Hybrid Synergy Drive combines a gasoline engine with electric motors to optimize fuel efficiency and power by seamlessly switching between or combining power sources. e-POWER uses a gasoline engine solely to generate electricity for an electric motor that drives the wheels, providing a smoother, EV-like driving experience without needing external charging.
Table of Comparison
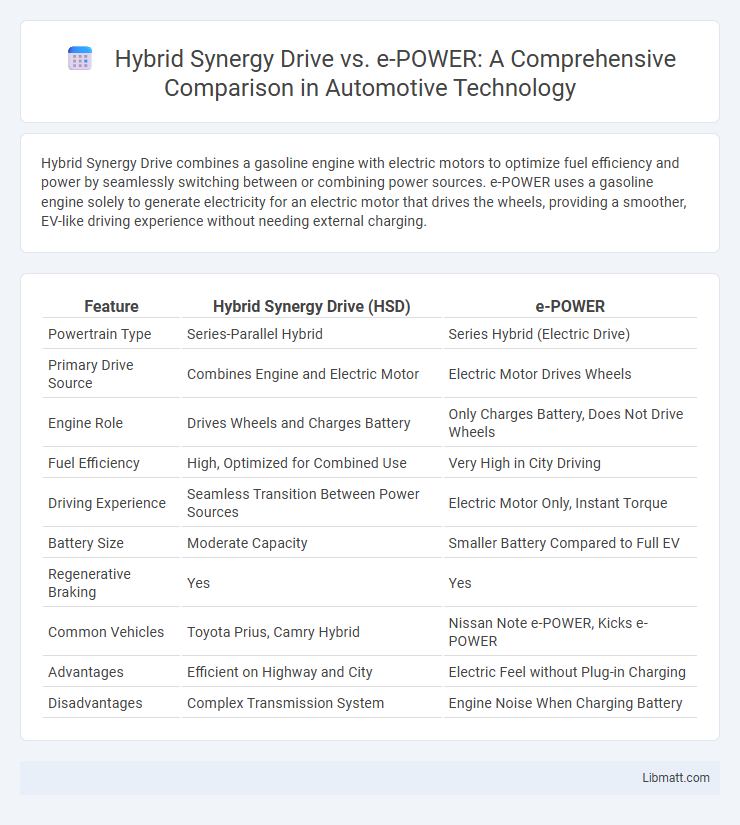
| Feature | Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD) | e-POWER |
|---|---|---|
| Powertrain Type | Series-Parallel Hybrid | Series Hybrid (Electric Drive) |
| Primary Drive Source | Combines Engine and Electric Motor | Electric Motor Drives Wheels |
| Engine Role | Drives Wheels and Charges Battery | Only Charges Battery, Does Not Drive Wheels |
| Fuel Efficiency | High, Optimized for Combined Use | Very High in City Driving |
| Driving Experience | Seamless Transition Between Power Sources | Electric Motor Only, Instant Torque |
| Battery Size | Moderate Capacity | Smaller Battery Compared to Full EV |
| Regenerative Braking | Yes | Yes |
| Common Vehicles | Toyota Prius, Camry Hybrid | Nissan Note e-POWER, Kicks e-POWER |
| Advantages | Efficient on Highway and City | Electric Feel without Plug-in Charging |
| Disadvantages | Complex Transmission System | Engine Noise When Charging Battery |
Introduction to Hybrid Synergy Drive and e-POWER
Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD) integrates a gasoline engine with electric motors to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by seamlessly switching between power sources or using both simultaneously. e-POWER, developed by Nissan, uses an internal combustion engine solely to generate electricity, while the electric motor drives the wheels, delivering a more responsive and efficient driving experience. Your choice between these systems depends on preferences for fuel economy, driving dynamics, and battery usage.
Key Technologies Behind Hybrid Synergy Drive
Hybrid Synergy Drive utilizes a combination of a gasoline engine, electric motor, and power split device for seamless energy management and fuel efficiency. Key technologies include a planetary gear set allowing simultaneous power flow from the engine and electric motor, along with regenerative braking for energy recovery. The system employs an intelligent control unit to optimize power distribution and battery charging, enhancing overall driving performance and reducing emissions.
