ranging from 31.25 kbps to 12 Mbps, optimized for control and automation tasks with deterministic communication. Ethernet's superior bandwidth enables faster data exchange and supports complex industrial applications requiring high-volume, real-time data processing.
Scalability and Flexibility
Fieldbus systems typically offer limited scalability due to fixed network topologies and slower data transfer rates, restricting the number of connected devices and ease of expansion. Ethernet, leveraging its standardized protocols and high-speed connectivity, provides superior scalability by supporting a virtually unlimited number of devices and enabling flexible network segmentation and reconfiguration. Industrial Ethernet solutions like Profinet and EtherCAT enhance adaptability, allowing seamless integration of diverse devices and real-time data exchange critical for expanding automation systems.
Reliability and Determinism in Industrial Networks
Fieldbus networks offer high reliability and deterministic performance essential for time-critical industrial applications, ensuring predictable communication cycles and minimal latency. Ethernet, while traditionally less deterministic, has evolved with protocols like EtherCAT and PROFINET that enhance real-time capabilities and maintain robust network reliability. Your choice depends on the required balance between legacy compatibility and advanced high-speed deterministic communication.
Integration with Modern Automation Systems
Fieldbus systems offer reliable, deterministic communication suited for legacy and mid-sized automation networks, but Ethernet-based protocols provide superior scalability and bandwidth for integrating complex, data-intensive modern automation systems. Ethernet supports seamless connectivity with IoT devices, cloud platforms, and advanced analytics tools, enabling real-time data exchange critical for Industry 4.0 applications. The widespread adoption of Ethernet standards, such as EtherNet/IP and PROFINET, facilitates easier integration and future-proofing of industrial automation infrastructure.
Cost Implications and Maintenance
Fieldbus systems generally have lower initial hardware costs and simpler maintenance due to their dedicated communication protocols and fewer network components. Ethernet networks, while offering higher data rates and scalability, often incur higher installation expenses and require more complex maintenance involving IT expertise and regular software updates. The total cost of ownership for Ethernet may be justified by future-proofing and integration capabilities despite increased operational costs.
Choosing the Right Solution: Fieldbus vs Ethernet
Choosing the right solution between Fieldbus and Ethernet depends on your industrial network requirements, including speed, scalability, and real-time communication needs. Fieldbus offers reliable, deterministic communication ideal for smaller, slower control systems, while Ethernet provides higher bandwidth and flexibility suited for complex, data-intensive environments. Assess your system's complexity, integration needs, and future expansion plans to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
Fieldbus vs Ethernet Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com