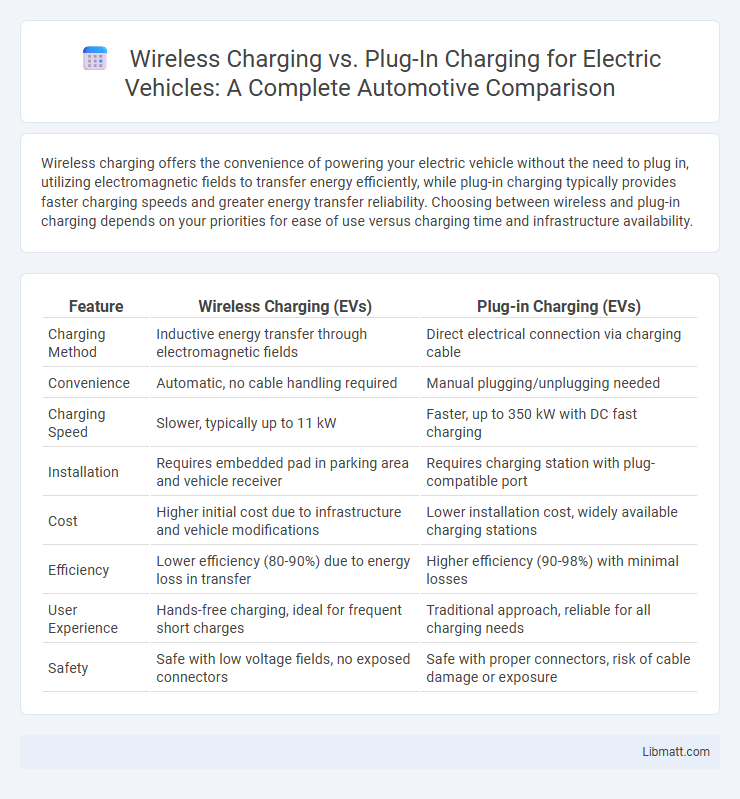
Wireless charging offers the convenience of powering your electric vehicle without the need to plug in, utilizing electromagnetic fields to transfer energy efficiently, while plug-in charging typically provides faster charging speeds and greater energy transfer reliability. Choosing between wireless and plug-in charging depends on your priorities for ease of use versus charging time and infrastructure availability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wireless Charging (EVs) | Plug-in Charging (EVs) |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Method | Inductive energy transfer through electromagnetic fields | Direct electrical connection via charging cable |
| Convenience | Automatic, no cable handling required | Manual plugging/unplugging needed |
| Charging Speed | Slower, typically up to 11 kW | Faster, up to 350 kW with DC fast charging |
| Installation | Requires embedded pad in parking area and vehicle receiver | Requires charging station with plug-compatible port |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to infrastructure and vehicle modifications | Lower installation cost, widely available charging stations |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency (80-90%) due to energy loss in transfer | Higher efficiency (90-98%) with minimal losses |
| User Experience | Hands-free charging, ideal for frequent short charges | Traditional approach, reliable for all charging needs |
| Safety | Safe with low voltage fields, no exposed connectors | Safe with proper connectors, risk of cable damage or exposure |
Introduction to EV Charging Methods
Wireless charging for electric vehicles (EVs) uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a charging pad and the vehicle without physical connectors, offering convenience and reducing wear on ports. Plug-in charging relies on direct electrical connections via cables, providing faster and more efficient energy transfer, widely supported by existing infrastructure. While wireless charging enhances user experience with hands-free operation, plug-in charging remains dominant due to higher power delivery and established technology standards.
How Wireless Charging Works for EVs
Wireless charging for EVs uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a charging pad on the ground and a receiver installed in the vehicle, eliminating the need for cables. This inductive charging system converts electricity into a magnetic field via a transmitter coil, which is then converted back to electrical energy by a receiver coil in the car. Your EV charges automatically when parked over the charging pad, offering convenient and seamless energy replenishment without physical connectors.
Understanding Plug-in Charging Technology
Plug-in charging technology for electric vehicles (EVs) relies on a physical connection between the vehicle and a charging station using cables and connectors, ensuring efficient and stable power transfer. It supports various charging levels, from Level 1 (slow, household outlets) to Level 3 (DC fast charging), enabling faster battery replenishment depending on your charging needs. Understanding these differences helps you optimize charging times and maintain battery health effectively.
Efficiency Comparison: Wireless vs Plug-in
Wireless charging for electric vehicles (EVs) typically offers lower energy transfer efficiency, ranging from 80% to 90%, compared to plug-in charging, which often exceeds 90% efficiency. The energy loss during wireless charging is mainly due to magnetic field dispersion and alignment sensitivity between the transmitter and receiver coils. For optimal battery recharge speed and minimizing energy waste, your EV benefits more from plug-in charging systems in terms of efficiency.
Convenience and User Experience
Wireless charging for EVs offers unparalleled convenience by allowing you to simply park over a charging pad without the need to physically connect cables, enhancing ease of use in daily routines. Plug-in charging, while requiring manual connection, often provides faster charging speeds and widespread availability at existing infrastructure. Your choice between these methods impacts overall user experience, balancing convenience against charging time and accessibility.
Installation Costs and Infrastructure
Wireless charging for electric vehicles typically involves higher installation costs due to advanced technology requirements and specialized equipment, including inductive pads and embedded infrastructure. Plug-in charging stations demand lower upfront investment and widespread standardization but require accessible power outlets and physical connectors. Both systems necessitate infrastructure upgrades, yet wireless charging offers enhanced user convenience while imposing greater initial capital expenditure.
Safety and Reliability Considerations
Wireless charging for EVs offers enhanced safety by eliminating exposed electrical connectors, reducing the risk of electric shock and corrosion, while plug-in charging requires secure, weather-resistant ports to prevent damage and ensure consistent performance. Reliability in wireless charging can be influenced by alignment precision between the vehicle and charging pad, potentially causing slower or interrupted energy transfer compared to the more direct, stable connection of plug-in systems. Both technologies must adhere to stringent safety standards and incorporate fail-safe mechanisms, but plug-in charging generally provides more predictable reliability under various environmental conditions.
Impact on Battery Life and Performance
Wireless charging for EVs tends to generate more heat during the charging process compared to traditional plug-in charging, which can accelerate battery degradation over time. Plug-in charging offers more efficient energy transfer with minimal heat build-up, thus preserving battery health and maintaining optimal performance. Studies indicate that maintaining lower battery temperatures through plug-in methods extends overall battery lifespan and ensures consistent vehicle range and power output.
Future Trends in EV Charging Solutions
Wireless charging for EVs is rapidly evolving with advancements in efficiency and scalability, enabling seamless energy transfer without physical connectors. Plug-in charging continues to benefit from faster charging speeds and widespread infrastructure expansion, supporting long-distance travel and high-power needs. Your future EV charging experience will likely integrate both methods, offering convenience through wireless options and reliability from traditional plug-in systems.
Which Charging Method Is Right for You?
Wireless charging offers the convenience of cable-free power replenishment, ideal for those seeking effortless daily top-ups and minimizing wear on charging ports. Plug-in charging provides faster energy transfer rates, making it optimal for drivers who require quick, reliable recharges during long trips or limited charging windows. Your choice depends on balancing the ease of wireless convenience with the speed and efficiency of traditional plug-in systems based on your driving habits and lifestyle.
Wireless Charging vs Plug-in Charging (EVs) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com