A belt tensioner maintains proper tension on a belt-driven system, ensuring optimal performance and preventing slippage, while a chain tensioner adjusts the tension in a chain-driven mechanism to avoid slack and reduce wear. Understanding the difference between belt and chain tensioners helps you choose the right component for maintaining your vehicle or machinery's efficiency and longevity.
Table of Comparison
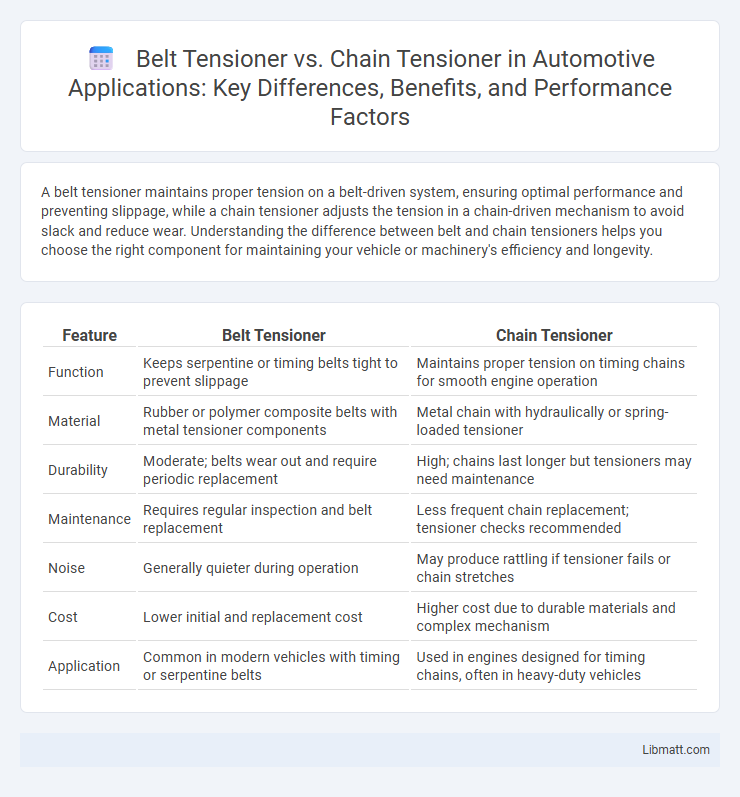
| Feature | Belt Tensioner | Chain Tensioner |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Keeps serpentine or timing belts tight to prevent slippage | Maintains proper tension on timing chains for smooth engine operation |
| Material | Rubber or polymer composite belts with metal tensioner components | Metal chain with hydraulically or spring-loaded tensioner |
| Durability | Moderate; belts wear out and require periodic replacement | High; chains last longer but tensioners may need maintenance |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection and belt replacement | Less frequent chain replacement; tensioner checks recommended |
| Noise | Generally quieter during operation | May produce rattling if tensioner fails or chain stretches |
| Cost | Lower initial and replacement cost | Higher cost due to durable materials and complex mechanism |
| Application | Common in modern vehicles with timing or serpentine belts | Used in engines designed for timing chains, often in heavy-duty vehicles |
Introduction to Belt and Chain Tensioners
Belt tensioners and chain tensioners are essential components in automotive and industrial machinery, ensuring optimal tension in belt and chain drives respectively to prevent slippage and wear. Belt tensioners use spring-loaded pulleys to maintain consistent pressure on the belt, while chain tensioners adjust the slack in the chain to improve performance and extend its lifespan. Understanding the differences in their operation helps you select the right tensioner for your specific mechanical system needs.
How Belt Tensioners Work
Belt tensioners use a spring-loaded arm to maintain constant pressure on the belt, ensuring optimal tension and preventing slippage in automotive engines. This mechanism automatically adjusts to belt wear and elongation, improving the efficiency and lifespan of the serpentine or timing belt system. Understanding how your belt tensioner works can help you identify premature wear and avoid costly repairs.
How Chain Tensioners Work
Chain tensioners maintain optimal tension in timing or drive chains by applying consistent pressure through a spring-loaded or hydraulic mechanism. This tension prevents slack, reducing chain vibration, noise, and premature wear, ensuring smooth engine or machinery operation. Unlike belt tensioners, chain tensioners adjust dynamically to accommodate chain elongation over time, maintaining precise alignment and performance.
Key Differences Between Belt and Chain Tensioners
Belt tensioners use springs or hydraulic mechanisms to maintain proper tension in serpentine or timing belts, ensuring smooth engine operation and reducing wear. Chain tensioners, commonly found in timing chain systems, apply precise pressure through hydraulic or mechanical means to prevent chain slack and maintain accurate timing. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right tensioner for optimal performance and longevity in your vehicle's engine system.
Advantages of Belt Tensioners
Belt tensioners provide smoother and quieter operation compared to chain tensioners, reducing noise and vibration in automotive engines. Their lightweight design contributes to improved fuel efficiency and lowers overall system weight. Maintenance is simplified with belt tensioners since they typically require less lubrication and exhibit less wear than chain tensioners.
Advantages of Chain Tensioners
Chain tensioners offer superior durability and longevity compared to belt tensioners due to their metal construction, which withstands higher stress and extreme temperatures. They maintain consistent tension over time, reducing slack and preventing chain skip, essential for precise timing and optimal engine performance. Your vehicle benefits from reduced maintenance intervals and enhanced reliability, making chain tensioners ideal for high-performance and heavy-duty applications.
Common Applications of Belt vs Chain Tensioners
Belt tensioners are commonly used in automotive engines to maintain proper tension on serpentine or timing belts, ensuring smooth operation of accessories like alternators, water pumps, and power steering pumps. Chain tensioners are frequently found in motorcycle engines, heavy-duty machinery, and internal combustion engines where timing chains require precise tension to avoid slack and maintain synchronization. Your choice between belt and chain tensioners depends on the application's need for flexibility, durability, and maintenance intervals.
Maintenance Requirements: Belt vs Chain Tensioners
Belt tensioners generally require less maintenance than chain tensioners due to the inherent durability and wear resistance of modern belts, which typically last longer without adjustment. Chain tensioners demand more frequent inspections and adjustments to prevent slack or over-tightening, which can lead to increased wear or failure of the chain and associated components. Understanding your system's tensioner type helps optimize maintenance schedules and extend the lifespan of your engine's timing mechanism.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Belt tensioners generally offer longer durability due to their smoother operation and resistance to corrosion, while chain tensioners tend to experience more wear from constant metal-on-metal contact. High-quality belt tensioners can last up to 100,000 miles, significantly outperforming chain tensioners that often require replacement closer to 60,000 miles. Your choice between the two should consider maintenance frequency and lifespan demands, with belt tensioners providing a more reliable, extended service life in most applications.
Choosing the Right Tensioner for Your System
Selecting the right tensioner depends on your system type and operational demands; belt tensioners are ideal for systems relying on flexible belts, offering easy maintenance and noise reduction, while chain tensioners are suited for heavy-duty applications requiring high durability and precise tension control. Consider factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and maintenance intervals when choosing between belt and chain tensioners to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper tensioner selection enhances system efficiency, reduces wear, and prevents premature component failure in industrial machinery and automotive engines.
Belt Tensioner vs Chain Tensioner Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com