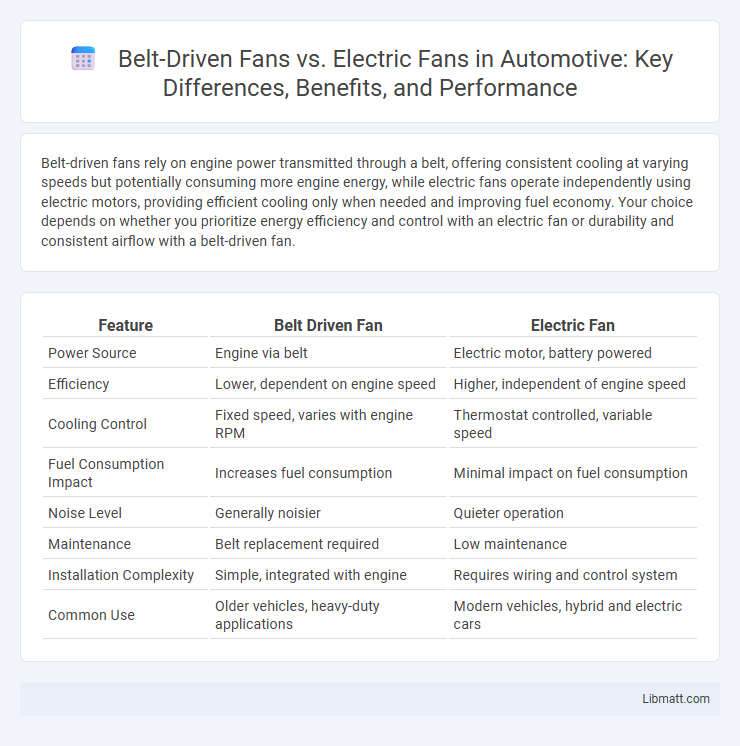
Belt-driven fans rely on engine power transmitted through a belt, offering consistent cooling at varying speeds but potentially consuming more engine energy, while electric fans operate independently using electric motors, providing efficient cooling only when needed and improving fuel economy. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize energy efficiency and control with an electric fan or durability and consistent airflow with a belt-driven fan.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Belt Driven Fan | Electric Fan |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Engine via belt | Electric motor, battery powered |
| Efficiency | Lower, dependent on engine speed | Higher, independent of engine speed |
| Cooling Control | Fixed speed, varies with engine RPM | Thermostat controlled, variable speed |
| Fuel Consumption Impact | Increases fuel consumption | Minimal impact on fuel consumption |
| Noise Level | Generally noisier | Quieter operation |
| Maintenance | Belt replacement required | Low maintenance |
| Installation Complexity | Simple, integrated with engine | Requires wiring and control system |
| Common Use | Older vehicles, heavy-duty applications | Modern vehicles, hybrid and electric cars |
Introduction to Belt Driven and Electric Fans
Belt driven fans use a motor connected by a belt to the fan blades, providing consistent airflow and durability in industrial applications. Electric fans have a motor directly attached to the blades, offering compact design and energy efficiency for residential and commercial use. Choosing the right fan depends on your specific airflow requirements and maintenance preferences.
How Belt Driven Fans Work
Belt driven fans operate through a mechanical system where a motor turns a pulley connected to the fan blades via a belt, transferring rotational energy efficiently. This design allows adjustable speed control and durability, especially in automotive cooling systems. You benefit from precise performance and quieter operation compared to electric fans, making belt driven fans ideal for heavy-duty applications.
How Electric Fans Operate
Electric fans operate using an electric motor that directly powers the fan blades, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to generate airflow. Unlike belt-driven fans that rely on belts and pulleys for motion transfer, electric fans provide more efficient and precise speed control through variations in motor speed. Their compact design, reduced maintenance, and energy efficiency make them suitable for diverse applications, from automotive cooling systems to household appliances.
Efficiency Comparison: Belt Driven vs Electric Fans
Belt driven fans typically offer greater durability and smooth operation but tend to be less energy-efficient due to mechanical losses in the belt system. Electric fans provide higher efficiency by directly converting electrical energy into airflow, reducing power consumption and maintenance needs. Your choice between the two should consider the balance between energy efficiency and long-term reliability in your specific application.
Maintenance Requirements
Belt driven fans require regular inspection and adjustment of belts to ensure proper tension and prevent wear, often necessitating occasional belt replacement and lubrication of moving parts. Electric fans demand less frequent maintenance, with periodic checks on motor function and electrical connections to avoid overheating or failure. Your choice between these fan types should consider the ease of maintaining belts versus the simplicity of servicing electric components.
Energy Consumption and Cost
Belt-driven fans typically consume more energy due to mechanical losses in the belt and pulley system, resulting in higher operational costs over time. Electric fans are generally more energy-efficient as they directly convert electrical energy into mechanical energy with minimal loss, reducing electricity bills. Choosing an electric fan for Your cooling needs ensures lower energy consumption and cost-effective performance.
Performance in Different Applications
Belt-driven fans excel in heavy-duty industrial applications requiring high airflow at lower speeds and can handle variable loads with durability and low maintenance. Electric fans offer superior efficiency and precise speed control, making them ideal for automotive cooling systems and environments demanding quick response and compact design. Performance in different applications hinges on factors like airflow requirements, energy consumption, space limitations, and noise levels.
Noise Levels and Vibration
Belt-driven fans typically produce higher noise levels and more vibration due to the mechanical friction and movement of the belt and pulleys, which can cause rattling and squeaking sounds. Electric fans generate less noise and vibration as their motors run smoothly without the need for belts, resulting in quieter and more stable operation. Noise reduction is critical in residential and office environments, making electric fans a preferred choice for minimizing acoustic disturbances.
Environmental Impact
Belt driven fans typically consume more energy due to mechanical friction losses and require regular maintenance that can lead to increased environmental waste. Electric fans are generally more energy-efficient, producing fewer emissions over their lifespan and reducing your carbon footprint. Choosing an electric fan supports sustainable energy use and lowers environmental impact compared to traditional belt driven systems.
Choosing the Right Fan for Your Needs
Belt driven fans provide durable, high airflow suitable for industrial applications where consistent performance and heavy-duty use are essential. Electric fans offer greater energy efficiency, quieter operation, and easier maintenance, making them ideal for residential or light commercial environments. Assess your space requirements, noise tolerance, and energy consumption to determine which fan type best matches your performance needs and budget.
belt driven fan vs electric fan Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com