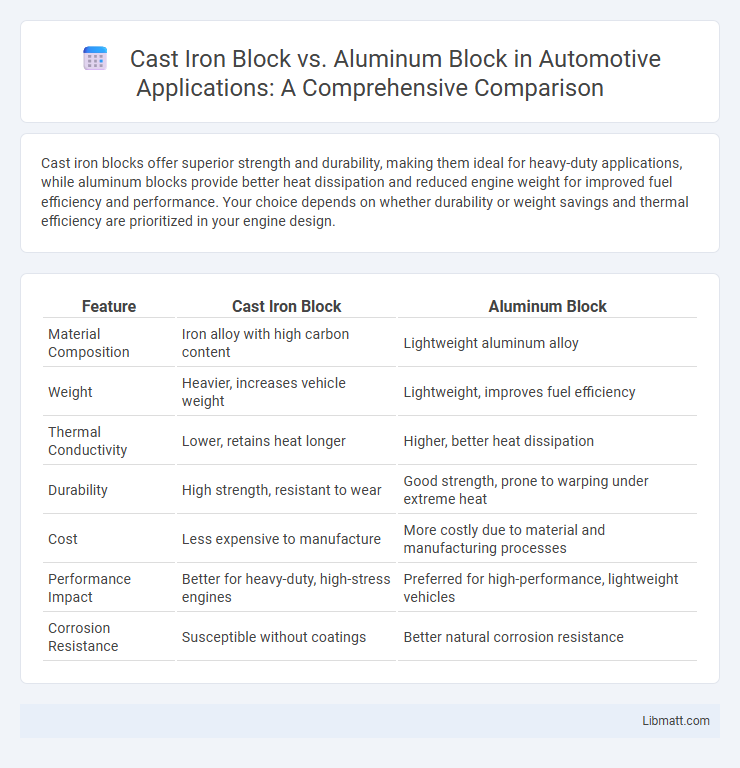
Cast iron blocks offer superior strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications, while aluminum blocks provide better heat dissipation and reduced engine weight for improved fuel efficiency and performance. Your choice depends on whether durability or weight savings and thermal efficiency are prioritized in your engine design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cast Iron Block | Aluminum Block |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Iron alloy with high carbon content | Lightweight aluminum alloy |
| Weight | Heavier, increases vehicle weight | Lightweight, improves fuel efficiency |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower, retains heat longer | Higher, better heat dissipation |
| Durability | High strength, resistant to wear | Good strength, prone to warping under extreme heat |
| Cost | Less expensive to manufacture | More costly due to material and manufacturing processes |
| Performance Impact | Better for heavy-duty, high-stress engines | Preferred for high-performance, lightweight vehicles |
| Corrosion Resistance | Susceptible without coatings | Better natural corrosion resistance |
Introduction to Engine Block Materials
Engine blocks are primarily constructed from cast iron or aluminum, each offering distinct advantages in durability and weight. Cast iron blocks provide exceptional strength and wear resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications and high-performance engines. Aluminum blocks deliver significant weight reduction, improving fuel efficiency and handling, while often incorporating iron cylinder liners to maintain durability.
What Is a Cast Iron Engine Block?
A cast iron engine block is a heavy-duty cylinder block made from molten cast iron, known for its exceptional strength and durability under high temperatures and pressures. This material provides superior wear resistance and rigidity, which makes it ideal for engines subjected to intense mechanical stress. Your choice of a cast iron block can influence engine longevity and heat retention, important factors in performance and reliability.
What Is an Aluminum Engine Block?
An aluminum engine block is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant component used in modern vehicles to improve fuel efficiency and performance. Compared to cast iron blocks, aluminum blocks dissipate heat more effectively, allowing your engine to operate at optimal temperatures and reduce the risk of overheating. The enhanced thermal conductivity and reduced weight make aluminum blocks a preferred choice for high-performance and fuel-efficient engines.
Weight Comparison: Cast Iron vs Aluminum
Aluminum engine blocks weigh approximately 40-60% less than cast iron blocks, significantly reducing the overall vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency. Cast iron blocks offer superior durability and heat retention but add substantial mass, which can hinder performance in lightweight vehicles. The weight difference between the two materials directly impacts acceleration, handling, and emissions, making aluminum blocks the preferred choice for modern engines focused on efficiency.
Strength and Durability Considerations
Cast iron blocks offer superior strength and durability due to their high tensile strength and resistance to wear, making them ideal for heavy-duty and high-stress engine applications. Aluminum blocks provide lighter weight and better heat dissipation but generally lack the same level of strength, potentially leading to reduced longevity under extreme conditions. Your choice between these materials will impact engine lifespan and performance based on the balance between strength requirements and weight savings.
Heat Dissipation and Thermal Efficiency
Aluminum blocks exhibit superior heat dissipation and thermal efficiency compared to cast iron blocks due to aluminum's high thermal conductivity, which allows the engine to cool faster and maintain optimal operating temperatures. Cast iron blocks, although more durable, retain heat longer, leading to slower cooling and potentially higher engine temperatures under heavy loads. This difference impacts overall engine performance and efficiency, with aluminum blocks better suited for maximizing thermal management in high-performance and lightweight applications.
Performance Impact on Vehicles
Cast iron blocks provide superior strength and durability, resulting in better resistance to wear and higher engine longevity, which is ideal for heavy-duty performance applications. Aluminum blocks offer lighter weight, improving vehicle acceleration, fuel efficiency, and handling by reducing overall engine mass. The choice between cast iron and aluminum blocks significantly influences thermal conductivity, with aluminum dissipating heat more efficiently, thus affecting engine cooling and performance stability.
Cost Differences Between Cast Iron and Aluminum
Cast iron engine blocks generally cost less to produce than aluminum blocks due to lower material costs and simpler manufacturing processes. Aluminum blocks, while more expensive upfront, offer weight savings that can improve fuel efficiency and performance, potentially offsetting initial expenses. The price difference often influences automakers' choices based on budget constraints and desired vehicle characteristics.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Cast iron blocks offer superior durability and resistance to wear due to their high strength and heat tolerance, requiring less frequent maintenance over time. Aluminum blocks provide better heat dissipation and lighter weight but may demand more careful upkeep to prevent corrosion and warping under high stress. Understanding these maintenance and longevity factors can help you choose the right engine block material to suit your performance needs and long-term reliability.
Choosing the Right Engine Block for Your Needs
Cast iron blocks offer superior durability and heat retention, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications and high-performance engines requiring enhanced strength. Aluminum blocks provide significant weight savings and improved heat dissipation, benefiting fuel efficiency and overall vehicle handling in daily driving scenarios. Selecting the right engine block depends on balancing durability needs with performance goals, where cast iron suits toughness and aluminum supports lightweight efficiency.
Cast iron block vs Aluminum block Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com