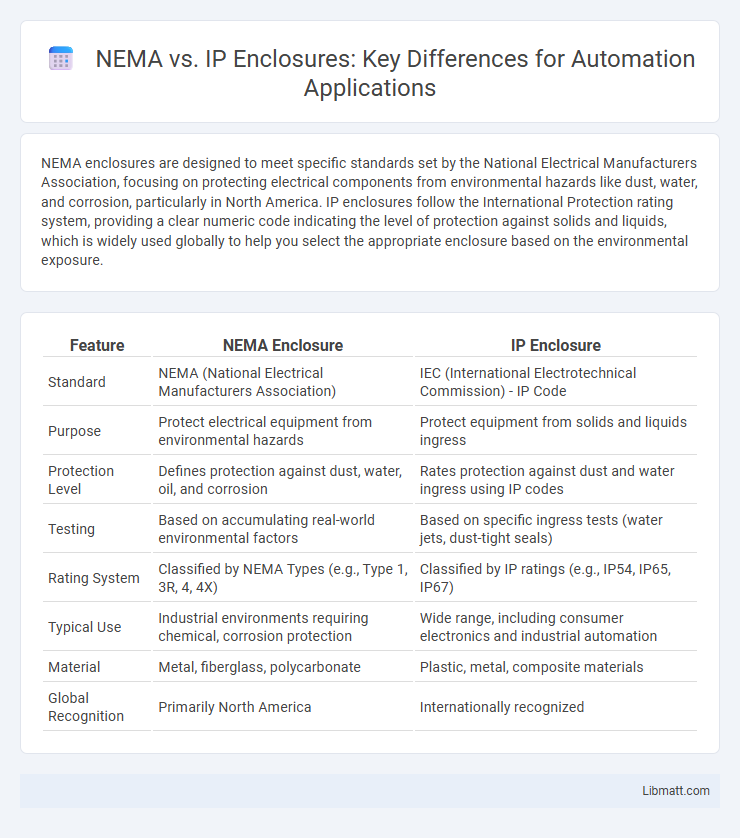
NEMA enclosures are designed to meet specific standards set by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, focusing on protecting electrical components from environmental hazards like dust, water, and corrosion, particularly in North America. IP enclosures follow the International Protection rating system, providing a clear numeric code indicating the level of protection against solids and liquids, which is widely used globally to help you select the appropriate enclosure based on the environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | NEMA Enclosure | IP Enclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) | IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) - IP Code |
| Purpose | Protect electrical equipment from environmental hazards | Protect equipment from solids and liquids ingress |
| Protection Level | Defines protection against dust, water, oil, and corrosion | Rates protection against dust and water ingress using IP codes |
| Testing | Based on accumulating real-world environmental factors | Based on specific ingress tests (water jets, dust-tight seals) |
| Rating System | Classified by NEMA Types (e.g., Type 1, 3R, 4, 4X) | Classified by IP ratings (e.g., IP54, IP65, IP67) |
| Typical Use | Industrial environments requiring chemical, corrosion protection | Wide range, including consumer electronics and industrial automation |
| Material | Metal, fiberglass, polycarbonate | Plastic, metal, composite materials |
| Global Recognition | Primarily North America | Internationally recognized |
Understanding NEMA and IP Enclosure Standards
NEMA enclosure standards classify protection levels based on environmental conditions such as dust, water, and corrosion resistance, primarily used in North American industrial applications. IP enclosure ratings, defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), quantify protection against solids and liquids through a two-digit code, widely accepted globally. Understanding these standards helps ensure proper equipment protection by matching enclosure capabilities to specific environmental hazards.
Key Differences Between NEMA and IP Ratings
NEMA enclosures primarily focus on protection against environmental hazards such as dust, water, oil, and corrosion, with specific performance criteria tailored to North American industrial standards. IP ratings, defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), classify enclosures based on protection against solid objects and water ingress using a two-digit numeric system. Key differences include NEMA's emphasis on durability and resistance to substances like oil and coolant, while IP ratings provide a more detailed, globally recognized scale measuring degrees of ingress protection against dust and water.
