Serpentine belts are single, continuous belts that drive multiple engine accessories, providing improved efficiency and easier maintenance compared to traditional V-belts, which are separate belts dedicated to individual components. Your vehicle benefits from the serpentine belt's streamlined design, ensuring consistent tension and reducing wear, while V-belts may require more frequent adjustments and replacements.
Table of Comparison
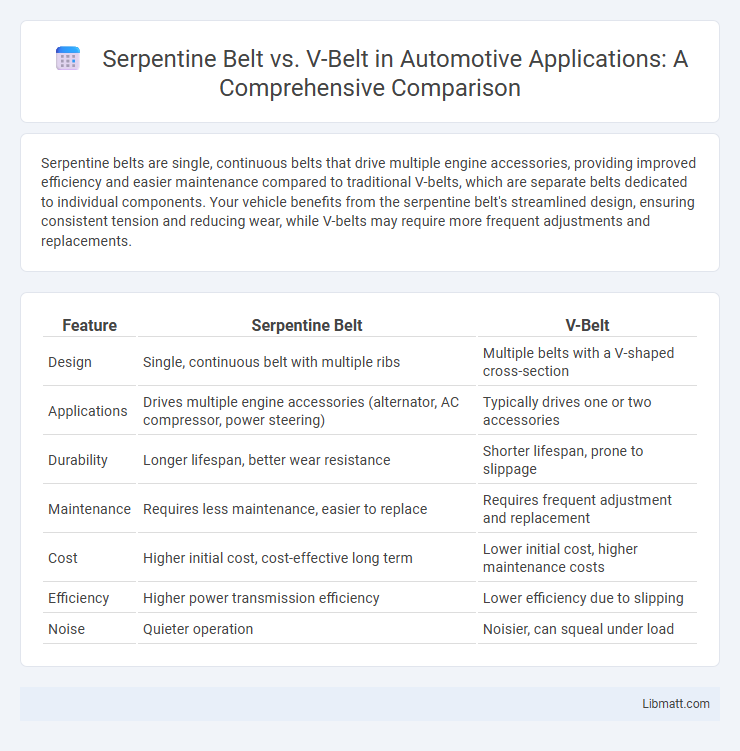
| Feature | Serpentine Belt | V-Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Single, continuous belt with multiple ribs | Multiple belts with a V-shaped cross-section |
| Applications | Drives multiple engine accessories (alternator, AC compressor, power steering) | Typically drives one or two accessories |
| Durability | Longer lifespan, better wear resistance | Shorter lifespan, prone to slippage |
| Maintenance | Requires less maintenance, easier to replace | Requires frequent adjustment and replacement |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, cost-effective long term | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance costs |
| Efficiency | Higher power transmission efficiency | Lower efficiency due to slipping |
| Noise | Quieter operation | Noisier, can squeal under load |
Introduction to Serpentine Belts and V-Belts
Serpentine belts are single, continuous belts that drive multiple peripheral devices in modern vehicles, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor, offering improved efficiency and ease of maintenance. V-belts, in contrast, are older technology consisting of multiple individual belts, each powering a specific component, often requiring more frequent adjustments and replacements. Understanding the differences between serpentine and V-belts helps you choose the right belt system for your vehicle's performance and maintenance needs.
Design and Construction Differences
Serpentine belts feature a single, continuous belt with multiple grooves designed to drive several engine accessories efficiently, while V-belts are typically single-ribbed and drive one or two components at a time. The flat, multi-rib design of serpentine belts offers better grip and flexibility, reducing slippage and wear compared to the trapezoidal cross-section of V-belts. Understanding these design and construction differences helps you choose the right belt for optimal engine performance and maintenance.
How Serpentine Belts Work
Serpentine belts operate by winding through multiple engine components, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor, using a single continuous belt that maintains tension via an automatic tensioner. This design enhances efficiency by reducing slippage and wear compared to traditional V-belts, which require multiple belts for different accessories. The serpentine belt's flat, multi-ribbed surface provides superior grip and durability, contributing to improved engine performance and easier maintenance.
How V-Belts Function
V-belts function by transmitting power through a trapezoidal cross-section that fits into the corresponding pulley grooves, creating friction that drives engine accessories like the alternator and water pump. Their design allows for efficient power transfer with reduced slippage and noise compared to flat belts. Understanding how your V-belt operates is essential for maintaining proper tension and ensuring optimal engine performance.
Comparative Efficiency and Performance
Serpentine belts offer superior efficiency and performance compared to V-belts due to their single, continuous design that reduces slippage and spreads tension evenly across multiple pulleys. They provide better power transmission with less maintenance, improving engine accessory operation and fuel economy. V-belts, while effective for simpler systems, have higher friction losses and require more frequent adjustments, making them less optimal for modern automotive applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Serpentine belts require less frequent replacement due to their design, but proper tensioning using an automatic tensioner during installation is crucial for optimal performance. V-belts demand manual adjustment for tension and often need more frequent inspections and replacements because they experience greater wear from friction. Following your vehicle's specific guidelines for installation and maintenance ensures longer belt life and prevents engine accessory malfunctions.
Common Applications in Modern Vehicles
Serpentine belts are commonly used in modern vehicles to drive multiple accessories such as the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor with a single continuous belt, enhancing efficiency and reducing maintenance. V-belts typically power individual components or simpler systems, often found in older or less complex vehicle models. The serpentine belt's design supports compact engine layouts and improved belt tension control, making it the preferred choice in contemporary automotive engineering.
Durability and Lifespan Considerations
Serpentine belts generally offer superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to V-belts due to their construction from high-quality synthetic rubber and multiple grooved ribs that distribute stress evenly. V-belts, while typically less expensive, are prone to quicker wear and may require more frequent replacement because their design concentrates stress on fewer contact points. The extended lifespan of serpentine belts reduces maintenance costs and improves engine reliability in automotive applications.
Cost Implications: Serpentine Belts vs V-Belts
Serpentine belts typically offer cost savings over time due to their longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs compared to V-belts. Initial replacement costs for serpentine belts may be higher, but the consolidated design reduces the need for multiple belts, lowering cumulative expenses. V-belts generally incur higher ongoing costs because they wear out faster and require more frequent adjustments or replacements.
Choosing the Right Belt for Your Vehicle
Selecting the right belt for your vehicle depends on engine configuration and accessory layout; serpentine belts are versatile, driving multiple components with a single, continuous belt, which reduces maintenance and enhances efficiency. V-belts are suitable for simpler setups with fewer accessories, offering ease of replacement and cost-effectiveness in older or less complex engines. Understanding the belt's application, durability needs, and engine compatibility ensures optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle's drive system.
serpentine belt vs V-belt Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com