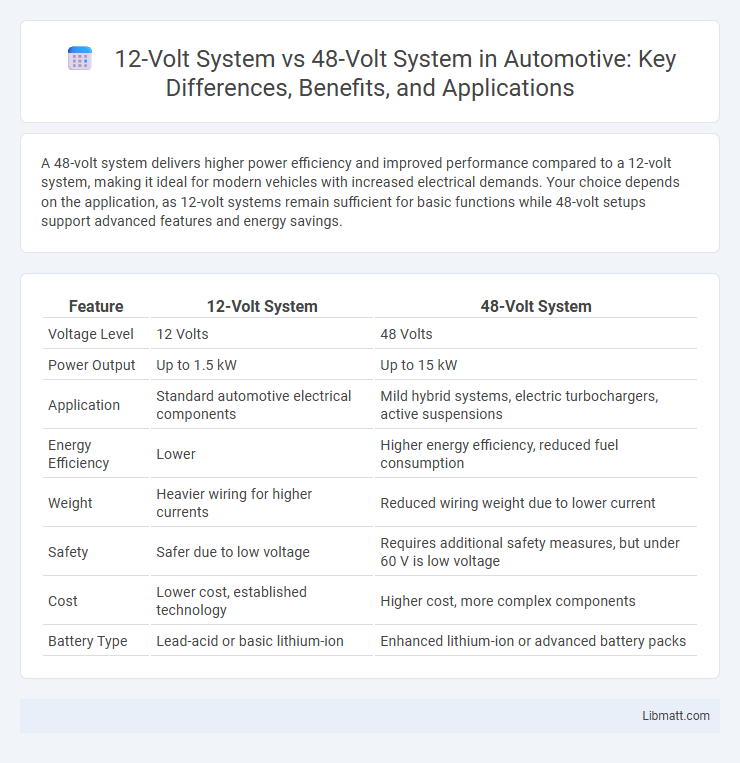
A 48-volt system delivers higher power efficiency and improved performance compared to a 12-volt system, making it ideal for modern vehicles with increased electrical demands. Your choice depends on the application, as 12-volt systems remain sufficient for basic functions while 48-volt setups support advanced features and energy savings.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 12-Volt System | 48-Volt System |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Level | 12 Volts | 48 Volts |
| Power Output | Up to 1.5 kW | Up to 15 kW |
| Application | Standard automotive electrical components | Mild hybrid systems, electric turbochargers, active suspensions |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower | Higher energy efficiency, reduced fuel consumption |
| Weight | Heavier wiring for higher currents | Reduced wiring weight due to lower current |
| Safety | Safer due to low voltage | Requires additional safety measures, but under 60 V is low voltage |
| Cost | Lower cost, established technology | Higher cost, more complex components |
| Battery Type | Lead-acid or basic lithium-ion | Enhanced lithium-ion or advanced battery packs |
Introduction to Low-Voltage Electrical Systems
Low-voltage electrical systems in vehicles and industrial applications typically operate at 12 volts or 48 volts, each offering distinct advantages. A 12-volt system provides simplicity and widespread compatibility for conventional automotive and small equipment use, while a 48-volt system enables higher power delivery with improved efficiency and reduced current flow, supporting advanced technologies like mild hybrid drivetrains. The shift toward 48-volt architectures addresses increasing electrical demand, enhanced fuel economy, and emission reduction requirements.
Overview: 12-Volt vs 48-Volt Systems
A 12-volt system is a standard electrical setup in most vehicles, providing sufficient power for basic functions such as lighting, ignition, and accessories. In contrast, a 48-volt system enables higher power delivery, supporting advanced features like mild hybrid drivetrains, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. The 48-volt architecture allows for enhanced energy recovery and smoother power assist compared to the traditional 12-volt system.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
A 48-volt system significantly improves energy efficiency by reducing current flow and minimizing resistive losses compared to a 12-volt system. This higher voltage allows for thinner wiring and more efficient power delivery in electric vehicles and hybrid configurations. Consequently, 48-volt systems enhance overall fuel economy and reduce carbon emissions by optimizing electrical component performance.
Power Output and Performance
A 48-volt system delivers higher power output and enhanced performance compared to a traditional 12-volt system, enabling more efficient energy use and greater torque in electric and hybrid vehicles. This increased voltage supports advanced components like powerful electric motors and regenerative braking systems, resulting in improved acceleration and fuel efficiency. Your choice between these systems affects overall vehicle responsiveness and energy management capabilities.
Component Size and Weight Differences
A 48-volt system significantly reduces component size and weight compared to a 12-volt system by enabling higher power delivery at lower currents, which decreases the need for thick, heavy wiring and bulky components. This higher voltage allows the use of smaller conductors, lighter connectors, and compact power electronics, improving overall system efficiency and vehicle packaging. Manufacturers adopting 48-volt architecture often see notable weight savings and enhanced design flexibility in electric and hybrid vehicles.
Safety Considerations
A 48-volt system offers enhanced safety over a 12-volt system by reducing the risk of electric shock due to its lower current and voltage levels. Your electrical installations are less prone to overheating and short circuits with 48-volt systems, improving overall safety during operation and maintenance. Proper insulation and circuit protection remain crucial regardless of system voltage to ensure safe and reliable performance.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
A 12-volt system typically incurs lower initial installation costs due to simpler components and widespread availability of parts, making it more accessible for small-scale applications. Maintenance expenses for 12-volt systems tend to be minimal, as their established technology allows for easier troubleshooting and replacement of standard components. Conversely, 48-volt systems, while offering higher efficiency and performance benefits, require more specialized equipment and expertise, leading to increased installation and maintenance costs.
Applications in Automotive and Renewable Energy
12-volt systems remain prevalent in automotive applications for traditional starting, lighting, and accessory power due to their simplicity and compatibility with existing components. In contrast, 48-volt systems enable higher efficiency and power delivery in mild hybrid vehicles and renewable energy setups, supporting advanced motor functions and energy storage with reduced electrical losses. Your choice between these systems impacts overall performance, efficiency, and compatibility in automotive innovation and solar or wind energy integration.
Future Trends in Voltage Systems
Future trends in voltage systems show a shift toward 48-volt architectures, driven by the demand for increased energy efficiency and enhanced performance in automotive and renewable energy applications. The 48-volt system enables higher power delivery with reduced current, minimizing energy losses and supporting advanced technologies like mild hybrid vehicles and smart grid solutions. You can expect wider adoption of 48-volt systems as manufacturers prioritize sustainability and scalability in electric powertrains and energy storage solutions.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Choosing the right electrical system depends on your power requirements and efficiency goals, with 12-volt systems commonly used for smaller applications like automotive or marine setups due to simplicity and wide compatibility. In contrast, 48-volt systems offer higher power output and improved energy efficiency, making them ideal for larger, more energy-intensive installations such as renewable energy storage or advanced electric vehicle platforms. Evaluating your specific energy demands, system size, and budget will help you determine whether a 12-volt or 48-volt system best suits your needs.
12-volt system vs 48-volt system Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com