Telescopic shock absorbers use hydraulic fluid to dampen suspension movement, offering smooth and consistent performance ideal for everyday driving conditions. Gas-filled shock absorbers incorporate pressurized nitrogen gas to reduce foam and improve responsiveness, enhancing handling and stability for more aggressive or off-road driving.
Table of Comparison
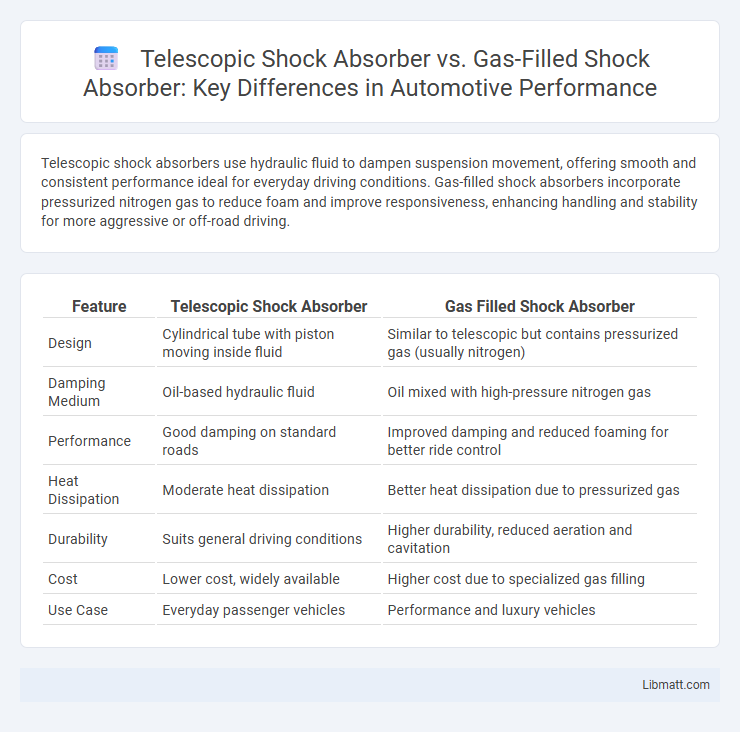
| Feature | Telescopic Shock Absorber | Gas Filled Shock Absorber |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Cylindrical tube with piston moving inside fluid | Similar to telescopic but contains pressurized gas (usually nitrogen) |
| Damping Medium | Oil-based hydraulic fluid | Oil mixed with high-pressure nitrogen gas |
| Performance | Good damping on standard roads | Improved damping and reduced foaming for better ride control |
| Heat Dissipation | Moderate heat dissipation | Better heat dissipation due to pressurized gas |
| Durability | Suits general driving conditions | Higher durability, reduced aeration and cavitation |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to specialized gas filling |
| Use Case | Everyday passenger vehicles | Performance and luxury vehicles |
Introduction to Shock Absorbers
Shock absorbers are critical components in vehicle suspension systems, designed to dampen vibrations and improve ride quality by controlling spring oscillations. Telescopic shock absorbers operate with a piston moving inside a fluid-filled cylinder, effectively absorbing shocks through hydraulic fluid resistance. Gas filled shock absorbers enhance this mechanism by incorporating pressurized gas, typically nitrogen, to reduce fluid aeration and improve responsiveness under high-performance conditions.
What is a Telescopic Shock Absorber?
A telescopic shock absorber is a suspension component designed to absorb and dampen the impact and vibrations from rough road surfaces, enhancing vehicle stability and comfort. It consists of a piston moving inside a cylinder filled with hydraulic fluid, which controls the motion by converting kinetic energy into heat. Your vehicle benefits from improved handling and reduced wear on other suspension parts thanks to the efficient design of telescopic shock absorbers.
What is a Gas Filled Shock Absorber?
A gas filled shock absorber uses pressurized nitrogen gas to reduce foaming and improve damping performance compared to traditional telescopic shock absorbers. The gas pressure minimizes oil aeration, ensuring consistent hydraulic fluid flow and enhanced ride comfort. This design results in better handling stability and quicker response to road irregularities.
Construction Differences
Telescopic shock absorbers feature a simple design with a piston moving inside a hydraulic fluid-filled cylinder, using oil and sometimes gas for damping control. Gas-filled shock absorbers incorporate pressurized nitrogen gas alongside hydraulic fluid to reduce aeration and improve response time, typically housed within a twin-tube or monotube structure. The construction difference centers on gas pressurization in gas-filled shocks, which enhances damping efficiency compared to the more straightforward, oil-only telescopic design.
Working Principle Comparison
Telescopic shock absorbers operate by using hydraulic fluid to dampen suspension movement through a piston and cylinder mechanism, converting kinetic energy into heat. Gas-filled shock absorbers enhance this system by incorporating pressurized gas, usually nitrogen, to reduce cavitation and improve responsiveness under dynamic loads. The primary difference lies in the gas-filled design's ability to maintain consistent damping performance and reduce foaming, resulting in smoother ride quality compared to standard telescopic shocks.
Performance and Efficiency
Telescopic shock absorbers deliver smooth damping performance by utilizing hydraulic fluid to absorb and dissipate energy, making them efficient for general road conditions due to their straightforward design. Gas-filled shock absorbers, infused with pressurized nitrogen, reduce aeration and foaming within the hydraulic fluid, significantly enhancing responsiveness and maintaining consistent performance under high-stress conditions. The gas-filled variant's superior heat dissipation and reduced fade contribute to greater handling stability and efficiency during aggressive or off-road driving.
Ride Comfort and Stability
Telescopic shock absorbers enhance ride comfort by providing smooth damping through a piston-cylinder mechanism, effectively absorbing road irregularities and reducing vibrations. Gas-filled shock absorbers maintain vehicle stability by minimizing foaming and cavitation within the shock fluid, ensuring consistent performance under varying driving conditions. Your choice impacts how well your vehicle handles bumps and maintains control, with gas-filled shocks offering improved responsiveness and telescopic shocks delivering a softer ride.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
Telescopic shock absorbers generally offer higher durability due to their simpler design and robust construction, making them less prone to wear and tear under harsh conditions. Gas-filled shock absorbers, while providing improved performance by reducing foaming and enhancing responsiveness, often demand more frequent maintenance to monitor gas pressure and prevent seal leaks. Maintenance intervals for telescopic shocks tend to be longer, whereas gas-filled shocks require careful inspection to maintain optimal functionality and longevity.
Cost and Availability
Telescopic shock absorbers generally come at a lower cost due to their simpler design and widespread manufacturing, making them readily available for most vehicle models. Gas-filled shock absorbers, while more expensive because of their enhanced performance and nitrogen gas technology, may be less accessible depending on the vehicle type and aftermarket options. Your choice might hinge on balancing upfront expenses against durability and replacement frequency.
Choosing the Right Shock Absorber for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right shock absorber for your vehicle depends on your driving style and terrain. Telescopic shock absorbers provide consistent damping and are suitable for everyday driving and lighter loads, while gas-filled shock absorbers offer improved performance, better heat dissipation, and enhanced handling for off-road or high-performance vehicles. Understanding the differences in technology and application ensures optimal ride comfort and vehicle control tailored to your needs.
Telescopic Shock Absorber vs Gas Filled Shock Absorber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com