Core Concepts of Nissan's e-POWER System
Nissan's e-POWER system uniquely combines a gasoline engine with an electric motor, where the engine functions solely as a generator to charge the battery rather than directly driving the wheels, ensuring a pure electric driving experience. Unlike traditional hybrid systems like Toyota's Hybrid Synergy Drive that blend power from both engine and motor, e-POWER delivers immediate torque and smoother acceleration by relying entirely on electric propulsion for wheel movement. This design enhances fuel efficiency and reduces emissions while maintaining the driving dynamics typical of electric vehicles, providing you with a responsive and eco-friendly ride.
Powertrain Architecture: Parallel vs. Series Hybrid
Hybrid Synergy Drive features a parallel hybrid powertrain architecture where both the internal combustion engine and electric motor can directly drive the wheels, optimizing power delivery and fuel efficiency. e-POWER utilizes a series hybrid system, with the engine acting solely as a generator to charge the battery while the electric motor exclusively powers the wheels, delivering smooth acceleration and enhanced electric driving feel. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize direct mechanical connection in power delivery or an electric motor-driven driving experience.
Driving Experience Comparison
Hybrid Synergy Drive delivers a smooth, fuel-efficient ride by seamlessly combining a gasoline engine with electric motors, providing steady acceleration and regenerative braking. e-POWER offers a unique driving experience with a gasoline engine that solely charges the battery, allowing the electric motor to power the wheels for instant torque and quieter operation. Your choice between these systems depends on whether you prioritize the conventional hybrid feel or a more electric-like response without the need for plug-in charging.
Fuel Efficiency and Economy Analysis
Hybrid Synergy Drive delivers superior fuel efficiency by combining a gasoline engine with electric motors that optimize power based on driving conditions, reducing fuel consumption during city and highway use. In contrast, e-POWER uses a gasoline engine solely as a generator to charge the battery, allowing the electric motor to exclusively power the wheels, which enhances fuel economy particularly in stop-and-go traffic. Your choice between these technologies depends on your driving habits, with e-POWER often excelling in urban environments due to its consistent electric propulsion.
Battery Size and Charging Methods
Hybrid Synergy Drive features a relatively larger battery designed for regenerative braking and limited electric-only driving, while e-POWER utilizes a smaller battery primarily for powering the electric motor with the gasoline engine acting as a generator. Charging in Hybrid Synergy Drive occurs through regenerative braking and engine power without external plug-in options, whereas e-POWER systems charge the battery exclusively via the onboard engine and regenerative braking, lacking external charging capability as well. Your choice between these technologies should consider battery capacity preferences and the convenience of non-plug-in charging methods.
Maintenance and Long-Term Reliability
Hybrid Synergy Drive utilizes a combination of a gasoline engine and electric motor, which often results in lower maintenance costs due to fewer wear components and regenerative braking reducing brake wear. e-POWER systems rely primarily on an electric motor powered by a gasoline engine acting as a generator, offering the advantage of a simpler electric drivetrain with potentially higher long-term reliability and reduced engine stress. Your choice between these technologies can impact maintenance schedules and long-term vehicle durability based on driving habits and system complexity.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Sustainability
Hybrid Synergy Drive significantly reduces emissions by combining a gasoline engine with an electric motor, improving fuel efficiency and lowering CO2 output compared to conventional engines. e-POWER uses a gasoline engine solely to generate electricity for an electric motor that drives the wheels, resulting in smoother operation and reduced exhaust emissions, enhancing urban air quality. Both technologies promote sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels, but e-POWER's all-electric driving experience offers a cleaner alternative with fewer direct emissions.
Which System Is Better for Urban or Highway Driving?
Hybrid Synergy Drive excels in highway driving by seamlessly combining gasoline engine power with electric motor efficiency, maximizing fuel economy and performance on longer trips. E-POWER, on the other hand, is optimized for urban driving, utilizing an electric motor for propulsion with a gasoline engine solely charging the battery, resulting in a smooth, quiet, and responsive acceleration ideal for stop-and-go city traffic. Your choice depends on driving conditions; Hybrid Synergy Drive suits highway efficiency, while e-POWER offers superior urban fuel savings and reduced emissions.
Hybrid synergy drive vs e-POWER Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com