Applications of NEMA Enclosures
NEMA enclosures are designed for industrial environments requiring protection against harsh conditions such as dust, water, oil, and corrosion, making them ideal for manufacturing plants, chemical processing, and outdoor electrical installations. They are commonly used in applications involving heavy machinery, electrical panels, and control systems that demand robust protection and compliance with industry-specific standards like NEMA 4 and NEMA 12. The versatility of NEMA enclosures supports usage in food processing, wastewater treatment, and hazardous locations, ensuring equipment reliability and safety.
Common Uses for IP Enclosures
IP enclosures are primarily used in environments where protection against dust, water, and other liquids is critical, such as outdoor electrical installations, industrial automation, and marine applications. These enclosures are rated according to the Ingress Protection (IP) standard, which specifies the level of sealing effectiveness against intrusions from foreign bodies and moisture. Your choice of an IP enclosure ensures reliable safeguarding of sensitive equipment in harsh or wet conditions.
Environmental Protection: NEMA vs IP
NEMA enclosures offer distinct protection levels based on defined environmental conditions such as dust, water, oil, and corrosion resistance, with ratings ranging from Type 1 to Type 13. In contrast, IP enclosures use a two-digit code to specify protection against solids and liquids, where the first digit indicates dust ingress and the second denotes water ingress, with common ratings like IP65 and IP67. While NEMA focuses on broader environmental hazards including icing and oil immersion, IP ratings provide a more granular assessment of dust and water protection, making both standards complementary for selecting suitable enclosure protection.
Comparing Enclosure Construction Material
NEMA enclosures are primarily constructed from materials such as thermoplastic, stainless steel, and carbon steel, designed to provide robust protection against environmental hazards, including dust, water, and corrosion. IP enclosures, on the other hand, are rated based on their ingress protection level, with materials often ranging from ABS plastic to aluminum, focusing on sealing capabilities against solids and liquids rather than structural durability. Your choice between NEMA and IP enclosures should consider the specific environmental exposure and material strength required for optimal equipment safety.
Level of Dust and Water Protection
NEMA enclosures offer specific ratings for protection against dust, water, oil, and other environmental factors, with levels ranging from Type 1 (general purpose) to Type 13 (oil-tight and dust-tight). IP enclosures are rated using an ingress protection code, such as IP65 or IP68, where the first digit represents dust protection (ranging from 0 to 6) and the second digit indicates water protection (ranging from 0 to 9). Understanding your application's environment helps you select between NEMA's comprehensive standards and IP's internationally recognized dust and water resistance levels.
Cost Considerations: NEMA vs IP Enclosures
NEMA enclosures often have higher upfront costs due to their rigorous testing standards for protection against environmental factors such as dust, water, and corrosion. IP enclosures generally provide a cost-effective solution with clear ratings focused on ingress protection, making them suitable for specific applications where budget constraints exist. Your choice between NEMA and IP enclosures should consider not only initial costs but also long-term durability and compliance requirements.
Selecting the Right Enclosure for Your Needs
Selecting the right enclosure for your needs involves understanding the specific requirements of your environment and application. NEMA enclosures, rated by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, provide detailed protection standards against environmental hazards such as dust, water, and corrosion, making them ideal for industrial settings in North America. IP enclosures, defined by the International Protection Marking system, offer global standardization with clear protection levels against solids and liquids, allowing you to choose precise ingress resistance for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Industry Compliance and Certification Requirements
NEMA enclosures comply with standards set by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, focusing on protection against environmental hazards such as dust, water, and corrosion in North America. IP enclosures follow the international Ingress Protection (IP) rating system defined by IEC 60529, specifying degrees of protection against solids and liquids globally. Your choice between NEMA and IP enclosures depends on regional industry certification requirements and the specific environmental conditions your equipment will face.
NEMA Enclosure vs IP Enclosure Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com