PVDF coating offers superior durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting protection on metal surfaces exposed to harsh environments. Powder coating provides a cost-effective, versatile finish with excellent adhesion and a wide range of colors, perfect for projects where budget and aesthetics are key considerations.
Table of Comparison
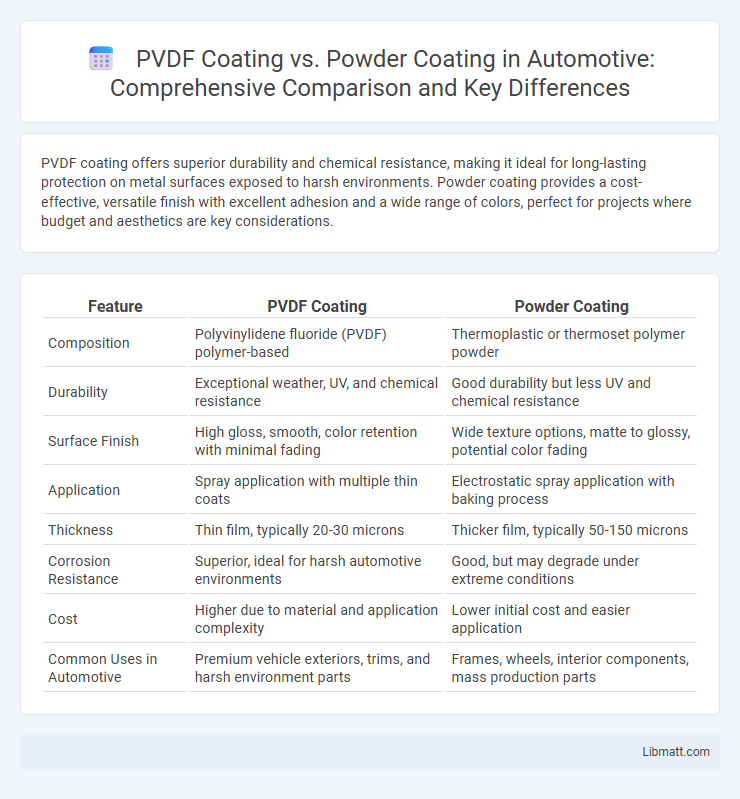
| Feature | PVDF Coating | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) polymer-based | Thermoplastic or thermoset polymer powder |
| Durability | Exceptional weather, UV, and chemical resistance | Good durability but less UV and chemical resistance |
| Surface Finish | High gloss, smooth, color retention with minimal fading | Wide texture options, matte to glossy, potential color fading |
| Application | Spray application with multiple thin coats | Electrostatic spray application with baking process |
| Thickness | Thin film, typically 20-30 microns | Thicker film, typically 50-150 microns |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior, ideal for harsh automotive environments | Good, but may degrade under extreme conditions |
| Cost | Higher due to material and application complexity | Lower initial cost and easier application |
| Common Uses in Automotive | Premium vehicle exteriors, trims, and harsh environment parts | Frames, wheels, interior components, mass production parts |
Introduction to PVDF Coating and Powder Coating
PVDF coating, composed of polyvinylidene fluoride resin, offers superior weather resistance, UV protection, and chemical durability, making it ideal for architectural applications and harsh environments. Powder coating uses dry powder, typically epoxy or polyester-based, applied electrostatically and cured under heat, providing a thick, uniform finish with excellent corrosion resistance and a wide range of colors. Both coatings enhance metal surfaces, but PVDF excels in long-term outdoor performance, while powder coating is favored for its cost-effectiveness and versatility in industrial uses.
Composition and Chemical Properties
PVDF coating consists of polyvinylidene fluoride, a highly non-reactive and pure thermoplastic fluoropolymer known for its superior resistance to UV radiation, chemicals, and corrosion. Powder coating, typically made from thermosetting polymers like epoxy or polyester, offers a thick, durable finish created by electrostatically applying and curing dry powder, which provides strong adhesion and impact resistance but may lack the same chemical resistance as PVDF. Your choice between PVDF and powder coating depends on the specific environmental exposure and durability requirements, with PVDF favored for long-term outdoor applications due to its exceptional chemical stability and weather resistance.
Application Methods and Processes
PVDF coating employs a liquid application process involving spray or roller methods followed by curing at high temperatures, ensuring a uniform, durable finish ideal for complex structures. Powder coating uses electrostatic spray deposition of dry powder particles that are subsequently cured in an oven, producing a tough, even layer suited for heavy-duty protection. Your choice depends on the substrate and desired finish quality, with PVDF favored for architectural aluminum and powder coating preferred for metal parts requiring robust abrasion resistance.
Durability and Weather Resistance
PVDF coating offers superior durability and weather resistance compared to powder coating, with exceptional UV resistance that prevents fading and chalking over time. Powder coatings provide good protection against corrosion and impact but may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to harsh weather conditions. Your choice should prioritize PVDF coatings for long-lasting performance in demanding outdoor environments.
Color and Finish Options
PVDF coatings offer superior color retention and UV resistance, maintaining vibrant finishes for over 20 years, making them ideal for exterior architectural applications. Powder coatings provide a wide range of colors and textures, including matte, gloss, and textured finishes, but generally exhibit less long-term color stability compared to PVDF. The smooth, high-performance finish of PVDF is often preferred for metal surfaces exposed to harsh weather conditions, while powder coatings excel in versatility and environmental friendliness.
Cost Comparison
PVDF coating generally incurs higher upfront costs due to its advanced chemical composition and application process, making it more expensive than standard powder coating. Powder coating offers a cost-effective alternative with lower material and application expenses, suitable for budget-sensitive projects requiring durable finishes. However, PVDF's superior weather resistance and longevity can reduce long-term maintenance costs, potentially offsetting the initial investment in applications exposed to harsh environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
PVDF coating offers superior environmental benefits due to its longer lifespan and excellent UV resistance, reducing the frequency of recoating and minimizing waste. Powder coating is free of solvents and emits negligible VOCs during application, promoting a low-impact manufacturing process. Choosing PVDF or powder coating depends on your priorities for durability and eco-friendly production methods.
Typical Uses and Industry Applications
PVDF coating is widely used in architectural applications, such as metal roofing, wall panels, and facades, due to its excellent weather resistance and color retention properties. Powder coating is commonly applied in automotive, appliance, and industrial equipment manufacturing, offering durability and a wide range of color options for metal surfaces. Your choice between PVDF and powder coating depends on specific industry requirements, including exposure conditions and aesthetic preferences.
Maintenance and Longevity
PVDF coating offers superior resistance to UV radiation, chemicals, and environmental pollutants, resulting in minimal maintenance and extended longevity compared to powder coating. Powder coating may require more frequent touch-ups and cleaning due to its susceptibility to chipping and fading over time. By choosing PVDF coating, you ensure your surfaces maintain their appearance and durability with less effort and longer-lasting protection.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Project
PVDF coating offers exceptional durability, UV resistance, and color retention, making it ideal for architectural metal surfaces exposed to harsh weather conditions. Powder coating provides a cost-effective, versatile finish with excellent corrosion resistance and environmental friendliness, suitable for various industrial and decorative applications. Selecting the right coating depends on project requirements such as exposure conditions, budget constraints, and desired aesthetic longevity.
Pvdf coating vs Powder coating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com