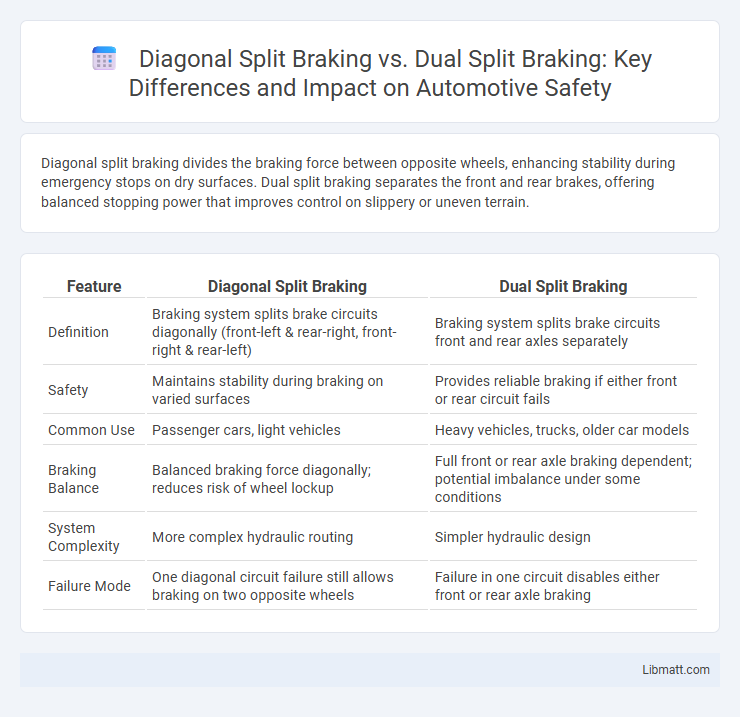
Diagonal split braking divides the braking force between opposite wheels, enhancing stability during emergency stops on dry surfaces. Dual split braking separates the front and rear brakes, offering balanced stopping power that improves control on slippery or uneven terrain.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Diagonal Split Braking | Dual Split Braking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Braking system splits brake circuits diagonally (front-left & rear-right, front-right & rear-left) | Braking system splits brake circuits front and rear axles separately |
| Safety | Maintains stability during braking on varied surfaces | Provides reliable braking if either front or rear circuit fails |
| Common Use | Passenger cars, light vehicles | Heavy vehicles, trucks, older car models |
| Braking Balance | Balanced braking force diagonally; reduces risk of wheel lockup | Full front or rear axle braking dependent; potential imbalance under some conditions |
| System Complexity | More complex hydraulic routing | Simpler hydraulic design |
| Failure Mode | One diagonal circuit failure still allows braking on two opposite wheels | Failure in one circuit disables either front or rear axle braking |
Introduction to Automotive Braking Systems
Automotive braking systems are essential for vehicle safety and control, with Diagonal Split Braking and Dual Split Braking representing two fundamental hydraulic circuit designs. Diagonal Split Braking divides braking force diagonally across opposite wheels, enhancing vehicle stability during front or rear brake failure, while Dual Split Braking separates the braking system into front and rear circuits for simpler hydraulic design and maintenance. These systems optimize stopping power distribution by managing hydraulic pressure to individual wheels, crucial for effective braking performance and accident prevention.
What is Diagonal Split Braking?
Diagonal Split Braking is a vehicle braking system where the front left and rear right wheels share one hydraulic circuit, while the front right and rear left wheels form a separate circuit. This configuration ensures balanced braking force during a failure in one circuit, maintaining vehicle stability and control. Your safety improves as this system reduces the risk of skidding by evenly distributing braking pressure across opposite wheels.
How Dual Split Braking Works
Dual split braking system separates the braking circuits diagonally, where the front left and rear right brakes operate on one circuit, and the front right and rear left brakes on the other. This design ensures balanced braking force distribution during sudden stops, enhancing vehicle stability and control. By isolating two wheels on opposite corners, dual split braking minimizes the risk of skidding or loss of control if one circuit fails.
Key Differences Between Diagonal and Dual Split Braking
Diagonal split braking divides the braking system so that each brake circuit controls one front wheel and the diagonally opposite rear wheel, ensuring balanced braking if one circuit fails. Dual split braking separates the system into front and rear circuits, where one circuit controls both front wheels and the other controls both rear wheels, which can lead to less stable braking if a circuit fails. Diagonal split braking offers enhanced stability and safety by maintaining vehicle control during brake system failure, unlike dual split braking.
Safety Implications of Diagonal Split Braking
Diagonal Split Braking offers enhanced safety by independently controlling opposite front and rear wheels, maintaining vehicle stability during braking on uneven or slippery surfaces. This system reduces the risk of skidding and loss of control by distributing braking force diagonally, preventing wheel lockup and ensuring balanced deceleration. Compared to Dual Split Braking, which manages braking force front-to-rear, Diagonal Split Braking provides superior directional control and braking efficiency in emergency situations.
Advantages of Dual Split Braking
Dual Split Braking offers enhanced safety by operating separate hydraulic circuits for front and rear brakes, minimizing the risk of total brake failure. This system provides balanced braking performance and improved control during emergency stops, ensuring your vehicle remains stable. Dual Split Braking also simplifies maintenance by isolating circuits, making it easier to identify and repair issues.
Maintenance Considerations for Each System
Diagonal split braking systems typically require less frequent maintenance due to their simpler hydraulic circuit, reducing the chances of uneven brake wear. Dual split braking systems offer enhanced safety by separately managing front and rear brakes but involve more complex components that can increase maintenance needs, including more frequent inspections and fluid replacements. Your decision should consider the balance between maintenance intensity and safety benefits each system offers.
Performance Comparison: Diagonal vs Dual Split
Diagonal split braking divides brake circuits diagonally across the vehicle, enhancing stability during front or rear wheel failures, while dual split braking separates front and rear circuits, offering simpler design but potentially less balanced control. Diagonal split systems typically provide superior vehicle control and shorter stopping distances under uneven braking conditions. Your choice impacts safety and performance, especially in emergency braking scenarios where balanced braking force distribution is critical.
Choosing the Right Braking System for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right braking system for your vehicle depends on driving conditions and safety priorities. Diagonal split braking offers balanced braking performance by distributing pressure diagonally, improving stability during emergency stops, while dual split braking separates front and rear circuits for enhanced control under varying load conditions. Understanding your vehicle's typical use and terrain can help determine whether diagonal split or dual split braking best meets your safety and handling needs.
Future Trends in Automotive Braking Technology
Future trends in automotive braking technology emphasize the integration of advanced diagonal split braking systems that enhance vehicle stability and control by independently modulating brake force across diagonally opposite wheels. Innovations in dual split braking focus on improving safety through adaptive hydraulic circuits that dynamically adjust brake pressure in real-time, optimizing performance under diverse driving conditions. Both systems are increasingly complemented by electronic brake-force distribution (EBD) and autonomous emergency braking (AEB) technologies, contributing to smarter, more reliable braking solutions in next-generation vehicles.
Diagonal Split Braking vs Dual Split Braking Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com