Fruit puree contains the entire fruit, including fiber, which helps improve digestion and provides a thicker texture, while fruit juice is extracted liquid that often lacks fiber and can cause rapid sugar absorption. Choosing fruit puree supports your nutritional needs better due to its higher fiber content and lower glycemic impact compared to fruit juice.
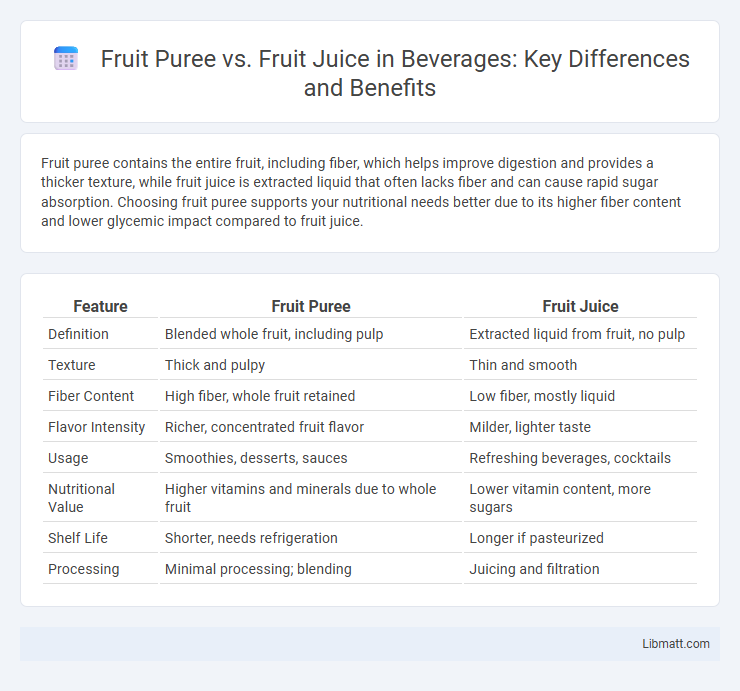
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fruit Puree | Fruit Juice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blended whole fruit, including pulp | Extracted liquid from fruit, no pulp |
| Texture | Thick and pulpy | Thin and smooth |
| Fiber Content | High fiber, whole fruit retained | Low fiber, mostly liquid |
| Flavor Intensity | Richer, concentrated fruit flavor | Milder, lighter taste |
| Usage | Smoothies, desserts, sauces | Refreshing beverages, cocktails |
| Nutritional Value | Higher vitamins and minerals due to whole fruit | Lower vitamin content, more sugars |
| Shelf Life | Shorter, needs refrigeration | Longer if pasteurized |
| Processing | Minimal processing; blending | Juicing and filtration |
Understanding Fruit Puree and Fruit Juice
Fruit puree is made by blending whole fruits into a thick, smooth consistency, retaining fiber, vitamins, and natural sugars, while fruit juice is extracted by pressing or squeezing fruits to obtain a clear liquid that contains vitamins and natural sugars but lacks fiber. The higher fiber content in fruit puree aids digestion and provides a more filling option compared to fruit juice, which is often lower in calories but higher in sugar concentration per serving. Understanding the nutritional differences and processing methods of fruit puree versus fruit juice helps consumers make informed choices based on dietary needs and desired texture.
Nutritional Differences Between Fruit Puree and Juice
Fruit puree retains all the fiber, vitamins, and minerals found in whole fruit, making it richer in nutrients like dietary fiber and antioxidants compared to fruit juice. Fruit juice often lacks fiber due to the extraction process and can have higher sugar concentrations, leading to quicker spikes in blood sugar levels. Choosing fruit puree can better support your digestive health and provide a more balanced source of nutrients.
Fiber Content: Puree vs. Juice
Fruit puree retains the natural fiber present in whole fruits, providing dietary fiber that supports digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels. In contrast, fruit juice is typically strained, removing most of the insoluble fiber and leaving primarily liquid with sugars and some vitamins. The higher fiber content in fruit puree contributes to greater satiety and slower sugar absorption compared to the faster sugar spike associated with fruit juice consumption.
Sugar Levels and Glycemic Impact
Fruit puree retains the natural fiber found in whole fruits, which slows sugar absorption and reduces the glycemic impact compared to fruit juice. Fruit juice often contains higher sugar concentrations and lacks fiber, leading to rapid blood sugar spikes and increased glycemic load. Choosing fruit puree over juice can help you manage sugar intake and maintain more stable blood glucose levels.
Processing Methods: How Are They Made?
Fruit puree is made by crushing whole fruits, including the pulp, skin, and sometimes seeds, creating a thick and textured product with all the natural fiber intact. Fruit juice is produced by pressing or squeezing fruits to extract the liquid, removing most of the pulp and fiber, resulting in a clear or slightly cloudy beverage. Understanding these processing methods helps you choose between the nutrient-rich, fiber-containing puree and the lighter, more concentrated juice depending on your dietary needs.
Taste and Flavor Profiles Compared
Fruit puree offers a richer, more concentrated taste and a thicker texture compared to fruit juice, retaining the natural sweetness and intense flavor of whole fruits. Fruit juice typically has a lighter, more refreshing flavor profile, with less fiber and a clearer consistency, emphasizing acidity and brightness. The choice between puree and juice depends on the desired mouthfeel and flavor intensity in culinary or beverage applications.
Uses in Cooking and Baking
Fruit puree provides a thicker texture and richer flavor, making it ideal for sauces, fillings, and moistening cakes or muffins. Fruit juice is more commonly used to add liquid flavor in beverages, marinades, or glazes without altering texture. Your choice depends on whether you need moisture and density from puree or a lighter, more fluid component from juice.
Health Benefits: Which Is Better?
Fruit puree retains more fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to fruit juice, which often loses nutrients during processing and filtration. The higher fiber content in purees supports better digestion, blood sugar regulation, and satiety, making it a healthier option for metabolic health. Fruit juice, while rich in antioxidants and quick to absorb, typically contains higher sugar concentration and lower fiber, increasing the risk of blood sugar spikes and decreased nutritional benefits.
Storage and Shelf Life
Fruit puree retains more fiber and nutrients due to minimal processing, allowing it to maintain quality longer under refrigeration, typically up to 7-10 days, while freezing can extend shelf life to several months. Fruit juice, being more liquid and often pasteurized, has a shorter refrigerated shelf life of about 5-7 days once opened but can last up to a year unopened when properly sealed and stored. Proper storage temperature and airtight containers are essential for both to prevent spoilage and preserve flavor and nutritional value.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Needs
Fruit puree retains more fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to fruit juice, making it a healthier choice for those seeking better nutrition and satiety. Fruit juice, often lower in fiber and higher in natural sugars, provides quicker hydration and energy, ideal for immediate refreshment or post-exercise recovery. Choosing the right option depends on your dietary goals, whether you prioritize nutrient density and fullness from fruit puree or the convenience and rapid absorption offered by fruit juice.
Fruit puree vs fruit juice Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com