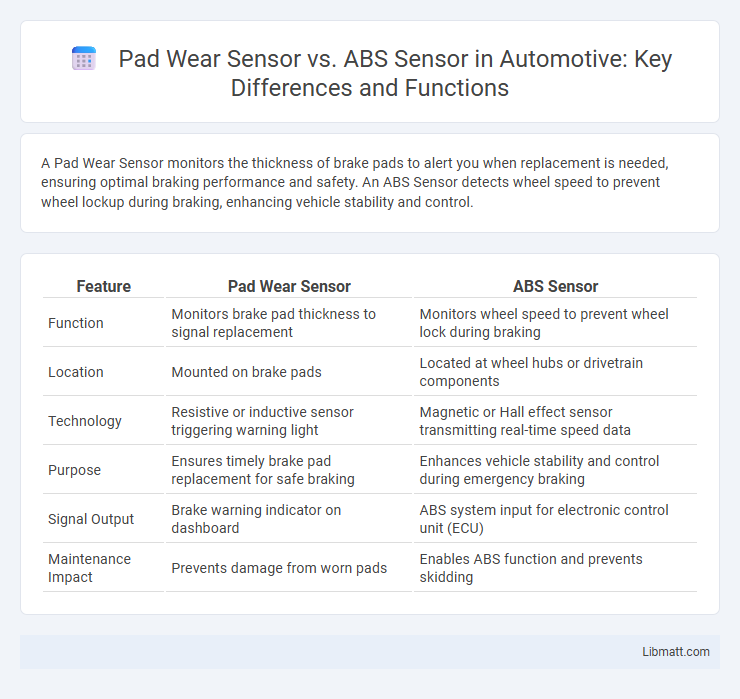
A Pad Wear Sensor monitors the thickness of brake pads to alert you when replacement is needed, ensuring optimal braking performance and safety. An ABS Sensor detects wheel speed to prevent wheel lockup during braking, enhancing vehicle stability and control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pad Wear Sensor | ABS Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Monitors brake pad thickness to signal replacement | Monitors wheel speed to prevent wheel lock during braking |
| Location | Mounted on brake pads | Located at wheel hubs or drivetrain components |
| Technology | Resistive or inductive sensor triggering warning light | Magnetic or Hall effect sensor transmitting real-time speed data |
| Purpose | Ensures timely brake pad replacement for safe braking | Enhances vehicle stability and control during emergency braking |
| Signal Output | Brake warning indicator on dashboard | ABS system input for electronic control unit (ECU) |
| Maintenance Impact | Prevents damage from worn pads | Enables ABS function and prevents skidding |
Introduction to Pad Wear Sensors and ABS Sensors
Pad wear sensors monitor the thickness of brake pads, alerting you when replacement is necessary to maintain optimal braking performance and safety. ABS sensors measure wheel speed to prevent wheel lockup during braking, enhancing vehicle control and stability. Both sensors are crucial components in modern braking systems, ensuring effective stopping power and safety under various driving conditions.
Key Differences Between Pad Wear Sensors and ABS Sensors
Pad wear sensors monitor brake pad thickness to alert drivers when pads need replacement, enhancing safety by preventing brake failure. ABS sensors, also known as wheel speed sensors, detect wheel rotation speed to prevent wheel lockup during braking, improving vehicle stability and control. Unlike ABS sensors that focus on wheel dynamics, pad wear sensors specifically track brake component wear and maintenance.
How Pad Wear Sensors Work
Pad wear sensors monitor brake pad thickness by embedding a small electrical circuit within the pad that completes a connection when the pad wears down to a critical level, triggering a warning light on Your dashboard. These sensors provide real-time feedback on brake pad life, ensuring timely maintenance and preventing damage to the brake rotor. Unlike ABS sensors, which detect wheel speed and assist in anti-lock braking, pad wear sensors specifically focus on pad condition for safety and performance.
Functionality of ABS Sensors
ABS sensors monitor wheel speed by detecting rotational velocity, providing real-time data to the anti-lock braking system to prevent wheel lockup during braking. These sensors enhance vehicle safety by ensuring optimal traction and stability under various driving conditions. Unlike pad wear sensors, which focus on brake pad thickness, ABS sensors play a critical role in dynamic vehicle control and accident avoidance systems.
Signs of a Faulty Pad Wear Sensor
A faulty pad wear sensor often triggers warning lights on your dashboard, indicating brake pads are worn or damaged. You might notice unusual brake noises such as squealing or grinding, signaling the sensor's inability to monitor pad thickness accurately. Reduced braking performance or inconsistent brake pedal feel can also be signs that the pad wear sensor needs inspection or replacement.
Symptoms of ABS Sensor Failure
ABS sensor failure commonly causes warning lights on your dashboard, erratic braking behavior, and increased stopping distances due to loss of wheel speed data. You may also experience unusual noises during braking or the ABS system engaging unexpectedly. These symptoms indicate the need to inspect or replace the faulty ABS sensor to maintain optimal vehicle safety.
Impact on Vehicle Safety: Pad Wear vs ABS Sensors
Pad wear sensors monitor brake pad thickness to alert you when replacement is necessary, directly preventing brake failure and maintaining optimal stopping power. ABS sensors detect wheel speed to regulate braking pressure, preventing wheel lockup and enhancing vehicle control during emergency braking. Both sensors are crucial for vehicle safety by ensuring effective braking performance and reducing the risk of accidents.
Maintenance and Replacement Tips
To maintain optimal vehicle safety, regularly inspect the pad wear sensor for signs of damage or abnormal wear, as it alerts you when brake pads need replacing. ABS sensors require cleaning to remove dirt and debris that can cause malfunction, ensuring accurate wheel speed detection and proper ABS function. You should replace the pad wear sensor whenever you change brake pads and replace the ABS sensor if it triggers warning lights or shows erratic performance during diagnostics.
Cost Comparison: Pad Wear Sensor vs ABS Sensor
Pad wear sensors typically cost significantly less than ABS sensors due to their simpler design and function, with prices often ranging between $10 to $50 per unit. ABS sensors, integral to a vehicle's anti-lock braking system, tend to be more complex and expensive, usually priced between $50 to $200 or more depending on the make and model. The cost difference is primarily driven by the technology involved, with ABS sensors requiring advanced electronics and precise calibration compared to the straightforward mechanical or electrical nature of pad wear sensors.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Vehicle
Selecting the right sensor for your vehicle depends on its specific diagnostic needs and safety features. Pad wear sensors are crucial for monitoring brake pad thickness to prevent damage and maintain braking efficiency, while ABS sensors detect wheel speed to optimize traction and prevent wheel lock during braking. Understanding the roles of pad wear sensors for brake maintenance and ABS sensors for stability control helps ensure accurate diagnostics and vehicle safety.
Pad Wear Sensor vs ABS Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com