A chassis dyno measures the power output of a vehicle by testing the entire drivetrain including wheels, transmission, and differential, providing a realistic representation of real-world performance. An engine dyno isolates the engine itself to measure power and torque, offering precise data on engine performance without drivetrain losses, which helps you tune or diagnose the engine directly.
Table of Comparison
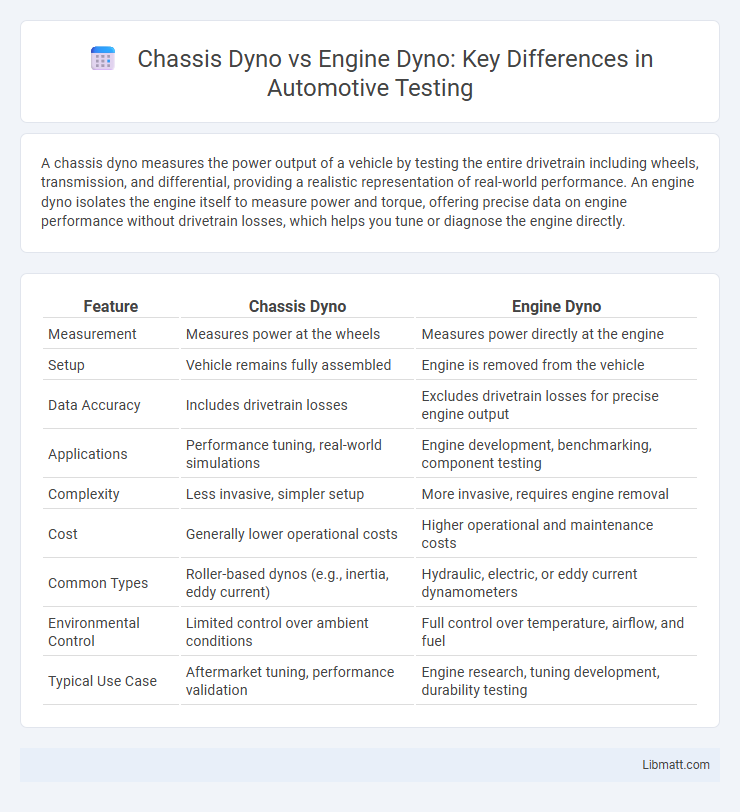
| Feature | Chassis Dyno | Engine Dyno |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Measures power at the wheels | Measures power directly at the engine |
| Setup | Vehicle remains fully assembled | Engine is removed from the vehicle |
| Data Accuracy | Includes drivetrain losses | Excludes drivetrain losses for precise engine output |
| Applications | Performance tuning, real-world simulations | Engine development, benchmarking, component testing |
| Complexity | Less invasive, simpler setup | More invasive, requires engine removal |
| Cost | Generally lower operational costs | Higher operational and maintenance costs |
| Common Types | Roller-based dynos (e.g., inertia, eddy current) | Hydraulic, electric, or eddy current dynamometers |
| Environmental Control | Limited control over ambient conditions | Full control over temperature, airflow, and fuel |
| Typical Use Case | Aftermarket tuning, performance validation | Engine research, tuning development, durability testing |
Introduction to Chassis Dyno and Engine Dyno
A chassis dyno measures the power output of a vehicle by testing the entire drivetrain, including the engine, transmission, and wheels, providing real-world performance data. An engine dyno isolates the engine from the vehicle, allowing precise measurement of engine power and torque under controlled conditions without drivetrain losses. Understanding the differences helps in selecting the appropriate testing method for tuning, diagnostics, or performance evaluation.
Understanding How a Chassis Dyno Works
A chassis dyno measures the power output of a vehicle by simulating road conditions while the entire car is mounted on rollers, capturing real-world performance data including drivetrain losses and tire behavior. Unlike an engine dyno, which tests the engine in isolation on a stand, a chassis dyno provides a comprehensive assessment of the vehicle's power delivery through the transmission and wheels. This method enables precise tuning and diagnostics by monitoring horsepower, torque, and RPM under dynamic operating conditions.
How an Engine Dyno Operates
An engine dyno operates by directly measuring the power output of an engine on a test stand, isolating it from the vehicle's drivetrain and chassis components. It uses precise sensors to capture data such as torque, RPM, and fuel consumption while the engine runs under controlled conditions, allowing accurate performance tuning and diagnostics. You benefit from detailed engine performance insights that help optimize efficiency and power before installation into a vehicle.
Key Differences Between Chassis Dyno and Engine Dyno
Chassis dynos measure the power output of a vehicle by testing the entire drivetrain, including wheels, tires, and transmissions, which provides real-world performance data under load conditions. Engine dynos directly assess the engine's power and torque on a test bench without drivetrain losses, offering precise tuning for engine components. Your choice depends on whether you need comprehensive vehicle testing or detailed engine-specific diagnostics.
Accuracy and Data Comparison
Chassis dynos measure power output at the wheels, accounting for drivetrain losses, providing real-world performance data, while engine dynos test the engine alone for precise torque and horsepower without external factors. Engine dynos offer higher accuracy for tuning internal engine components, whereas chassis dynos offer comprehensive data reflecting your vehicle's actual on-road performance. Choosing between them depends on whether you prioritize pure engine metrics or overall vehicle power delivery.
Advantages of Chassis Dyno Testing
Chassis dyno testing measures the total power output delivered to the wheels, providing a more accurate representation of real-world vehicle performance by accounting for drivetrain losses. This method allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of upgrades and modifications under various load conditions while running the complete vehicle system. It also supports testing of different vehicle setups without engine removal, saving time and preserving the integrity of your vehicle.
Benefits of Engine Dyno Testing
Engine dyno testing offers precise measurement of engine power and torque under controlled conditions, allowing for accurate tuning and performance optimization. It isolates the engine from drivetrain losses and variables, providing detailed insights into engine efficiency and combustion characteristics. Your ability to identify issues early and enhance engine durability makes engine dyno testing invaluable for maximizing engine performance and reliability.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Dyno
Chassis dynos face limitations such as drivetrain losses and tire slip, which can distort power readings and reduce measurement accuracy. Engine dynos encounter challenges including the need for complete engine removal, complex setup, and lack of real-world load simulation affecting performance data relevance. Understanding your specific testing goals helps determine whether the drivetrain-inclusive chassis dyno or the controlled environment of an engine dyno is more suitable.
Choosing the Right Dyno for Your Needs
Selecting the right dyno depends on your testing goals and vehicle setup; chassis dynos measure power at the wheels, accounting for drivetrain losses and offering real-world performance data. Engine dynos test the engine alone, providing precise control over engine conditions and detailed analysis of power output without external variables. Understanding whether you need comprehensive vehicle performance or isolated engine data is crucial for optimizing tuning and diagnostics.
Conclusion: Chassis Dyno vs Engine Dyno
Chassis dynos measure the power delivered to the wheels, accounting for drivetrain losses, while engine dynos test the engine output directly before power reaches the transmission. Your choice depends on whether you need real-world performance data or precise engine tuning metrics. For comprehensive vehicle assessment, a chassis dyno offers practical insights, whereas an engine dyno is ideal for detailed engine development.
chassis dyno vs engine dyno Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com